
Ascorbic acid is an organic compound with formula C
6H
8O
6, originally called hexuronic acid. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves freely in water to give mildly acidic solutions. It is a mild reducing agent.

Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives, such as vinegar (pickling), salt (salting), smoke (smoking) and sugar (crystallization), have been used for centuries to preserve food. This allows for longer-lasting foods, such as bacon, sweets or wines.
A preservative is a substance or a chemical that is added to products such as food products, beverages, pharmaceutical drugs, paints, biological samples, cosmetics, wood, and many other products to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or by undesirable chemical changes. In general, preservation is implemented in two modes, chemical and physical. Chemical preservation entails adding chemical compounds to the product. Physical preservation entails processes such as refrigeration or drying. Preservative food additives reduce the risk of foodborne infections, decrease microbial spoilage, and preserve fresh attributes and nutritional quality. Some physical techniques for food preservation include dehydration, UV-C radiation, freeze-drying, and refrigeration. Chemical preservation and physical preservation techniques are sometimes combined.

Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription dietary supplement. As a therapy, it is used to prevent and treat scurvy, a disease caused by vitamin C deficiency.

Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), also known as dibutylhydroxytoluene, is a lipophilic organic compound, chemically a derivative of phenol, that is useful for its antioxidant properties. BHT is widely used to prevent free radical-mediated oxidation in fluids and other materials, and the regulations overseen by the U.S. F.D.A.—which considers BHT to be "generally recognized as safe"—allow small amounts to be added to foods. Despite this, and the earlier determination by the National Cancer Institute that BHT was noncarcinogenic in an animal model, societal concerns over its broad use have been expressed. BHT has also been postulated as an antiviral drug, but as of December 2022, use of BHT as a drug is not supported by the scientific literature and it has not been approved by any drug regulatory agency for use as an antiviral.
Rancidification is the process of complete or incomplete autoxidation or hydrolysis of fats and oils when exposed to air, light, moisture, or bacterial action, producing short-chain aldehydes, ketones and free fatty acids.
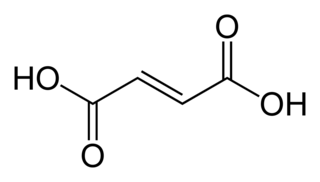
Fumaric acid or trans-butenedioic acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH=CHCO2H. A white solid, fumaric acid occurs widely in nature. It has a fruit-like taste and has been used as a food additive. Its E number is E297. The salts and esters are known as fumarates. Fumarate can also refer to the C
4H
2O2−
4 ion (in solution). Fumaric acid is the trans isomer of butenedioic acid, while maleic acid is the cis isomer.

Canthaxanthin is a keto-carotenoid pigment widely distributed in nature. Carotenoids belong to a larger class of phytochemicals known as terpenoids. The chemical formula of canthaxanthin is C40H52O2. It was first isolated in edible mushrooms. It has also been found in green algae, bacteria, crustaceans, and bioaccumulates in fish such as carp, golden grey mullet, seabream and trush wrasse.

Erythorbic acid is a stereoisomer of ascorbic acid. It is synthesized by a reaction between methyl 2-keto-D-gluconate and sodium methoxide. It can also be synthesized from sucrose or by strains of Penicillium that have been selected for this feature. It is denoted by E number E315, and is widely used as an antioxidant in processed foods.
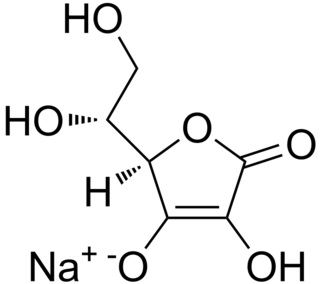
Sodium erythorbate (C6H7NaO6) is a food additive used predominantly in meats, poultry, and soft drinks. Chemically, it is the sodium salt of erythorbic acid.
Autoxidation refers to oxidations brought about by reactions with oxygen at normal temperatures, without the intervention of flame or electric spark. The term is usually used to describe the gradual degradation of organic compounds in air at ambient temperatures. Many common phenomena can be attributed to autoxidation, such as food going rancid, the 'drying' of varnishes and paints, and the perishing of rubber. It is also an important concept in both industrial chemistry and biology. Autoxidation is therefore a fairly broad term and can encompass examples of photooxygenation and catalytic oxidation.

Betanin, or beetroot red, is a red glycosidic food dye obtained from beets; its aglycone, obtained by hydrolyzing the glucose molecule, is betanidin. As a food additive, its E number is E162. As a food additive, betanin has no safety concerns.

Mineral ascorbates are a group of salts of ascorbic acid. They are composed of a mineral cation bonded to ascorbate.

Ascorbyl palmitate is an ester formed from ascorbic acid and palmitic acid creating a fat-soluble form of vitamin C. In addition to its use as a source of vitamin C, it is also used as an antioxidant food additive. It is approved for use as a food additive in the EU, the U.S., Canada, Australia, and New Zealand.

Propyl gallate, or propyl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate, is an ester formed by the condensation of gallic acid and propanol. Since 1948, this antioxidant has been added to foods containing oils and fats to prevent oxidation. As a food additive, it is used under the E number E310.

Potassium ascorbate is a compound with formula KC6H7O6. It is the potassium salt of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and a mineral ascorbate. As a food additive, it has E number E303, INS number 303. Although it is not a permitted food additive in the UK, USA and the EU, it is approved for use in Australia and New Zealand. According to some studies, it has shown a strong antioxidant activity and antitumoral properties.
Polymer stabilizers are chemical additives which may be added to polymeric materials to inhibit or retard their degradation. Mainly they protect plastic and rubber products against heat, oxidation, and UV light. The biggest quantity of stabilizers is used for polyvinyl chloride (PVC), as the production and processing of this type of plastic would not be possible without stabilizing chemicals. Common polymer degradation processes include oxidation, UV-damage, thermal degradation, ozonolysis, combinations thereof such as photo-oxidation, as well as reactions with catalyst residues, dyes, or impurities. All of these degrade the polymer at a chemical level, via chain scission, uncontrolled recombination and cross-linking, which adversely affects many key properties such as strength, malleability, appearance and colour.

Anthocyanins, also called anthocyans, are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue, or black. In 1835, the German pharmacist Ludwig Clamor Marquart named a chemical compound that gives flowers a blue color, Anthokyan, in his treatise "Die Farben der Blüthen". Food plants rich in anthocyanins include the blueberry, raspberry, black rice, and black soybean, among many others that are red, blue, purple, or black. Some of the colors of autumn leaves are derived from anthocyanins.

Phenylpropanoic acid or hydrocinnamic acid is a carboxylic acid with the formula C9H10O2 belonging to the class of phenylpropanoids. It is a white, crystalline solid with a sweet, floral scent at room temperature. Phenylpropanoic acid has a wide variety of uses including cosmetics, food additives, and pharmaceuticals.













