
Microcotyle is a genus which belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea. Species of Microcotyle are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated.

Microcotyle angelichthys is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle branchiostegi is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle caudata is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.

Microcotyle centropristis is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.

Microcotyle donavini is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
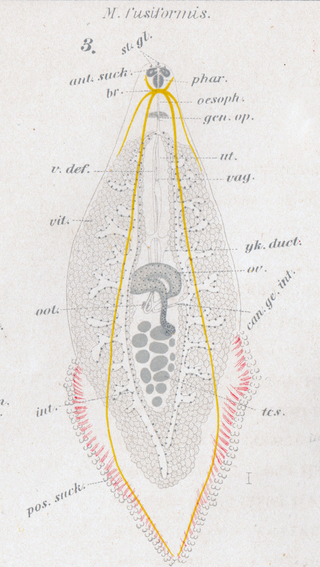
Microcotyle fusiformis is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish, described by Seitarō Gotō in 1894. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. This species was first.
Microcotyle eueides is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle furcata is a species of monogenean that is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle gimpo is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle victoriae is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle hiatulae is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. This species was first described by Goto in 1899.

Microcotyle pomatomi is a species of monogenean that is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Cynoscionicola is a genus which belongs to the family Microcotylidae and class Monogenea. Species of Cynoscionicola are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated. This genus was proposed by Price in 1962, to accommodate Cynoscionicola heteracantha and Cynoscionicola pseudoheteracantha . Members of Cynoscionicola are characterised by a genital atrium with two anterior muscular pockets armed with single row of hooked spines, and two posterior lateral muscular pouches armed with spines.

Microcotylinae is a subfamily within family Microcotylidae and class Monogenea. This subfamily was created by Taschenberg in 1879.
Diplostamenides is a genus which belongs to the family Microcotylidae and class Monogenea. As all Monogenea, species of Atriostella are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated.
Gamacallum is a genus which belongs to the family Microcotylidae and class Monogenea. As all Monogenea, species of Gamacallum are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated.
Polynemicola is a genus of monegenean. As all Monogenea, species of Polynemicola are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated.
Solostamenides is a genus which belongs to the family Microcotylidae and class Monogenea.




