
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.

A mass driver or electromagnetic catapult is a proposed method of non-rocket spacelaunch which would use a linear motor to accelerate and catapult payloads up to high speeds. Existing and proposed mass drivers use coils of wire energized by electricity to make electromagnets, though a rotary mass driver has also been proposed. Sequential firing of a row of electromagnets accelerates the payload along a path. After leaving the path, the payload continues to move due to momentum.

A centrifugal governor is a specific type of governor with a feedback system that controls the speed of an engine by regulating the flow of fuel or working fluid, so as to maintain a near-constant speed. It uses the principle of proportional control.

A projectile is an object that is propelled by the application of an external force and then moves freely under the influence of gravity and air resistance. Although any objects in motion through space are projectiles, they are commonly found in warfare and sports.
The Biefeld–Brown effect is an electrical phenomenon, first noticed by inventor Thomas Townsend Brown in the 1920s, where high voltage applied to the electrodes of an asymmetric capacitor causes a net propulsive force toward the smaller electrode. Brown believed effect was an anti-gravity force, and referred to as "electrogravitics" based on it being an electricity/gravity phenomenon. It has since been determined that force is due to ionic wind that transfers its momentum to surrounding neutral particles.

A railgun or rail gun, sometimes referred to as a rail cannon, is a linear motor device, typically designed as a weapon, that uses electromagnetic force to launch high-velocity projectiles. The projectile normally does not contain explosives, instead relying on the projectile's high kinetic energy to inflict damage. The railgun uses a pair of parallel conductors (rails), along which a sliding armature is accelerated by the electromagnetic effects of a current that flows down one rail, into the armature and then back along the other rail. It is based on principles similar to those of the homopolar motor.
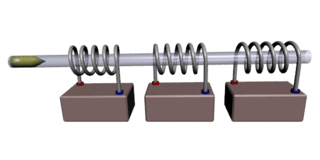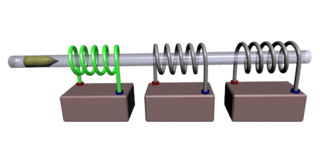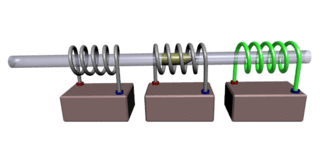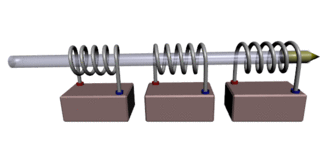
A coilgun is a type of mass driver consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almost all coilgun configurations, the coils and the gun barrel are arranged on a common axis. A coilgun is not a rifle as the barrel is smoothbore.
Muzzle velocity is the speed of a projectile with respect to the muzzle at the moment it leaves the end of a gun's barrel. Firearm muzzle velocities range from approximately 120 m/s (390 ft/s) to 370 m/s (1,200 ft/s) in black powder muskets, to more than 1,200 m/s (3,900 ft/s) in modern rifles with high-velocity cartridges such as the .220 Swift and .204 Ruger, all the way to 1,700 m/s (5,600 ft/s) for tank guns firing kinetic energy penetrator ammunition. To simulate orbital debris impacts on spacecraft, NASA launches projectiles through light-gas guns at speeds up to 8,500 m/s (28,000 ft/s). FPS and MPH are the most common American measurements for bullets. Several factors, including the type of firearm, the cartridge, and the barrel length, determine the bullet's muzzle velocity.

A mercury switch is an electrical switch that opens and closes a circuit when a small amount of the liquid metal mercury connects metal electrodes to close the circuit. There are several different basic designs but they all share the common design strength of non-eroding switch contacts.

Anti-gravity is a hypothetical phenomenon of creating a place or object that is free from the force of gravity. It does not refer to either the lack of weight under gravity experienced in free fall or orbit, or to balancing the force of gravity with some other force, such as electromagnetism or aerodynamic lift. Anti-gravity is a recurring concept in science fiction. Examples are the gravity blocking substance "Cavorite" in H. G. Wells's The First Men in the Moon and the Spindizzy machines in James Blish's Cities in Flight.

