
Corynexochida is an order of trilobite that lived from the Lower Cambrian to the Late Devonian. Like many of the other trilobite orders, Corynexochida contains many species with widespread characteristics.
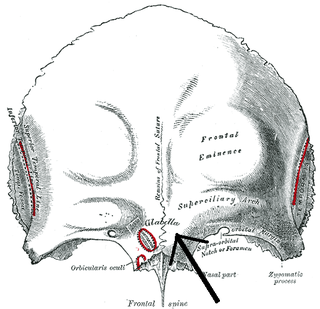
The glabella, in humans, is the area of skin between the eyebrows and above the nose. The term also refers to the underlying bone that is slightly depressed, and joins the two brow ridges. It is a cephalometric landmark that is just superior to the nasion.

The smooth-billed ani is a bird in the cuckoo family. It is a resident breeding species from southern Florida, the Caribbean, parts of Central America, south to western Ecuador, Brazil, northern Argentina and southern Chile. It was introduced to Galápagos around the 1960s and is potentially impacting native and endemic species across the archipelago.

Balcoracania dailyi is a small trilobite of the family Emuellidae. Its fossils have been found in south Australia and Antarctica. It can be recognised by a short field between the front of the axis in the head and the border ridge, and a semi-circular headsheald, as compared to touching glabella and border, and the sub-pentagonal head, in the sister-genus Emuella. Both emuellid genera share eye ridges that are positioned parallel to the frontal and lateral border of the head, prominent genal spines that are a smooth continuation of the lateral margin of the head, a prothorax of 6 segments, with the 5th and 6th merged and carrying large trailing spines. Both genera have in adulthood a highly variable but large number of segments of the opistothorax, although the largest number found in B. dailyi with 97 is much larger than in Emuella (52). B. dailyi is the only known species in this genus.

Emuella is a genus of trilobites of the family Emuellidae. Its fossils have been found in South Australia. It can be recognised by touching glabella and frontal border, and the sub-pentagonal head, as compared to, a short field between the front of the axis in the head or glabella and the border ridge, and a semi-circular headsheald in the sister-genus Balcoracania. Both emuellid genera share eye ridges that are positioned parallel to the frontal and lateral border of the head, prominent genal spines that are a smooth continuation of the lateral margin of the head, a prothorax of 6 segments, with the 5th and 6th merged and carrying large trailing spines. Both genera have in adulthood a highly variable but large number of segments of the opistothorax, although the largest number found in B. dailyi with 97 is much larger than in Emuella (52).

Redlichiina is a suborder of the order Redlichiida of Trilobites. The suborder contains three superfamilies: Emuelloidea, Redlichioidea and Paradoxidoidea. These trilobites are some of the oldest trilobites known. They originated at the beginning of the Cambrian Period and disappeared at the end of the middle Cambrian.

The copper underwing, humped green fruitworm or pyramidal green fruitworm is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae.

Svensson's copper underwing is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Charles E. Rungs in 1949. It is distributed throughout Europe including Russia east to the Urals.

The mouse moth is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is a widespread species with a Holarctic distribution.

Amphipyra is a genus of moths in the family Noctuidae, the only genus in the tribe Amphipyrini.

Marginella is a very large genus of small tropical and temperate sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the subfamily Marginellinae of the family Marginellidae, the margin snails. It is the type genus of the family.

Marginellidae, or the margin shells, are a taxonomic family of small, often colorful, sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the clade Neogastropoda.
Conjectura glabella is a species of small sea snail or micromollusc, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Conradiidae.

Pellaea glabella is the smooth cliffbrake. For much of pteridological history, it was regarded as a reduced form or variety of Pellaea atropurpurea. P. glabella is known to exist in two cryptic species, one diploid and one tetraploid. The diploid reproduces sexually, while the tetraploid is normally apogamous. It is now known that the tetraploid form of the species is one of the parents of the original hybrid P. × atropurpurea that became the apogamous species.

Glabella is a genus of small tropical and warm-water sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Marginellidae, the margin snails.

Marginellinae is a taxonomic subfamily within the larger family of Marginellidae, a group of small sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the superfamily Volutoidea.

Cassytha glabella, commonly known as the slender devil's twine, is a common twining plant of the Laurel family, found in many of the moister parts of Australia. A hemi-parasitic climber. The specific epithet glabella is from Latin, referring to the lack of hairs. The fruit are sweet and mucousy to taste. The Devil's Twine and Cassytha melantha are similar, but with thicker hairier stems.

Amphipyra fuscusa is a moth in the family Noctuidae first described by Wei-Chun Chang in 1989. It is found in Taiwan.

The Olenelloidea are a superfamily of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. They lived during the late Lower Cambrian and species occurred on all paleocontinents.

















