Order of Wearing
Order of wearing decorations and awards within the Australian honours system. [4]
Honours and Awards listed are:
- those within the Australian System of Honours and Awards;
- those conferred by The Sovereign in exercise of the royal prerogative;
- those within the Order of St John; and
- foreign awards, the acceptance and wearing of which have been authorised by the Governor-General.
Note that awards of the British Empire/United Kingdom are now considered foreign (if awarded after 5 October 1992), and should be worn accordingly. [5]
-
 Victoria Cross/Victoria Cross for Australia [6] VC
Victoria Cross/Victoria Cross for Australia [6] VC -
 Cross of Valour CV
Cross of Valour CV -
 Knight/Lady Companion of the Order of the Garter [note 1] KG/LG
Knight/Lady Companion of the Order of the Garter [note 1] KG/LG -
 Knight/Lady of the Order of the Thistle [note 1] KT/LT
Knight/Lady of the Order of the Thistle [note 1] KT/LT -
 Member of the Order of Merit [note 1] OM (Civil Division and Military Division)
Member of the Order of Merit [note 1] OM (Civil Division and Military Division) -
 Knight/Dame of the Order of Australia [note 2] AK/AD
Knight/Dame of the Order of Australia [note 2] AK/AD -
 Knight/Dame Grand Cross of the Royal Victorian Order [note 1] GCVO
Knight/Dame Grand Cross of the Royal Victorian Order [note 1] GCVO -
 Companion of the Order of Australia (General Division) AC
Companion of the Order of Australia (General Division) AC  (Military Division)
(Military Division) -
 Knight/Dame Commander of the Royal Victorian Order [note 1] KCVO/DCVO
Knight/Dame Commander of the Royal Victorian Order [note 1] KCVO/DCVO -
 Officer of the Order of Australia (General Division) AO
Officer of the Order of Australia (General Division) AO  (Military Division)
(Military Division) -
 Commander of the Royal Victorian Order [note 1] CVO
Commander of the Royal Victorian Order [note 1] CVO -
 Star of Gallantry SG
Star of Gallantry SG -
 Star of Courage SC
Star of Courage SC -
 Distinguished Service Cross DSC
Distinguished Service Cross DSC -
 Member of the Order of Australia (General Division) AM
Member of the Order of Australia (General Division) AM  (Military Division)
(Military Division) -
 Lieutenant of the Royal Victorian Order [note 1] LVO
Lieutenant of the Royal Victorian Order [note 1] LVO -
 Member of the Royal Victorian Order [note 1] MVO
Member of the Royal Victorian Order [note 1] MVO -
 Conspicuous Service Cross CSC
Conspicuous Service Cross CSC -
 Nursing Service Cross NSC
Nursing Service Cross NSC -
 Medal for Gallantry MG
Medal for Gallantry MG -
 Bravery Medal BM
Bravery Medal BM -
 Distinguished Service Medal DSM
Distinguished Service Medal DSM -
 Public Service Medal PSM
Public Service Medal PSM -
 Australian Police Medal APM
Australian Police Medal APM -
 Australian Fire Service Medal AFSM
Australian Fire Service Medal AFSM -
 Ambulance Service Medal ASM
Ambulance Service Medal ASM -
 Emergency Services Medal ESM
Emergency Services Medal ESM -
 Australian Corrections Medal [note 3] ACM
Australian Corrections Medal [note 3] ACM -
 Australian Intelligence Medal [note 4] AIM
Australian Intelligence Medal [note 4] AIM -
 Medal of the Order of Australia (General Division) OAM
Medal of the Order of Australia (General Division) OAM  (Military Division)
(Military Division) -
 Order of St John [note 1] [7]
Order of St John [note 1] [7] -
 Conspicuous Service Medal CSM
Conspicuous Service Medal CSM -
 Australian Antarctic Medal AAM
Australian Antarctic Medal AAM -
 Royal Victorian Medal RVM
Royal Victorian Medal RVM -
 Commendation for Gallantry
Commendation for Gallantry -
 Commendation for Brave Conduct
Commendation for Brave Conduct -
 Commendation for Distinguished Service
Commendation for Distinguished Service -
 Australia Service Medal 1939-45
