Google Authenticator is a software-based authenticator by Google that implements two-step verification services using the Time-based One-time Password Algorithm and HMAC-based One-time Password algorithm, for authenticating users of software applications.

Vitaly Dmitriyevich "Vitalik" Buterin is a Russian-Canadian programmer and writer. He is best known as a co-founder of Ethereum and as a co-founder of Bitcoin Magazine.

Ethereum is the second-largest cryptocurrency platform by market capitalization, behind Bitcoin. It is a decentralized open source blockchain featuring smart contract functionality. Ether (ETH) is the cryptocurrency generated by Ethereum miners as a reward for computations performed to secure and add blocks to the blockchain. Ethereum serves as the platform for over 1,900 different cryptocurrencies and tokens, including 47 of the top 100 cryptocurrencies by market capitalization.
A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO), sometimes labeled a decentralized autonomous corporation (DAC), is an organization represented by rules encoded as a computer program that is transparent, controlled by the organization members and not influenced by a central government. A DAO's financial transaction record and program rules are maintained on a blockchain. The precise legal status of this type of business organization is unclear.
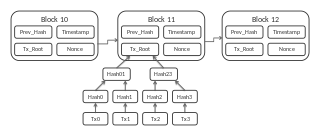
A blockchain, originally block chain, is a growing list of records, called blocks, that are linked using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.

Augur is a decentralized prediction market platform built on the Ethereum blockchain. Augur is developed by Forecast Foundation, which was founded in 2014 by Jack Peterson, Joey Krug, and Jeremy Gardner. Forecast Foundation is advised by Ron Bernstein, founder of now-defunct company Intrade, and Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin.
ConsenSys is a blockchain software technology company founded by Joseph Lubin with headquarters in Brooklyn and additional United States offices in Washington, DC and San Francisco.
The DAO was a digital decentralized autonomous organization, and a form of investor-directed venture capital fund. It launched in April 2016 after a crowdfunding campaign. By September 2016, it was delisted and had, in effect, become defunct.

Dragonchain is a hybrid blockchain platform for enterprises and developers. It was originally developed at The Walt Disney Company in Seattle in 2014 and then open-sourced in 2016. Despite extensive speculation, there is no current relationship between Disney and Dragonchain. The open source code is maintained by the Dragonchain Foundation. The commercial blockchain platform is maintained by the commercial entity named The Dragon Company. Dragonchain is a public/private hybrid blockchain platform that allows integration with other blockchain protocols, legacy systems, oracles, and API's. Developers can use existing smart contracts from the library or write their own smart contracts to build (decentralized) blockchain applications in known languages. In 2020, Medek Health launched Covid SafePass with the City of Apopka, using Dragonchain blockchain solutions in line with the FDA guidance on Digital Health Policies and Public Health Solutions for COVID-19.

STEEM is a cryptocurrency based on the social media and content-focused Steem blockchain, which was created on March 24, 2016 by Ned Scott and the blockchain developer Dan Larimer. In terms of total market capitalization, STEEM is currently ranked at place 40. with a market capitalization of more than 159 million USD..
EOS.IO is a blockchain protocol powered by the native cryptocurrency EOS. The smart contract platform claims to eliminate transaction fees and also conduct millions of transactions per second.

NEO is an open-source blockchain decentralized application platform founded in 2014 by Da HongFei and Erik Zhang. Since its rebranding to NEO from Antshares in 2017, the project's vision is to realise a "smart economy" by utilizing blockchain technology and smart contracts to issue and manage digitized assets.

IOTA is an open-source distributed ledger and cryptocurrency designed for the Internet of things (IoT). It uses a directed acyclic graph to store transactions on its ledger, motivated by a potentially higher scalability over blockchain based distributed ledgers. IOTA does not use miners to validate transactions, instead, users that issue a new transaction must approve two previous transactions and perform a small amount of proof of work. Transactions can therefore be issued without fees, facilitating microtransactions.

DAV Foundation is a blockchain-based open source global transportation company.

Mateusz Mach is a Polish entrepreneur and investor. Founder of the world's first sign language messenger Five App and venture house Nextrope. Finalist of the ranking of the most influential European entrepreneurs under the age of thirty, Forbes 30 Under 30.

Samer Hassan is a computer scientist, activist and researcher, focused on the use of decentralized technologies to support commons-based collaboration. He is Associate Professor at Universidad Complutense de Madrid (Spain) and Faculty Associate at the Berkman Klein Center for Internet & Society at Harvard University. He is the recipient of an ERC Grant of 1.5M€ with the P2P Models project, to research blockchain-based decentralized autonomous organizations for the collaborative economy.
TRON is a Blockchain-based decentralized operating system based on a cryptocurrency native to the system, known as TRX.
Origin Protocol is a sharing economy organization founded in 2017.
Bancor Protocol is a standard for decentralized exchange networks used to allow for the automated conversion of cryptocurrency tokens into other tokens, including across blockchains, without the need for an order book or counterparty to facilitate the exchange. Bancor invented the world’s first blockchain-based automated liquidity pool, or automated market maker (AMM) called a Smart Token, a digital currency with an embedded converter that allows it to be issued or exchanged automatically for any token in its network. Bancor Network consists of all the different tokens utilizing the Bancor Protocol and connected through BNT, the Bancor Network Token, which serves as the hub token for the network through which any token can be converted into any other token.










