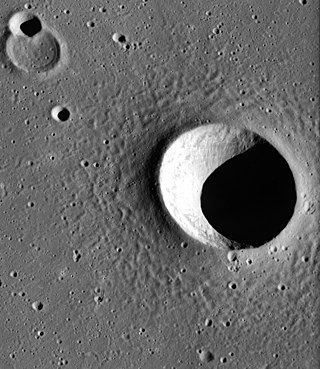
Wollaston is a relatively small lunar impact crater located in the Oceanus Procellarum. To the northwest is the similar Nielsen. To the southeast is the somewhat larger Krieger. There are several small rilles to the southwest of Wollaston, forming part of the Rimae Prinz.

Bobillier is a tiny, cup-shaped lunar impact crater in the southwest part of Mare Serenitatis. It was named after French geometer Étienne Bobillier in 1976. It lies to the north-northwest of the crater Bessel. To the south and west is a wrinkle ridge designated Dorsum Buckland. Bobillier was previously identified as Bessel E.

Ameghino is a lunar impact crater located to the north of the Sinus Successus, a bay in the northeast part of Mare Fecunditatis. Less than 15 kilometers to the northwest of Ameghino were the landing sites of the Soviet Luna 18 and Luna 20 probes.

Euclides is a small lunar impact crater located near the eastern edge of Oceanus Procellarum, about 30 kilometers to the west of the Montes Riphaeus mountains. The mare in the vicinity is devoid of significant craters, but to the west is an area of low rises. The crater is named after the Greek mathematician Euclid.

Apollonius is a lunar impact crater located near the eastern limb of the Moon. It lies in the region of uplands to the west of Mare Undarum and northeast of the Sinus Successus on the Mare Fecunditatis. It was named after Greek mathematician Apollonius of Perga. It is southwest of the crater Firmicus, and north of Condon.

Euler is a lunar impact crater located in the southern half of the Mare Imbrium, and is named after the Swiss mathematician, physician and astronomer Leonhard Euler. The most notable nearby feature is Mons Vinogradov to the west-southwest. There is a cluster of low ridges to the southwest, and this formation includes the small crater Natasha and the tiny Jehan. About 200 kilometers to the east-northeast is the comparably sized crater Lambert.
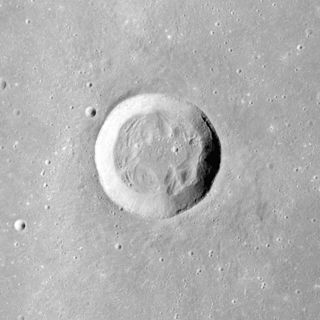
Bessel is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the southern half of the Mare Serenitatis. The crater was named after the German astronomer Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel in 1935. Despite its small size, this is the largest crater to lie entirely within the mare. It lies to the north-northeast of the crater Menelaus.

Bohnenberger is a lunar impact crater that lies near the east edge of the Mare Nectaris, in the foothills of the Montes Pyrenaeus mountain range that forms the perimeter of the mare. To the east beyond the mountains is the larger crater Colombo. The crater has a low rim along the north wall, and the floor is somewhat irregular with a ridge crossing the floor. There is a small crater along the western inner wall.

Bonpland is the remains of a lunar impact crater that is attached to the walled plain Fra Mauro to the north and Parry to the east. The intersection of their rims forms a three-pointed mountainous rise. To the southeast is the small crater Tolansky. Bonpland lies on the eastern edge of Mare Cognitum. It is named after Aimé Bonpland, a French explorer and botanist.

Borman is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. It lies across the southeast section of the mountainous inner ring, within the walled basin named Apollo.

Krieger is a lunar impact crater on the eastern part of the Oceanus Procellarum. It is located to the north-northwest of the flooded crater Prinz, and north-northeast of the prominent ray crater Aristarchus. To the northwest lies the small Wollaston. The crater was formally named in 1935.

Condorcet is a lunar impact crater that is located in the eastern part of the Moon's near side, to the southeast of the Mare Crisium. It was named after French mathematician Marquis de Condorcet. To the northeast of Condorcet are the craters Hansen and Alhazen.
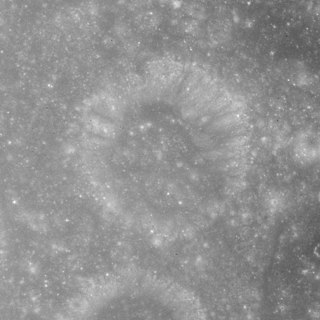
Krogh is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the eastern part of the Moon, to the southeast of the crater Auzout. It was named after Danish zoologist, physiologist and Nobel laureate August Krogh. This crater was previously designated Auzout B. The crater is roughly circular and bowl-shaped, with an inner wall that is wider in the north than the south. It is otherwise an undistinguished formation.

van Albada is a lunar impact crater that is attached to the south-southeastern rim of Auzout. It lies southeast of Mare Crisium, and north-northeast of the larger crater Firmicus. Directly to the east is Krogh.
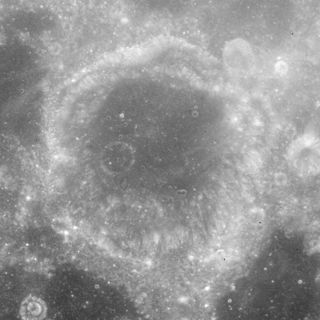
Dubyago is a lunar impact crater that lies in the eastern limb of the Moon. It was named after Russian astronomers Dmitry Dubyago and Alexander Dubyago. It appears significantly foreshortened when viewed from the Earth. It lies along the southern shore of the Mare Undarum, to the southeast of the crater Firmicus.

Firmicus is a lunar impact crater that lies in the eastern part of the Moon's near side, so that from Earth it appears oval in shape due to foreshortening. It is, however, very nearly circular. The crater is located to the west of the Mare Undarum, and northeast of the similar-sized crater Apollonius. To the north of Firmicus are the craters van Albada and Auzout. Attached to its northwest rim is the Lacus Perseverantiae, a miniature lunar mare.

De Roy is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, just behind the southwestern limb. This portion of the lunar surface is brought into view during favorable librations, allowing observation of this formation. However the crater is viewed from the side when watched from the Earth, and little detail can be seen. De Roy lies to the west of the crater Arrhenius, and east of the larger Boltzmann.

Dollond is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the central region of the Moon, to the north of the crater Abulfeda. It was named after British optician John Dollond. Due west of Dollond is Anděl. Dollond is circular and cone shaped, with a tiny floor at the midpoint of the sloping interior walls.

Fox is a small lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is named after the American astronomer Philip Fox. It lies near the northern rim of the crater Wyld, and to the southeast of Babcock. This crater is bowl-shaped, with a roughly circular rim, simple sloping walls and a relatively level, featureless interior. There is some talus along the northern inner wall.
Fibiger is a lunar impact crater located on the lunar near side near the northern pole. The nearest major feature is the Byrd crater. The crater was adopted and named after Danish pathologist Johannes Andreas Grib Fibiger in 2009 by the IAU. Located just north of Fibiger are craters Erlanger and Peary, which are 9.9 km and 73 km in diameter, respectively.























