
The National Security Act of 1947 was a law enacting major restructuring of the United States government's military and intelligence agencies following World War II. The majority of the provisions of the act took effect on September 18, 1947, the day after the Senate confirmed James Forrestal as the first secretary of defense.

Dean Gooderham Acheson was an American politician and lawyer. As the 51st U.S. Secretary of State, he set the foreign policy of the Harry S. Truman administration from 1949 to 1953. He was also Truman's main foreign policy advisor from 1945 to 1947 during early years of the Cold War. Acheson helped design the Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan, as well as the North Atlantic Treaty Organization. He was in private law practice from July 1947 to December 1948. After 1949, Acheson came under political attack from Republicans led by Senator Joseph McCarthy over Truman's policy toward the People's Republic of China.
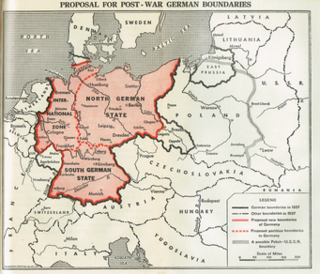
The Morgenthau Plan was a proposal to weaken Germany following World War II by eliminating its arms industry and removing or destroying other key industries basic to military strength. This included the removal or destruction of all industrial plants and equipment in the Ruhr. It was first proposed by United States Secretary of the Treasury Henry Morgenthau Jr. in a 1944 memorandum entitled Suggested Post-Surrender Program for Germany.

The Trading with the Enemy Act (TWEA) of 1917 is a United States federal law, enacted on October 6, 1917, in response to the United States declaration of war on Germany on April 6, 1917. It continues to give the President of the United States the power to oversee or restrict any and all trade between the United States and its enemies in times of war. TWEA was amended in 1933 by the Emergency Banking Act to extend the president’s authority also in peace time. It was amended again in 1977 by the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (IEEPA) to restrict again the application of TWEA only to times of war, while the IEEPA was intended to be used in peace time.

Charles Woodruff Yost was a career U.S. Ambassador who was assigned as his country's representative to the United Nations from 1969 to 1971.
The Army of Occupation Medal was a military award of the United States military which was established by the United States War Department on 5 April 1946. The medal was created in the aftermath of the Second World War to recognize those who had performed occupation service in either Germany, Italy, Austria, Japan or Korea. The original Army of Occupation Medal was intended only for members of the United States Army, but was expanded in 1948 to encompass the United States Air Force shortly after that service's creation. The Navy and Marine equivalent of the Army of Occupation Medal is the Navy Occupation Service Medal, which features the same ribbon with its own medallion and clasps.

The Wirtschaftswunder, also known as the Miracle on the Rhine, was the rapid reconstruction and development of the economies of West Germany and Austria after World War II. The expression referring to this phenomenon was first used by The Times in 1950.

The entirety of Germany was occupied and administered by the Allies of World War II, from the Berlin Declaration on 5 June 1945 to the establishment of West Germany on 23 May 1949. Unlike occupied Japan, Nazi Germany was stripped of its sovereignty and former state: after Germany formally surrendered on 8 May 1945, the four countries representing the Allies asserted joint authority and sovereignty through the Allied Control Council (ACC).

The Assistant Secretary of State for Western Hemisphere Affairs is the head of the Bureau of Western Hemisphere Affairs within the United States Department of State, the foreign affairs department of the United States federal government. The Assistant Secretary of State guides operation of the U.S. diplomatic establishment in the countries of the Western Hemisphere and advises the Secretary of State and the Under Secretary for Political Affairs.

Joseph Morrell Dodge was a chairman of the Detroit Bank, now Comerica. He later served as an economic adviser for postwar economic stabilization programs in Germany and Japan, headed the American delegation to the Austrian Advisory commission, and worked as President Dwight D. Eisenhower's director of the Bureau of the Budget.

The Rusk documents are the official diplomatic correspondence sent by Dean Rusk, the United States Assistant Secretary of State for Far Eastern Affairs, to Yang You-chan, the South Korean ambassador to the U.S. on August 10, 1951.
The aftermath of World War II saw the rise of two global superpowers, the United States (U.S.) and the Soviet Union (USSR). The aftermath of World War II was also defined by the rising threat of nuclear warfare, the creation and implementation of the United Nations as an intergovernmental organization, and the decolonization of Asia, Oceania, South America and Africa by European and East Asian powers, most notably by the United Kingdom, France, and Japan.
Government Aid and Relief in Occupied Areas (GARIOA) was a program under which the United States after the 1945 end of World War II from 1946 onwards provided emergency aid to the occupied nations of Japan, Germany, and Austria. The aid was predominantly in the form of food to alleviate starvation in the occupied areas.

Austria was occupied by the Allies and declared independent from Nazi Germany on 27 April 1945, as a result of the Vienna offensive. The occupation ended when the Austrian State Treaty came into force on 27 July 1955.

Edwin McCammon Martin was an American economist and diplomat. He worked for the United States government from 1935 to 1975, first as an economist, then on the mobilization of the U.S. economy for World War II and finally as a diplomat both domestically and abroad.

The Federal Chancellery of Austria is the ministry led by the chancellor of Austria. Since the establishment of the First Austrian Republic in 1918, the Chancellery building has served as the venue for the sessions of the Austrian cabinet. It is located on the Ballhausplatz in the centre of Vienna, vis-à-vis the Hofburg Imperial Palace. Like Downing Street, Quai d'Orsay or – formerly – Wilhelmstrasse, the address has become a synecdoche for governmental power.

Major General John Henry Hilldring was a senior United States Army officer who fought during both World War I and World War II and served as Assistant Secretary of State for Occupied Areas from 1946 to 1947.

Theodorus Hendrikus "Theo" Bot was a Dutch politician and diplomat of the defunct Catholic People's Party (KVP) now merged into the Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA) party and jurist.

The main issues of the United States foreign policy during the 1945–1953 presidency of Harry S. Truman include:















