
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram. In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate.
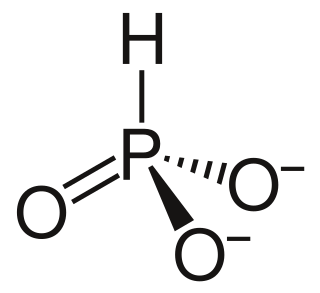
A phosphite anion or phosphite in inorganic chemistry usually refers to [HPO3]2− but includes [H2PO3]− ([HPO2(OH)]−). These anions are the conjugate bases of phosphorous acid (H3PO3). The corresponding salts, e.g. sodium phosphite (Na2HPO3) are reducing in character.

Zinc chloride is the name of inorganic chemical compounds with the formula ZnCl2. It forms hydrates. Zinc chloride, anhydrous and its hydrates are colorless or white crystalline solids, and are highly soluble in water. Five hydrates of zinc chloride are known, as well as four forms of anhydrous zinc chloride. This salt is hygroscopic and even deliquescent. Zinc chloride finds wide application in textile processing, metallurgical fluxes, and chemical synthesis. No mineral with this chemical composition is known aside from the very rare mineral simonkolleite, Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O.
An acidic oxide is an oxide that either produces an acidic solution upon addition to water, or acts as an acceptor of hydroxide ions effectively functioning as a Lewis acid. Acidic oxides will typically have a low pKa and may be inorganic or organic. A commonly encountered acidic oxide, carbon dioxide produces an acidic solution when dissolved.

Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula AlCl3. It forms a hexahydrate with the formula [Al(H2O)6]Cl3, containing six water molecules of hydration. Both the anhydrous form and the hexahydrate are colourless crystals, but samples are often contaminated with iron(III) chloride, giving them a yellow colour.

Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SOCl2. It is a moderately volatile, colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately 45,000 tonnes per year being produced during the early 1990s, but is occasionally also used as a solvent. It is toxic, reacts with water, and is also listed under the Chemical Weapons Convention as it may be used for the production of chemical weapons.

In chemistry, the term phosphonium describes polyatomic cations with the chemical formula PR+
4. These cations have tetrahedral structures. The salts are generally colorless or take the color of the anions.

Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides/oxychlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive solid, although commercial samples can be yellowish and contaminated with hydrogen chloride.

Phosphorus trichloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PCl3. A colorless liquid when pure, it is an important industrial chemical, being used for the manufacture of phosphites and other organophosphorus compounds. It is toxic and reacts readily with water to release hydrogen chloride.

Phosphorous acid (or phosphonic acid (singular)) is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic (readily ionizes two protons), not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds. Organic derivatives of phosphorous acid, compounds with the formula RPO3H2, are called phosphonic acids.
Hypophosphorous acid (HPA), or phosphinic acid, is a phosphorus oxyacid and a powerful reducing agent with molecular formula H3PO2. It is a colorless low-melting compound, which is soluble in water, dioxane and alcohols. The formula for this acid is generally written H3PO2, but a more descriptive presentation is HOP(O)H2, which highlights its monoprotic character. Salts derived from this acid are called hypophosphites.

Phosphoryl chloride is a colourless liquid with the formula POCl3. It hydrolyses in moist air releasing phosphoric acid and fumes of hydrogen chloride. It is manufactured industrially on a large scale from phosphorus trichloride and oxygen or phosphorus pentoxide. It is mainly used to make phosphate esters such as tricresyl phosphate.

Silver oxide is the chemical compound with the formula Ag2O. It is a fine black or dark brown powder that is used to prepare other silver compounds.
Arsenic pentoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula As2O5. This glassy, white, deliquescent solid is relatively unstable, consistent with the rarity of the As(V) oxidation state. More common, and far more important commercially, is arsenic(III) oxide (As2O3). All inorganic arsenic compounds are highly toxic and thus find only limited commercial applications.
Organophosphorus chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organophosphorus compounds, which are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents.

Thiophosphoryl chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula PSCl3. It is a colorless pungent smelling liquid that fumes in air. It is synthesized from phosphorus chloride and used to thiophosphorylate organic compounds, such as to produce insecticides.
Thiophosphates (or phosphorothioates, PS) are chemical compounds and anions with the general chemical formula PS
4−xO3−
x (x = 0, 1, 2, or 3) and related derivatives where organic groups are attached to one or more O or S. Thiophosphates feature tetrahedral phosphorus(V) centers.
Zinc compounds are chemical compounds containing the element zinc which is a member of the group 12 of the periodic table. The oxidation state of zinc in most compounds is the group oxidation state of +2. Zinc may be classified as a post-transition main group element with zinc(II). Zinc compounds are noteworthy for their nondescript behavior, they are generally colorless, do not readily engage in redox reactions, and generally adopt symmetrical structures.

Arsenic pentasulfide is an inorganic compound containing arsenic and sulfur.

Metal halides are compounds between metals and halogens. Some, such as sodium chloride are ionic, while others are covalently bonded. A few metal halides are discrete molecules, such as uranium hexafluoride, but most adopt polymeric structures, such as palladium chloride.

















