Related Research Articles
The halophiles, named after the Greek word for "salt-loving", are extremophiles that thrive in high salt concentrations. While most halophiles are classified into the domain Archaea, there are also bacterial halophiles and some eukaryotic species, such as the alga Dunaliella salina and fungus Wallemia ichthyophaga. Some well-known species give off a red color from carotenoid compounds, notably bacteriorhodopsin. Halophiles can be found in water bodies with salt concentration more than five times greater than that of the ocean, such as the Great Salt Lake in Utah, Owens Lake in California, the Urmia Lake in Iran, the Dead Sea, and in evaporation ponds. They are theorized to be a possible analogues for modeling extremophiles that might live in the salty subsurface water ocean of Jupiter's Europa and similar moons.

The Bacillaceae are a family of gram-positive, heterotrophic, rod-shaped bacteria that may produce endospores. Motile members of this family are characterized by peritrichous flagella. Some Bacillaceae are aerobic, while others are facultative or strict anaerobes. Most are not pathogenic, but Bacillus species are known to cause disease in humans.
The Gemmatimonadota are a phylum of bacteria established in 2003. The phylum contains two classes Gemmatimonadetes and Longimicrobia.
Marinobacter hydrocarbonoclasticus is a species of bacteria found in sea water which are able to degrade hydrocarbons. The cells are rod-shaped and motile by means of a single polar flagellum.
Chromohalobacter beijerinckii is a motile, rod-like, salt-loving, Gram-negative soil bacterium, 0.4–0.6 μm by 1.8–2.5 μm.
Haloarcula is a genus of extreme halophilic Archaea in the class of Halobactaria.
Armatimonas rosea is a Gram-negative bacterium and also the first species to be characterized within the phylum Armatimonadota. The Armatimonadota were previously known as candidate phylum OP10. OP10 was composed solely of environmental 16S rRNA gene clone sequences prior to A. rosea's discovery.
Chthonomonas calidirosea is a Gram-negative bacterium and also the first representative of the new class Chthonomonadetes within the phylum Armatimonadota. The Armatimonadota were previously known as candidate phylum OP10. OP10 was composed solely of environmental 16S rRNA gene clone sequences prior to C. calidirosea's relative, Armatimonas rosea's discovery. It is now known that bacterial communities from geothermal environments, are generally constituted by, at least 5–10% of bacteria belonging to Armatimonadota.
Fimbriimonas ginsengisoli is a Gram-negative bacterium and the first representative of the class Fimbriimonadia within the phylum Armatimonadota. The Armatimonadota were previously known as candidate phylum OP10. OP10 was composed solely of environmental 16S rRNA gene clone sequences prior to F. ginsengisoli's relative, Armatimonas rosea's discovery.

Haloquadratum walsbyi is of the genus Haloquadratum, within the archaea domain. First discovered in a brine pool in the Sinai peninsula of Egypt, H. walsbyi is noted for its flat, square-shaped cells, and its unusual ability to survive in aqueous environments with high concentrations of sodium chloride and magnesium chloride. The species' genus name Haloquadratum translates from Greek and Latin as "salt square". In accordance with its name, Haloquadratum walsbyi are most abundantly observed in salty environments.
Persephonella marina is a Gram-negative, rod shaped bacteria that is a member of the Aquificota phylum. Stemming from Greek, the name Persephonella is based upon the mythological goddess Persephone. Marina stems from a Latin origin, meaning "belonging to the sea". It is a thermophile with an obligate chemolithoautotrophic metabolism. Growth of P. marina can occur in pairs or individually, but is rarely seen aggregating in large groups. The organism resides on sulfidic chimneys in the deep ocean and has never been documented as a pathogen.
Halobacterium noricense is a halophilic, rod-shaped microorganism that thrives in environments with salt levels near saturation. Despite the implication of the name, Halobacterium is actually a genus of archaea, not bacteria. H. noricense can be isolated from environments with high salinity such as the Dead Sea and the Great Salt Lake in Utah. Members of the Halobacterium genus are excellent model organisms for DNA replication and transcription due to the stability of their proteins and polymerases when exposed to high temperatures. To be classified in the genus Halobacterium, a microorganism must exhibit a membrane composition consisting of ether-linked phosphoglycerides and glycolipids.
Haloferax larsenii is a gram-negative, aerobic, neutrophilic, extremely halophilic archaeon. It was named in honor of Professor Helge Larsen, who pioneered research on halophiles.
Hahella gaghwensis is a marine strain of Gram-negative, aerobic, and obligately halophilic bacteria of the gammaproteobacteria. Unlike its relative, H. chejuensis, H. ganghwensis is obligately halophilic, and both have distinctly different metabolic capabilities and fatty acid content.
Salinibacter ruber is an extremely halophilic red bacterium, first found in Spain in 2002.
Marinobacter salsuginis is a Gram-negative and moderately halophilic bacterium from the genus of Marinobacter which has been isolated from seawater from the Shaban Deep from the Red Sea. The strain BS2 of Marinobacter salsuginis can reduce the mortality of the shrimps Penaeus monodon and Litopenaeus vannamei by killing the dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans. The strain 5N-3 can degrade 1,2-Dichloroethene (cis-DCE) in the absence of inducing substrates like phenol.[6]
Dokdonia donghaensis is a strictly aerobic, gram-negative, phototrophic bacterium that thrives in marine environments. The organism can grow at a broad range of temperatures on seawater media. It has the ability to form biofilms, which increases the organism's resistance to antimicrobial agents, such as tetracycline.
Dokdonia is a genus of bacteria in the family Flavobacteriaceae and phylum Bacteroidota.
Salinicoccus kunmingensis is a standard gram-positive bacteria in the genus Salinicoccus and Staphylococcaceae family. It is moderaly halophilic growing in 0.5-25% NaCl solution, with an optimum at 8-10% NaCl solution.
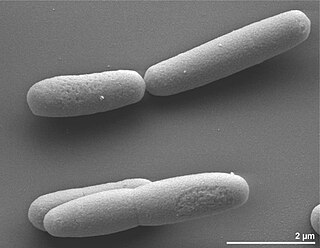
Halanaerobium praevalens is a moderately alkaliphilic, extremely halophilic bacterium that was first isolated from surface sediments of the Great Salt Lake, Utah and described by J.G. Zeikus et al. in 1983, with IJSB validation in 1984.
References
- ↑ Parte, A.C. "Arhodomonas". LPSN .
- ↑ Arhodomonas aquaeolei gen. nov., sp. nov., an Aerobic, Halophilic Bacterium Isolated from a Subterranean Brine
- ↑ Arhodomonas aquaeolei