
Atriplex cinerea, commonly known as grey saltbush, coast saltbush, barilla or truganini, is a plant species in the family Amaranthaceae. It occurs in sheltered coastal areas and around salt lakes in the Australian states of Western Australia, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and New South Wales.

Ficus fraseri, the white sandpaper fig or shiny sandpaper fig, is one of several fig species commonly known as sandpaper figs. It is native to New South Wales, Queensland and the Northern Territory in Australia and to New Caledonia and Vanuatu. Other common names are "figwood" and "watery fig".

Hicksbeachia pinnatifolia is a small tree in the family Proteaceae. This rare species is native to subtropical rainforest in New South Wales and Queensland in Australia. Common names include red bopple nut, monkey nut, red nut, beef nut, rose nut and ivory silky oak. The tree produces fleshy, red fruits during spring and summer. These contain edible seeds.

Grevillea ramosissima, commonly known as fan grevillea, is a shrub species of the family Proteaceae. It is native to south-eastern Australia.

Haemodorum brevicaule is a perennial herb from 0.025 to 0.3 m tall, in the bloodroot family, the Haemodoraceae, native to northern Australia. It has deep-red to purplish-black flowers which are seen from September to December, and it grows on red clay and basalt.

Seringia integrifolia is a shrub of the family Malvaceae native to inland Australia in New South Wales, South Australia, Western Australia, Queensland, and the Northern Territory.

Eucalyptus brevifolia, commonly known as snappy white gum or northern white gum, is a tree that is endemic to northern Australia. It has smooth, powdery white bark, lance-shaped adult leaves, buds arranged in group of seven, white flowers and cup-shaped or barrel-shaped fruit.

Ficus coronulata, commonly known as the peach-leaf fig, and in the Northern Territory as river fig and crown fig, is one of several fig species commonly known as sandpaper figs. It is native to Western Australia and the Northern Territory.

Boronia lanuginosa is a plant in the citrus family Rutaceae and is endemic to northern Australia. It is a shrub with woolly pinnate leaves.

Scaevola canescens is a species of plant in the family Goodeniaceae. It is endemic to Western Australia where it occurs "from Shark Bay to Perth, in open forest and heath in sandy soil".
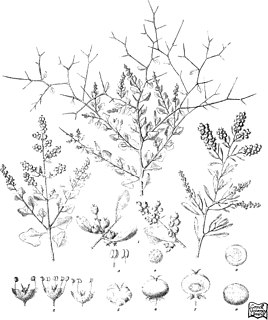
Chenopodium spinescens is a species of plant in the family Amaranthaceae, endemic to Australia. It is found in all states and territories of Australia with the exception of Tasmania.

Bossiaea stephensonii is a perennial multistemmed shrub in the pea family (Fabaceae), and is native to New South Wales.

Scaevola browniana is a shrub in the family Goodeniaceae, endemic to Western Australia, the Northern Territory and Queensland.

Atriplex holocarpa is a low-growing species of Atriplex (saltbush) found throughout arid regions of Australia. A. holocarpa is commonly known as pop saltbush, because its carpals pop when stepped upon.

Atriplex stipitata, known as mallee saltbush and kidney saltbush, is a species of shrub in the family Amaranthaceae, found in all mainland states of Australia.

Dampiera candicans is a plant in the family Goodeniaceae, native to Western Australia and the Northern Territory.

Dicrastylis beveridgei is a species of plant within the genus, Dicrastylis, in the family Lamiaceae. It is found in Western Australia, the Northern Territory, and South Australia.

Dicrastylis doranii is a species of plant within the genus, Dicrastylis, in the family Lamiaceae. It is found in Western Australia, the Northern Territory, and South Australia.

Dicrastylis lewellinii is a species of plant within the genus, Dicrastylis, in the family Lamiaceae. It is found in Western Australia, the Northern Territory, New South Wales, Queensland and South Australia.

Phlebocarya pilosissima is a plant in the Haemodoraceae family, native to Western Australia.




















