In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula R−C(=O)−NR′R″, where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, as in asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a derivative of a carboxylic acid with the hydroxyl group replaced by an amine group ; or, equivalently, an acyl (alkanoyl) group joined to an amine group.
In chemistry, an alkali is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline, and less often, alkalescent, is commonly used in English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases.

In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as R−COOH or R−CO2H, sometimes as R−C(O)OH with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.

In chemistry, peroxides are a group of compounds with the structure R−O−O−R, where R is any element. The O−O group in a peroxide is called the peroxide group or peroxy group. The nomenclature is somewhat variable, and the term was introduced by Thomas Thomson in 1804 for an oxide with the greatest quantity of oxygen.

In polymer chemistry and materials science, a resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses mainly on naturally occurring resins.

Glutamic acid is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABAergic neurons.
Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain isopropyl group, making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid. Valine is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it; it must be obtained from dietary sources which are foods that contain proteins, such as meats, dairy products, soy products, beans and legumes. It is encoded by all codons starting with GU (GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG).

Phosphoric acid is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula H3PO4. It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, which is a colourless, odourless, and non-volatile syrupy liquid. It is a major industrial chemical, being a component of many fertilizers.

Tallow is a rendered form of beef or mutton suet, primarily made up of triglycerides.

Liquorice or licorice is the common name of Glycyrrhiza glabra, a flowering plant of the bean family Fabaceae, from the root of which a sweet, aromatic flavouring is extracted.

Acid jazz is a music genre that combines elements of funk, soul, and hip hop, as well as jazz and disco. Acid jazz originated in clubs in London during the 1980s with the rare groove movement and spread to the United States, Japan, Eastern Europe, and Brazil. Acts included The Brand New Heavies, D'Influence, Incognito, Us3, and Jamiroquai from the UK and Buckshot LeFonque and Digable Planets from the U.S. The rise of electronic club music in the middle to late 1990s led to a decline in interest, and in the twenty-first century, the movement became indistinct as a genre. Many acts that might have been defined as acid jazz are seen as jazz-funk, neo soul, or jazz rap.

Kombucha is a fermented, lightly effervescent, sweetened black tea drink. Sometimes the beverage is called kombucha tea to distinguish it from the culture of bacteria and yeast. Juice, spices, fruit or other flavorings are often added.

Shea butter is a fat extracted from the nut of the African shea tree. It is ivory in color when raw and commonly dyed yellow with borututu root or palm oil. It is widely used in cosmetics as a moisturizer, salve or lotion. It is edible and is used in food preparation in some African countries. It is occasionally mixed with other oils as a substitute for cocoa butter, although the taste is noticeably different.

Saprotrophic nutrition or lysotrophic nutrition is a process of chemoheterotrophic extracellular digestion involved in the processing of decayed organic matter. It occurs in saprotrophs, and is most often associated with fungi and soil bacteria. Saprotrophic microscopic fungi are sometimes called saprobes. Saprotrophic plants or bacterial flora are called saprophytes, although it is now believed that all plants previously thought to be saprotrophic are in fact parasites of microscopic fungi or other plants. The process is most often facilitated through the active transport of such materials through endocytosis within the internal mycelium and its constituent hyphae.

Aceburic acid (INN), also known as 4-acetoxybutanoic acid or 4-hydroxybutyric acid acetate, is a drug described as an analgesic which was never marketed. It is the acetyl ester of gamma-hydroxybutyrate, and based on its structural relation to GHB, is likely to behave as a prodrug to it.

Acetic acid, systematically named ethanoic acid, is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH. Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. It has been used, as a component of vinegar, throughout history from at least the third century BC.

Methallenestril, also known as methallenoestril and as methallenestrol, as well as Horeau's acid, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen and a derivative of allenolic acid and allenestrol that was formerly used to treat menstrual issues but is now no longer marketed. It is a seco-analogue of bisdehydrodoisynolic acid, and although methallenestril is potently estrogenic in rats, in humans it is only weakly so in comparison. Vallestril was a brand of methallenestril issued by G. D. Searle & Company in the 1950s. Methallenestril is taken by mouth. By the oral route, a dose of 25 mg methallenestril is approximately equivalent to 1 mg diethylstilbestrol, 4 mg dienestrol, 20 mg hexestrol, 25 mg estrone, 2.5 mg conjugated estrogens, and 0.05 mg ethinylestradiol.
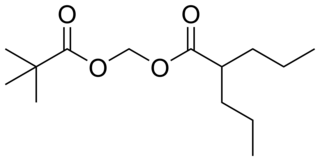
Valproate pivoxil is an anticonvulsant used in the treatment of epilepsy. It is the pivaloyloxymethyl ester derivative of valproic acid. It is likely a prodrug of valproic acid, as pivoxil esters are commonly employed to make prodrugs in medicinal chemistry.

Doisynolic acid is a synthetic, orally active, nonsteroidal estrogen that was never marketed. The reaction of estradiol or estrone with potassium hydroxide, a strong base, results in doisynolic acid as a degradation product, which retains high estrogenic activity, and this reaction was how the drug was discovered, in the late 1930s. The drug is a highly active and potent estrogen by the oral or subcutaneous route. The reaction of equilenin or dihydroequilenin with potassium hydroxide was also found to produce bisdehydrodoisynolic acid, whose levorotatory isomer is an estrogen with an "astonishingly" high degree of potency, while the dextrorotatory isomer is inactive. Doisynolic acid was named after Edward Adelbert Doisy, a pioneer in the field of estrogen research and one of the discoverers of estrone.

Allenestrol, or allenoestrol, also known as α,α-dimethyl-β-ethylallenolic acid or as methallenestrilphenol, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen and a derivative of allenolic acid that was never marketed. A methyl ether of allenestrol, methallenestril (methallenestrol), is also an estrogen, but, in contrast to allenestrol, has been marketed.