
APNIC is the regional Internet address registry (RIR) for the Asia–Pacific region. It is one of the world's five RIRs and is part of the Number Resource Organization (NRO).

Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation is an inter-governmental forum for 21 member economies in the Pacific Rim that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region. Following the success of ASEAN's series of post-ministerial conferences launched in the mid-1980s, APEC started in 1989, in response to the growing interdependence of Asia-Pacific economies and the advent of regional trade blocs in other parts of the world; it aimed to establish new markets for agricultural products and raw materials beyond Europe. Headquartered in Singapore, APEC is recognized as one of the highest-level multilateral blocs and oldest forums in the Asia-Pacific region, and exerts significant global influence.

The 1997 Asian financial crisis was a period of financial crisis that gripped much of East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998–1999 was rapid, and worries of a meltdown quickly subsided.

The International Conference of Asian Political Parties (ICAPP) is a forum of political parties of Asia-Oceanian countries, which was launched in Manila, Philippines in September 2000. The objectives of the conference are to promote exchanges and cooperation between political parties from different countries in the area and with various ideologies; to enhance mutual understanding and trust among Asian countries; to promote Asia's regional cooperation through the unique role and channel of political parties; to create an environment for sustained peace and shared prosperity in the region.
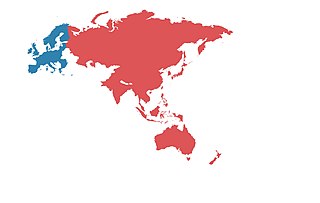
The Asia–Europe Meeting (ASEM) is an Asian–European political dialogue forum to enhance relations and various forms of cooperation between its partners. It was officially established on 1 March 1996 at the 1st ASEM Summit (ASEM1) in Bangkok, Thailand, by the then 15 Member States of the European Union (EU) and the European Commission, the then 7 Member States of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), and the individual countries of China, Japan, and South Korea. A series of enlargements saw additional EU Member States join as well as India, Mongolia, Pakistan and the ASEAN Secretariat in 2008, Australia, New Zealand and Russia in 2010, Bangladesh, Norway, and Switzerland in 2012, as well as Croatia, and Kazakhstan in 2014.

The Asia Pacific Greens Federation(APGF), formerly the Asia Pacific Greens Network, is a federation of national Green parties and related organisations in countries in the Pacific Ocean and Asia, and is one of the four Federations that constitute the Global Greens.

The G20 or Group of 20 is an intergovernmental forum comprising 19 sovereign countries, the European Union (EU), and the African Union (AU). It works to address major issues related to the global economy, such as international financial stability, climate change mitigation and sustainable development, through annual meetings of Heads of State and Heads of Government.

The Asia-Pacific Scout Region is one of the five regions of the World Organization of the Scout Movement, with a World Scout Bureau Regional Support Center based in Makati, Philippines. The Asia-Pacific Region services Scouting in the land area of Asia, from Russia, parts of Central Asia, and the bulk of the Pacific Basin, with the exception of the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands and Palau, which are under the Interamerican Region by way of the Aloha Council of the Boy Scouts of America.
The Pacific Science Association (PSA) is a regional, non-governmental, scholarly organization that seeks to advance science and technology in support of sustainable development in the Pacific Rim. It was founded in 1920 and its secretariat is based at the Bishop Museum in Honolulu, United States.
The Pacific Economic Cooperation Council (PECC) is a network of member committees composed of individuals and institutions dedicated to promoting cooperation across the Asia Pacific region, headquartered in Singapore. PECC has 23 full member committees Australia; Brunei Darussalam; Canada; Chile; China; Colombia; Ecuador; Hong Kong; Indonesia; Japan; Korea; Malaysia; Mexico; Mongolia; New Zealand; Peru; the Philippines; Singapore; Taiwan; Thailand; the United States; Vietnam and the Pacific Islands Forum, one associate member: France, and 2 institutional members: Pacific Trade and Development Conference (PAFTAD) and the Pacific Basin Economic Council (PBEC).

The Melanesian Spearhead Group (MSG) is an intergovernmental organization, composed of the four Melanesian states of Fiji, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands and Vanuatu, and the Kanak and Socialist National Liberation Front of New Caledonia. In June 2015, Indonesia was recognized as an associate member.

The Colombo Plan Staff College for Technician Education (CPSC) is a regional inter-governmental organization in Asia Pacific region mandated to enhance Vocational Education and Training in its member countries.

The Asia/Pacific Group on Money Laundering (APG) is a FATF-style regional inter-governmental (international) body, the members of which are committed to effectively implementing the international standards against money laundering, combating the financing of terrorism (CFT) and financing the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction. APG was founded in 1997 in Bangkok, Thailand, and currently consists of 42 member jurisdictions in the Asia-Pacific region and a number of observer jurisdictions and international/regional observer organisations.
The Consultative Group on Indonesia (CGI) gathered Indonesia's international donors from 1992 to 2007 to coordinate the flow of foreign aid to Indonesia. It was set up by the Indonesian government and the World Bank.

International asset recovery is any effort by governments to repatriate the proceeds of corruption hidden in foreign jurisdictions. Such assets may include monies in bank accounts, real estate, vehicles, arts and artifacts, and precious metals. As defined under the United Nations Convention against Corruption, asset recovery refers to recovering the proceeds of corruption, rather than broader terms such as asset confiscation or asset forfeiture which refer to recovering the proceeds or instrumentalities of crime in general.

The inauguration of Benigno Aquino III as the 15th president of the Philippines took place on Wednesday, June 30, 2010, at the Quirino Grandstand in Manila. The oath of office was administered by Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the Philippines Conchita Carpio-Morales.

The Asian Parliamentary Assembly (APA) aims to promote peace in general, and in the Asian region in particular. It was established as the Association of Asian Parliaments for Peace (AAPP) in September 1999 by Sheikh Hasina, acquiring its current name in 2006 during the Seventh Session of the AAPP. The APA consisted, as of 2007, of 41 Member Parliaments and 17 observers. Each Member Parliament has a specific number of seats in the Assembly based on the size of their population. The number of total seats, and therefore, number of votes, is currently 206. Members of Assembly must be elected by members of the Member Parliaments. The APA Charter and Tehran Declaration lay out a framework of cooperation among Asian countries, and point out to a vision; that is Asian Integration.
The Global Forum on Migration and Development (GFMD) is a state-led, informal and non-binding process, which helps shape the global debate on migration and development. It provides a flexible, multi-stakeholder space where governments can discuss the multi-dimensional aspects, opportunities and challenges related to migration, development, and the link between these two areas. The GFMD process allows governments - in partnership with civil society, the private sector, the UN system, and other relevant stakeholders – to analyze and discuss sensitive issues, create consensus, pose innovative solutions, and share policy and practices.
The Bali Democracy Forum (BDF) is a meeting held in Bali, and attended by representatives from nations in the Asia Pacific region. The forum was initiated by Indonesia in 2008 with the stated aim of fostering democracy, human rights, equality, and mutual respect.

The ASEAN Inter-Parliamentary Assembly (AIPA) is a regional parliamentary body which acts as a primary point for communication and information sharing between member countries. Its primary objectives are to provide information to Southeast Asian citizens about policies aimed at establishing an ASEAN community by 2025 and to foster mutual understanding and collaboration among these parliaments.















