Roman theatres derive from and are part of the overall evolution of earlier Greek theatres. Much of the architectural influence on the Romans came from the Greeks, and theatre structural design was no different from other buildings. However, Roman theatres have specific differences, such as generally being built upon their own foundations instead of earthen works or a hillside and being completely enclosed on all sides.

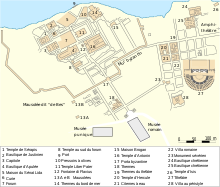
Sabratha, in the Zawiya District of Libya, was the westernmost of the ancient "three cities" of Roman Tripolis, alongside Oea and Leptis Magna. From 2001 to 2007 it was the capital of the former Sabratha wa Sorman District. It lies on the Mediterranean coast about 70 km (43 mi) west of modern Tripoli. The extant archaeological site was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1982.

Falerone is a town and comune in the province of Fermo, in the Italian region of the Marche, southeast of Urbisaglia.

Roman Carthage was an important city in ancient Rome, located in modern-day Tunisia. Approximately 100 years after the destruction of Punic Carthage in 146 BC, a new city of the same name was built on the same land by the Romans in the period from 49 to 44 BC. By the 3rd century, Carthage had developed into one of the largest cities of the Roman Empire, with a population of several hundred thousand. It was the center of the Roman province of Africa, which was a major breadbasket of the empire. Carthage briefly became the capital of a usurper, Domitius Alexander, in 308–311. Conquered by the Vandals in 439, Carthage served as the capital of the Vandal Kingdom for a century. Re-conquered by the Eastern Roman Empire in 533–534, it continued to serve as an Eastern Roman regional center, as the seat of the praetorian prefecture of Africa.

The Roman theatre of Philippopolis is one of the world's best-preserved ancient Roman theatres, located in the city center of modern Plovdiv, Bulgaria, once the ancient city of Philippopolis. It was constructed in the 1st century AD, probably during the reign of Domitian. The theatre can host between 5,000 and 7,000 spectators and it is currently in use.

The Amphiareion of Oropos, situated in the hills 6 km southeast of the fortified port of Oropos, was a sanctuary dedicated in the late 5th century BCE to the hero Amphiaraos, where pilgrims went to seek oracular responses and healing. It became particularly successful during the 4th century BCE, to judge from the intensive building at the site. The hero Amphiaraos was a descendant of the seer Melampos and initially refused to participate in the attack on Thebes because he could foresee that it would be a disaster. In some versions of the myth, the earth opens and swallows the chariot of Amphiaraos, transforming him into a chthonic hero. Today the site is found east of the modern town Markopoulo Oropou in the Oropos municipality of Attica, Greece.

The Odeon of Philippopolis was the house of the city council of citizens of ancient Plovdiv.

Roman amphitheatres are theatres — large, circular or oval open-air venues with tiered seating — built by the ancient Romans. They were used for events such as gladiator combats, venationes and executions. About 230 Roman amphitheatres have been found across the area of the Roman Empire. Early amphitheatres date from the Republican period, though they became more monumental during the Imperial era.

The Roman Theatre of Mérida is a Roman theatre in the Roman colonia of Emerita Augusta –present-day Mérida, Spain–, capital of the Roman province of Lusitania. Its construction was promoted by the consul Vipsanius Agrippa and was built in 16–15 BCE. It was used for Roman theatrical performances during ancient Rome. Since 1933, it houses the International Festival of Classical Theatre of Mérida.

The Roman Theatre of Cartagena is a Roman theatre in the Roman colonia of Cartago Nova—present-day Cartagena, Spain. Built between the years 5 and 1 BCE, it had a capacity of some 6,000 spectators and was used for Roman theatrical performances during ancient Rome.

The Roman Theatre is an ancient Roman edifice in Benevento, southern Italy. It was built in the 2nd century by emperor Hadrian near the city's cardo maximus. Abandoned in Lombard times, it is now surrounded by the medieval Rione (district) Triggio. The structures is still used for concerts, representations and other spectacles.

The Roman Theatre at Palmyra is a Roman theatre in ancient Palmyra in the Syrian Desert. The unfinished theatre dates back to the second-century CE Severan period. The theatre's remains have since been restored. It was occupied by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) in May 2015 and recaptured by the government forces in March 2016 with the support of Russian airstrikes.

The Curia of Pompey, sometimes referred to as the Curia Pompeia, was one of several named meeting halls from Republican Rome of historic significance. A curia was a designated structure for meetings of the senate. The Curia of Pompey was located at the entrance to the Theater of Pompey.

The Greek theatre of Syracuse lies on the south slopes of the Temenite hill, overlooking the modern city of Syracuse in southeastern Sicily, Italy. It was first built in the 5th century BC, rebuilt in the 3rd century BC and renovated again in the Roman period. Today, it is a part of the Unesco World Heritage Site of "Syracuse and the Rocky Necropolis of Pantalica".

The Roman Theatre of Tarraco is a Roman theatre in the Roman colonia of Tarraco –present-day Tarragona, Spain–, capital of the Roman province of Hispania Tarraconensis. Built at the end of the 1st century BC, in the time of Augustus, in the area of the local forum and the port, it was used for Roman theatrical performances.

The Argos Theater was built in 320 BC. and is located in Argos, Greece against Larissa Hill. Nearby from this site is Agora, Roman Odeon, and the Baths of Argos. The theater is one of the largest architectural developments in Greece and was renovated in ca 120 AD.

The largest building of the Archaeological Park of Dion in northern Greece is the Hellenistic-era theatre. It is located in the south of the village of Dion, Pieria and is often used during the summer for performances of the Olympus Festival.

The Roman theatre of Volterra was uncovered in the 1950s, during archaeological excavations of the ancient Roman city conducted by Enrico Fiumi. 19th-century guide to the city mentions efforts in 1817 by the commune to start excavating what was considered a luxurious amphitheater at this site. It is one of the best-preserved Roman theatres in Italy. It is located just outside the Porta Fiorentina, in an area called Vallebuona.

The Greek Theatre of Cyrene was the largest and oldest of the five known theatres in Cyrene, Libya. It was built on the north slope of the Acropolis, west of the Sanctuary of Apollo and was originally built as a standard Greek theatre, probably in the late sixth century BC. The structure underwent several phases of renovation and was eventually converted into a Roman amphitheatre in the second century AD.

The ancient theater of Alauna is a Roman-era structure located in the French commune of Valognes, in the department of Manche.