This article explains terms used for the British Armed Forces' ordnance (weapons) and ammunition. The terms may have different meanings depending on its usage in another country's military.

The BL 15-inch Mark I succeeded the BL 13.5-inch Mk V naval gun. It was the first British 15-inch (380 mm) gun design and the most widely used and longest lasting of any British designs, and arguably the most successful heavy gun ever developed by the Royal Navy. It was deployed on capital ships from 1915 until 1959 and was a key Royal Navy gun in both World Wars.

The BL 18-inch Mk I naval gun was a breech-loading naval rifle used by the Royal Navy during World War I. It was the largest and heaviest gun ever used by the British. Only the Second-World-War Japanese 46 cm/45 Type 94 had a larger calibre, 18.1 inches (46 cm), and it fired a lighter shell. The gun was a scaled-up version of the BL 15 inch Mk I naval gun and was developed to equip the "large light cruiser" Furious. Its barrel length of 60 ft (18 m) was just 40 calibres, slightly limiting its muzzle velocity.

The BL 6-inch gun Mark VII was a British naval gun dating from 1899, which was mounted on a heavy travelling carriage in 1915 for British Army service to become one of the main heavy field guns in the First World War, and also served as one of the main coast defence guns throughout the British Empire until the 1950s.

The 6-inch/47-caliber Mark 16 gun was used in the main batteries of several pre-war and World War II US Navy light cruisers. They were primarily mounted in triple turrets and used against surface targets. The Mark 16DP gun was a dual-purpose fitting of the Mark 16 for use against aircraft as well as surface ships. It was installed in the postwar Worcester-class light cruisers and the anti-aircraft gunnery training ship Mississippi.

The QF 4 inch Mk XVI gun was the standard British Commonwealth naval anti-aircraft and dual-purpose gun of World War II.

The BL 9.2-inch Mk IX and Mk X guns were British breech loading 9.2-inch (234 mm) guns of 46.7 calibre, in service from 1899 to the 1950s as naval and coast defence guns. They had possibly the longest, most varied and successful service history of any British heavy ordnance.
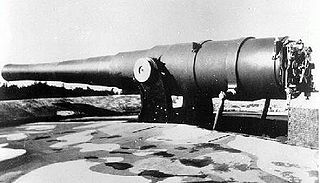
The BL 9.2-inch Mk I–VII guns were a family of early British heavy breechloading naval and coast defence guns in service from 1881 to the end of World War I. They were originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants.

The BL 6-inch gun Marks II, III, IV and VI were the second and subsequent generations of British 6-inch rifled breechloading naval guns, designed by the Royal Gun Factory in the 1880s following the first 6-inch breechloader, the relatively unsuccessful BL 6-inch 80-pounder gun designed by Elswick Ordnance. They were originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants but from the mid-1890s onwards were adapted to use the new cordite propellant. They were superseded on new warships by the QF 6-inch gun from 1891.

The QF 4-inch gun Mk IV was the main gun on most Royal Navy and British Empire destroyers in World War I. It was introduced in 1911 as a faster-loading light gun successor to the BL 4 inch Mk VIII gun. Of the 1,141 produced, 939 were still available in 1939. Mk XII and Mk XXII variants armed many British interwar and World War II submarines.

The BL 6-inch Mark XII naval gun was a British 45 calibre naval gun which was mounted as primary armament on light cruisers and secondary armament on dreadnought battleships commissioned in the period 1914–1926, and remained in service on many warships until the end of World War II.

The BL 12-inch Mark XI and Mark XII gun were British breech loading (BL) naval guns of 50-calibres length mounted as primary armament on dreadnought battleships from 1910.

The 6"/53 caliber gun formed the main battery of some United States Navy light cruisers and three US submarines built during the 1920s.
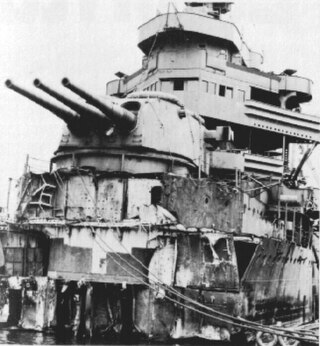
The 8"/55 caliber gun formed the main battery of United States Navy heavy cruisers and two early aircraft carriers. United States naval gun terminology indicates the gun barrel had an internal diameter of 8 inches (203 mm), and the barrel was 55 calibers long.

The BL 8 inch gun Mark VIII was the main battery gun used on the Royal Navy's County-class cruisers, in compliance with the Washington Naval Treaty of 1922. This treaty allowed ships of not more than 10,000 tons standard displacement and with guns no larger than 8 inches (203 mm) to be excluded from total tonnage limitations on a nation's capital ships. The 10,000 ton limit was a major factor in design decisions such as turrets and gun mountings. A similar gun formed the main battery of Spanish Canarias-class cruisers. In 1930, the Royal Navy adopted the BL 6 inch Mk XXIII naval gun as the standard cruiser main battery in preference to this 8-inch gun.

The BL 7.5-inch gun Mark VI was the 45 calibre naval gun forming the main battery of Royal Navy Hawkins-class cruisers. These ships with seven single gun mounts were significant to the cruiser limitations defined by the Washington Naval Treaty.

Third year type 20 cm/50 caliber guns formed the main battery of Japan's World War II heavy cruisers. These guns were also mounted on two early aircraft carriers, the Kaga and the Akagi before their 1935 reconstruction. The typical installation was ten 20 cm/50 guns; although Tone-class cruisers carried eight while Furutaka and Aoba-class cruisers carried six. After modernization, Akagi and Kaga carried only six, divided in three casemates per side, after the removal of the four guns in two turrets on both ships placed on the second deck.

The 20.3 cm SK C/34 was the main battery gun used on the German Admiral Hipper-class heavy cruisers.

The BL 6-inch Mk XXII gun was a British high-velocity 6-inch 50-calibre wire-wound naval guns deployed on the Nelson-class battleships from the 1920s to 1945.

The 152 mm /55 Model 1934–1936 were built for the Italian Navy in the years before World War II. These guns were used on the Duca degli Abruzzi-class Light cruisers, which were the final series of the Condottieri-class cruisers as their primary armament and as secondary armament on the Littorio-class battleships.






