Hiram Percy Maxim was an American radio pioneer and inventor, and co-founder of the American Radio Relay League (ARRL). Hiram Percy Maxim is credited with inventing and selling the first commercially successful firearm silencer, and also with developing mufflers for internal combustion engines.

Electromagnetic suspension (EMS) is the magnetic levitation of an object achieved by constantly altering the strength of a magnetic field produced by electromagnets using a feedback loop. In most cases the levitation effect is mostly due to permanent magnets as they have no power dissipation, with electromagnets only used to stabilise the effect.
The automotive industry in India is the world's fourth-largest by production and valuation as per 2022 statistics. As of 2023, India is the 3rd largest automobile market in the world in terms of sales.
A reactionless drive is a hypothetical device producing motion without the exhaust of a propellant. A propellantless drive is not necessarily reactionless when it constitutes an open system interacting with external fields; but a reactionless drive is a particular case of a propellantless drive that is a closed system, presumably in contradiction with the law of conservation of momentum. Reactionless drives are often considered similar to a perpetual motion machine. The name comes from Newton's third law, often expressed as: "For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction."
The history of the motorcycle begins in the second half of the 19th century. Motorcycles are descended from the "safety bicycle," a bicycle with front and rear wheels of the same size and a pedal crank mechanism to drive the rear wheel. Despite some early landmarks in its development, the motorcycle lacks a rigid pedigree that can be traced back to a single idea or machine. Instead, the idea seems to have occurred to numerous engineers and inventors around Europe at around the same time.

Non-rocket spacelaunch refers to theoretical concepts for launch into space where much of the speed and altitude needed to achieve orbit is provided by a propulsion technique that is not subject to the limits of the rocket equation. Although all space launches to date have been rockets, a number of alternatives to rockets have been proposed. In some systems, such as a combination launch system, skyhook, rocket sled launch, rockoon, or air launch, a portion of the total delta-v may be provided, either directly or indirectly, by using rocket propulsion.

A kinetic energy weapon is a projectile weapon based solely on a projectile's kinetic energy to inflict damage to a target, instead of using any explosive, incendiary/thermal, chemical or radiological payload. All kinetic weapons work by attaining a high flight speed — generally supersonic or even up to hypervelocity — and collide with their targets, converting its kinetic energy and relative impulse into destructive shock waves, heat and cavitation. In kinetic weapons with unpowered flight, the muzzle velocity or launch velocity often determines the effective range and potential damage of the kinetic projectile.
Internal combustion engines date back to between the 10th and 13th centuries, when the first rocket engines were invented in China. Following the first commercial steam engine by Thomas Savery in 1698, various efforts were made during the 18th century to develop equivalent internal combustion engines. In 1791, the English inventor John Barber patented a gas turbine. In 1794, Thomas Mead patented a gas engine. Also in 1794, Robert Street patented an internal-combustion engine, which was also the first to use liquid fuel (petroleum) and built an engine around that time. In 1798, John Stevens designed the first American internal combustion engine. In 1807, French engineers Nicéphore and Claude Niépce ran a prototype internal combustion engine, using controlled dust explosions, the Pyréolophore. This engine powered a boat on the river in France. The same year, the Swiss engineer François Isaac de Rivaz built and patented a hydrogen and oxygen-powered internal-combustion engine. Fitted to a crude four-wheeled wagon, François Isaac de Rivaz first drove it 100 metres in 1813, thus making history as the first car-like vehicle known to have been powered by an internal-combustion engine.
A ram accelerator is a device for accelerating projectiles or just a single projectile to extremely high speeds using jet-engine-like propulsion cycles based on ramjet or scramjet combustion processes. It is thought to be possible to achieve non-rocket spacelaunch with this technology.

Salvatore Cezar Pais is an American aerospace engineer and inventor, currently working for the United States Space Force. He formerly worked at the Naval Air Station Patuxent River. His patent applications for the US Navy attracted attention for their potential energy-producing applications, but also doubt about their feasibility, and speculation that they may be scams, pseudoscience, or disinformation intended to mislead the United States' adversaries.













