Carmine – also called cochineal, cochineal extract, crimson lake, or carmine lake – is a pigment of a bright-red color obtained from the aluminium complex derived from carminic acid. Specific code names for the pigment include natural red 4, C.I. 75470, or E120. Carmine is also a general term for a particularly deep-red color.

Anthraquinone, also called anthracenedione or dioxoanthracene, is an aromatic organic compound with formula C
14H
8O
2. Several isomers exist but these terms usually refer to 9,10-anthraquinone wherein the keto groups are located on the central ring. It is used as a digester additive to wood pulp for papermaking. Many anthraquinone derivatives are generated by organisms or synthesised industrially for use as dyes, pharmaceuticals, and catalysts. Anthraquinone is a yellow, highly crystalline solid, poorly soluble in water but soluble in hot organic solvents. It is almost completely insoluble in ethanol near room temperature but 2.25 g will dissolve in 100 g of boiling ethanol. It is found in nature as the rare mineral hoelite.

Aspergillus is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide.

For the parent molecule 9,10-anthraquinone, see anthraquinone
Mycotoxicology is the branch of mycology that focuses on analyzing and studying the toxins produced by fungi, known as mycotoxins. In the food industry it is important to adopt measures that keep mycotoxin levels as low as practicable, especially those that are heat-stable. These chemical compounds are the result of secondary metabolism initiated in response to specific developmental or environmental signals. This includes biological stress from the environment, such as lower nutrients or competition for those available. Under this secondary path the fungus produces a wide array of compounds in order to gain some level of advantage, such as incrementing the efficiency of metabolic processes to gain more energy from less food, or attacking other microorganisms and being able to use their remains as a food source.
In enzymology, a questin monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.43) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Solamargine is a cytotoxic chemical compound that occurs in plants of the family Solanaceae, such as potatoes, tomatoes, and eggplants. It has been also isolated from Solanum nigrum fungal endophyte Aspergillus flavus. It is a glycoalkaloid derived from the steroidal alkaloid solasodine.

Disperse dye is a category of synthetic dye intended for polyester and related hydrophobic fibers. Disperse dyes are polar molecules containing anthraquinone or azo groups. It is estimated that 85% of disperse dyes are azos or anthraquinone dyes.
Aspergillus sydowii is a pathogenic fungus that causes several diseases in humans. It has been implicated in the death of sea fan corals in the Caribbean Sea.

Spiculisporic acid is a bioactive γ-butenolide. It was originally isolated from Penicillium spiculisporum. Structural variants have been isolated from a marine Aspergillus.

Siderin is a coumarin derivative produced by Aspergillus versicolor, an endophytic fungus found in the green alga Halimeda opuntia in the Red Sea.

Evariquinone is a chemical compound of the anthraquinone class which has been isolated from a sponge-derived strain of the fungus Emericella variecolor and from Aspergillus versicolor.

Aspergillus versicolor is a slow-growing species of filamentous fungus commonly found in damp indoor environments and on food products. It has a characteristic musty odor associated with moldy homes and is a major producer of the hepatotoxic and carcinogenic mycotoxin sterigmatocystin. Like other Aspergillus species, A. versicolor is an eye, nose, and throat irritant.
Fungal isolates have been researched for decades. Because fungi often exist in thin mycelial monolayers, with no protective shell, immune system, and limited mobility, they have developed the ability to synthesize a variety of unusual compounds for survival. Researchers have discovered fungal isolates with anticancer, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, and other bio-active properties. The first statins, β-Lactam antibiotics, as well as a few important antifungals, were discovered in fungi.
Aspergillus austroafricanus is a species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus. It is from the Versicolores section. The species was first described in 2012. It has been isolated in South Africa.
Aspergillus bicolor is a species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus. It is from the Aenei section. The species was first described in 1978. It has been reported to produce sterigmatocystin, versicolorins, and some anthraquinones.
Aspergillus christenseniae is a species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus. It is from the Cervini section. The species was first described in 2016. It has been reported to produce 4-hydroxymellein, terremutin, orange-red anthraquinone, and chlorflavonin. The species was named for Martha Christensen.
Aspergillus carneus is a fast-growing, filamentous fungus found on detritus and in fertile soil worldwide. It is characterized by its yellow, thick-walled hyphae and biseriate sterigmata. The fungus produces citrinin and 5 unique depsipeptides, Aspergillicins A-E.
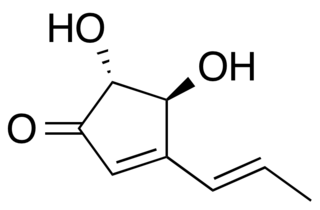
Terrein is a fungal metabolite of Aspergillus species. Terrein forms pale yellow crystal needles. Terrein has a strong cytotoxic activity against cells with colorectal carcinoma. The strain S020 from the fungus Aspergillus terreus has the highest rate in producing terrein.

Fallacinol (teloschistin) is an organic compound in the structural class of chemicals known as anthraquinones. It is found in some lichens, particularly in the family Teloschistaceae, as well as a couple of plants and non lichen-forming fungi. In 1936, Japanese chemists isolated a pigment named fallacin from the lichen Oxneria fallax, which was later refined and assigned a tentative structural formula; by 1949, Indian chemists had isolated a substance from Teloschistes flavicans with an identical structural formula to fallacin. Later research further separated fallacin into two distinct pigments, fallacin-A and fallacin-B (fallacinol). The latter compound is also known as teloschistin due to its structural match with the substance isolated earlier.











