Acidoton is a genus of plant of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1788. It is native to the Greater Antilles, Central America, and tropical South America.

Grias is a genus of flowering plants in the family Lecythidaceae, described by Linnaeus in 1759. It is native to northwestern South America, Central America, and Jamaica.
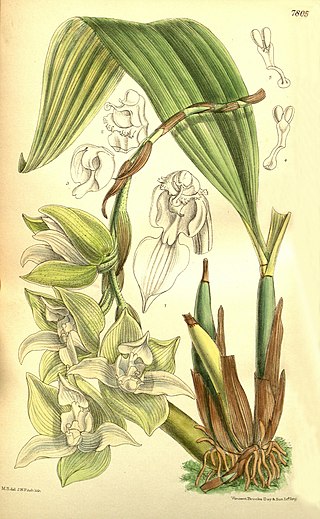
Trevoria is a genus of orchids native to southeastern Central America and northwestern South America. It grows in intermediate temperature and is found from Nicaragua and Costa Rica to Bolivia.

Dalechampia dioscoreifolia is a species of plant in the family Euphorbiaceae first described in 1841. It is native to Central America and northern and western South America.

Stenospermation is a genus of plant in family Araceae native to South America and Central America.

Teuscheria is a genus of orchids native to southern Mexico, Central America and northern South America. The genus is named for Henry Teuscher, an award-winning landscape artist and horticulturalist.

Sievekingia is a genus of orchid, comprising 20 species found in Central and South America, from Nicaragua east to the Guianas and south to Bolivia.

Bidens laevis is a species of flowering plant in the daisy family known by the common names larger bur-marigold and smooth beggarticks. It is native to South America, Mexico, and the southern and eastern United States. It grows in wetlands, including estuaries and riverbanks.

Psilochilus is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to South America, Central America, Mexico and the West Indies.
- Psilochilus carinatusGaray - Colombia
- Psilochilus dusenianusKraenzl. ex Garay & Dunst. - Venezuela, Brazil
- Psilochilus macrophyllus(Lindl.) Ames - widespread from central Mexico and the West indies south to Peru
- Psilochilus maderoi(Schltr.) Schltr. - Colombia
- Psilochilus modestusBarb.Rodr. - Venezuela, Brazil
- Psilochilus mollisGaray - Ecuador
- Psilochilus physurifolius(Rchb.f.) Løjtnant - Venezuela, Guyana
- Psilochilus vallecaucanusKolan. & Szlach. - Colombia

Schiedeella is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to the Western Hemisphere: Mexico, the West Indies and Central America, with one species (S. arizonica) in the southwestern United States.

Tinantia is a genus of plants in the Commelinaceae, first described in 1839. They are commonly called widow's tears or false dayflowers due to their resemblance of the closely related true dayflowers of the genus Commelina. Tinantia is native to North and South America from Texas + Hispaniola to Argentina, with a center of diversity from Mexico to Nicaragua. Tinantia pringlei, an alpine native of Mexico, is grown as an ornamental in temperate areas and is also a common greenhouse weed.
Anredera vesicaria, common names Texas madeiravine or sacasile, and the related A. cordifolia are the only two species of the family Basellaceae known to occur in the wild in the contiguous United States. Both are sometimes cultivated for their showy and fragrant floral displays. Anredera cordifolia is widespread throughout the warmer regions of the world. Anredera vesicaria is native to Texas as well as to Mexico, Central America, West Indies, and Venezuela and it is introduced in Florida. In Texas and Florida the species grows in thickets and in disturbed areas such as roadsides and fence rows at elevations less than 500 m.

Celtis ehrenbergiana, called the desert hackberry or spiny hackberry, is a plant species that has long been called C. pallida by many authors, including in the "Flora of North America" database. It is native to Arizona, Florida, New Mexico and Texas, and to Latin America as far south as central Argentina. It grows in dry locations such as deserts, brushlands, canyons, mesas and grasslands.
Calycolpus warscewiczianus is a plant species native to Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panamá and Venezuela.

Ludovia is a genus of plants first described as a genus in 1861. All the known species are native to Central and South America.

Gunnera magellanica is a perennial rhizomatous dioeceous herb native to Chile, Argentina and the Falkland Islands, and Andean areas of Peru, Ecuador. In the southern part of its range it grows in damper parts of the Magellanic Forests, and shrub formations on Tierra del Fuego, with an altitudinal range from sea level to 1500m.
Brickellia paniculata is a Mesoamerican species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is widespread from Tamaulipas west to Sinaloa and south as far as Costa Rica.

Erechtites valerianifolius, common name tropical burnweed is a New World species of plants in the sunflower family. It is native to Mexico, Central America, South America, and the West Indies. It is also naturalized as a weed in much of the tropical Old World.

Tagetes filifolia is a New World species of marigolds in the family Asteraceae. It is widespread across much of Latin America from northern Mexico to Argentina. Common name is Irish lace despite the fact that the plant does not grow in Ireland.

Lennoa is a monotypic genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Boraginaceae. It only contains one known species, Lennoa madreporoidesLex. It is within the subfamily of Lennoaceae.
