Australia Service Medal 1939-45 -
 Australian Active Service Medal 1945–1975 [note 5]
Australian Active Service Medal 1945–1975 [note 5] -
 Vietnam Medal
Vietnam Medal -
 Vietnam Logistic and Support Medal [note 6]
Vietnam Logistic and Support Medal [note 6] -
 Australian Active Service Medal [note 5]
Australian Active Service Medal [note 5] -
 International Force East Timor Medal (INTERFET)
International Force East Timor Medal (INTERFET) -
 Afghanistan Medal
Afghanistan Medal -
 Iraq Medal
Iraq Medal -
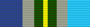 Australian Service Medal 1945–1975 [note 5]
Australian Service Medal 1945–1975 [note 5] -
 Australian General Service Medal for Korea
Australian General Service Medal for Korea -
 Australian Service Medal [note 5]
Australian Service Medal [note 5] -
Australian Operational Service Medal – Border Protection [8]
-
 Australian Operational Service Medal – Greater Middle East Operation
Australian Operational Service Medal – Greater Middle East Operation -
 Australian Operational Service Medal – Special Operations
Australian Operational Service Medal – Special Operations -
 Australian Operational Service Medal - Counter Terrorism/Special Recovery
Australian Operational Service Medal - Counter Terrorism/Special Recovery -
 Australian Operational Service Medal – Civilian
Australian Operational Service Medal – Civilian -
 Rhodesia Medal
Rhodesia Medal -
 Police Overseas Service Medal
Police Overseas Service Medal -
 Humanitarian Overseas Service Medal
Humanitarian Overseas Service Medal -
 National Emergency Medal [note 7]
National Emergency Medal [note 7] -
 Civilian Service Medal 1939–1945
Civilian Service Medal 1939–1945 -
 National Police Service Medal [note 8]
National Police Service Medal [note 8] -
 King Edward VII Coronation Medal (1902)
King Edward VII Coronation Medal (1902) -
 King George V Coronation Medal (1911)
King George V Coronation Medal (1911) -
 King George V Silver Jubilee Medal (1935)
King George V Silver Jubilee Medal (1935) -
 King George VI Coronation Medal (1937)
King George VI Coronation Medal (1937) -
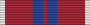 Queen Elizabeth II Coronation Medal (1953)
Queen Elizabeth II Coronation Medal (1953) -
 Queen Elizabeth II Silver Jubilee Medal (1977)
Queen Elizabeth II Silver Jubilee Medal (1977) -
 Queen Elizabeth II Golden Jubilee Medal [note 1] [note 9] (2002)
Queen Elizabeth II Golden Jubilee Medal [note 1] [note 9] (2002) -
 Queen Elizabeth II Diamond Jubilee Medal [note 1] [note 9] (2012)
Queen Elizabeth II Diamond Jubilee Medal [note 1] [note 9] (2012) -
 Queen Elizabeth II Platinum Jubilee Medal [note 1] [note 9] (2022)
Queen Elizabeth II Platinum Jubilee Medal [note 1] [note 9] (2022) -
 King Charles III Coronation Medal [note 1] [note 9] (2023)
King Charles III Coronation Medal [note 1] [note 9] (2023) -
 80th Anniversary Armistice Remembrance Medal (1999)
80th Anniversary Armistice Remembrance Medal (1999) -
 Australian Sports Medal (2000)
Australian Sports Medal (2000) -
 Centenary Medal (2001)
Centenary Medal (2001) -
 Defence Force Service Medal
Defence Force Service Medal -
 Reserve Force Decoration RFD
Reserve Force Decoration RFD -
 Reserve Force Medal
Reserve Force Medal -
 Defence Long Service Medal
Defence Long Service Medal -
 National Medal
National Medal -
 Australian Defence Medal
Australian Defence Medal -
 Australian Cadet Forces Service Medal
Australian Cadet Forces Service Medal -
 Champion Shots Medal
Champion Shots Medal - Long Service Medals [note 10] See United Kingdom Honours Order of Wearing
-
 Service Medal of the Order of St John [12]
Service Medal of the Order of St John [12] -
 Anniversary of National Service 1951–1972 Medal
Anniversary of National Service 1951–1972 Medal - Foreign Awards (in order of date of authorisation of their acceptance and wearing).






