
Tetraodon is a genus in the pufferfish family (Tetraodontidae) found in freshwater in Africa. It is the type genus of the family and historically included numerous other species; several Asian species were only moved to the genera Dichotomyctere, Leiodon and Pao in 2013.

African tetras are a group of characiform fish exclusively found in Africa. This family contains about 18 genera and 119 species. Among the best known members are the Congo tetra, and African tigerfish.

Sarotherodon is a genus of oreochromine cichlids that are native to the northern half of Africa, with a single species, S. galilaeus, also ranging into the Levant. A couple of species from this genus have been introduced far outside their native range, and are important in aquaculture. Most other species have small ranges and some are seriously threatened. They mainly inhabit fresh and brackish water, but a few can live in salt water. Species in this genus, as well as those in several other oreochromine and tilapiine genera, share the common name "tilapia" and historically they were included in the genus Tilapia.

Lamprologus is a genus of fishes from the cichlid family. They are native to Lake Tanganyika and the Congo River Basin in Africa. The type species for this genus is Lamprologus congoensis, a species from the Congo River. The genus is under some revision and may eventually be restricted to these riverine types.

Labeo is a genus of carps in the family Cyprinidae. They are found in freshwater habitats in the tropics and subtropics of Africa and Asia.

Synodontis is the largest genus of mochokid catfishes. It is the biggest genus within the 10 genera and 190 different species in the family Mochokidae. Synodontis has over 131 different species within the genus. Synodontis are also known as squeakers, due to their ability to make stridulatory sounds through their pectoral fin spines when handled or disturbed. Synodontis make a sound that sounds like squeaking by rubbing their spines together. They do this when they have been frightened or when they become angry. Synodontis may also squeak when they are taken out of the water. These catfish are small- to medium-sized fish with many species exhibiting attractive spotted markings. Some species are also known for naturally swimming belly-up, earning the name upside-down catfish. Some of these species are Synodontis contractus and Synodontis nigriventris. While some of these species are known to swim upside down, another species, Synodontis multipunctatus, is a brood parasitic cuckoo catfish.

Raiamas is a genus of cyprinid freshwater fishes. The majority of the species are from Africa, but R. bola and R. guttatus are from South and Southeast Asia.

Chiloglanis is a genus of upside-down catfishes native to Africa. These species have modified lips and barbels that form a suckermouth. They also have a naked (scaleless) body. Sexual dimorphism has been reported in Chiloglanis. The adult males of many of these species have elongate anal and caudal fins. Also, males may have an enlarged humeral process.

Euchilichthys is a genus of upside-down catfishes native to the Congo River Basin in Middle Africa.

Brycinus is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Alestiidae. Like other "African characids", they were formerly included in the Characidae but are actually somewhat more distantly related Characiformes.

Chrysichthys is a genus of claroteid catfishes native to Africa. Two fossil species are known. Chrysichthys macrotis, Van Neer, 1994, is known from the Miocene-Pliocene of the Albertine Rift in Uganda and Chrysichthys mahengeensis, Murray & Budney, 2003, is known from the Eocene of Mahenge, Tanzania.

Clariallabes is a genus of airbreathing catfishes found in Africa.

Distichodus is a genus of freshwater fish in the family Distichodontidae found in Africa.

Marcusenius is a genus of elephantfishes native to Africa. Its members are highly diverse in size, with the smallest species reaching less than 15 cm (6 in) and the largest more than 1 m (3.3 ft).

Mormyrus is a genus of fish in the family Mormyridae.

Trachyglanis is a genus of loach catfishes from Africa.

Parauchenoglanis is a genus of claroteid catfishes native to Africa.
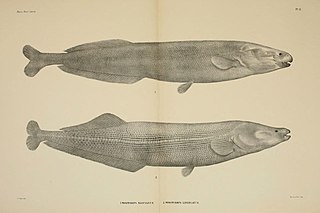
Mormyrops is a genus of weakly electric fish in the family Mormyridae from freshwater in Africa. They are characterized by an elongate head measuring twice as long as high, and no teeth on the palate or the tongue. The genus includes the largest member of the mormyrid family, the cornish jack at up to 1.5 m (4.9 ft) in length.

Labeobarbus is a mid-sized ray-finned fish genus in the family Cyprinidae. Its species are widely distributed throughout eastern Africa and especially southern Africa, but also in Lake Tana in Ethiopia. A common name, in particular for the southern species, is yellowfish. The scientific name refers to the fact that these large barbs remind of the fairly closely related "carps" in the genus Labeo in size and shape. As far as can be told, all Labeobarbus species are hexaploid.

Enteromius is a genus of small to medium-sized cyprinid fish native to tropical Africa. Most species were placed in the genus Barbus.




















