Chromosome 2 is one of the twenty-three pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 2 is the second-largest human chromosome, spanning more than 242 million base pairs and representing almost eight percent of the total DNA in human cells.
Chromosome 4 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 4 spans more than 193 million base pairs and represents between 6 and 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
Chromosome 5 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 5 spans about 182 million base pairs and represents almost 6% of the total DNA in cells. Chromosome 5 is the 5th largest human chromosome, yet has one of the lowest gene densities. This is partially explained by numerous gene-poor regions that display a remarkable degree of non-coding and syntenic conservation with non-mammalian vertebrates, suggesting they are functionally constrained.
Chromosome 8 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 8 spans about 146 million base pairs and represents between 4.5 and 5.0% of the total DNA in cells.
Chromosome 11 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Humans normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 11 spans about 135 million base pairs and represents between 4 and 4.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. The shorter arm is termed 11p while the longer arm is 11q. At about 21.5 genes per megabase, chromosome 11 is one of the most gene-rich, and disease-rich, chromosomes in the human genome.
Chromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 84 million base pairs and represents between 2.5 and 3% of the total DNA in cells.

Chromosome 20 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Chromosome 20 spans around 66 million base pairs and represents between 2 and 2.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Chromosome 20 was fully sequenced in 2001 and was reported to contain over 59 million base pairs. Since then, due to sequencing improvements and fixes, the length of chromosome 20 has been updated to just over 66 million base pairs.
An Error has occurred retrieving Wikidata item for infobox

BPI fold-containing family B, member 2, (BPIFB2) also known as bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein-like 1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BPIFB2 gene.

Putative ATP-binding cassette transporter sub-family C member 13 is a protein that is not present in humans. In humans, ABCC13 is a pseudogene.
GeneCards is a database of human genes that provides genomic, proteomic, transcriptomic, genetic and functional information on all known and predicted human genes. It is being developed and maintained by the Crown Human Genome Center at the Weizmann Institute of Science, in collaboration with LifeMap Sciences.
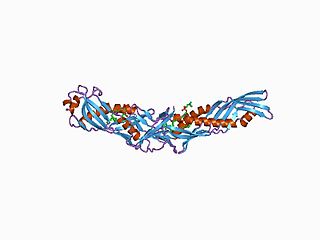
In molecular biology, the lipid-binding serum glycoproteins family, also known as the BPI/LBP/Plunc family or LBP/BPI/CETP family represents a family which includes mammalian lipid-binding serum glycoproteins and/or proteins containing a structural motif known as the BPI fold. Members of this family include:

BPI fold containing family A, member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BPIFA3 gene. The gene is also known as SPLUNC3 and C20orf71 in humans and the orthologous gene in mice is 1700058C13Rik.

The FAM185A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FAM185A gene. The FAM185A gene is found on the positive strand of Chromosome 7 at 7q22.1. The gene begins 102,389,399bp from the p-terminus of the chromosome and ends at 102,449,672bp from the p-terminus; it covers a total of 73,308 basepairs. The protein encoded by this gene is characterized by the presence of multiple copies of DUF4098 near its C-terminus. It is described as a Long Interspersed Nuclear Element (LINE), a subclass of penaeid repetitive elements (PREs).

BPI fold containing family B, member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BPIFB4 gene.

BPI fold containing family B, member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BPIFB1 gene. BPIFB1 is a member of the BPI fold protein superfamily defined by the presence of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein fold which is formed by two similar domains in a "boomerang" shape. The BPI fold creates apolar binding pockets that can interact with lipids, such as the acyl carbon chains of lipopolysaccharide found on Gram-negative bacteria, but members of this family may have many other functions.

Chromosome X Open Reading Frame 38 (CXorf38) is a protein which, in humans, is encoded by the CXorf38 gene. CXorf38 appears in multiple studies regarding the escape of X chromosome inactivation.

BPI fold containing family B, member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BPIFB3 gene. Two variants have been detected in humans.

BPI fold containing family B, member 6 (BPIFB6), also known as bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein-like 3 (BPIL3), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BPIFB6 gene, also known as BPIL3 and LPLUNC6. It is expressed at high levels in hypertrophic tonsils, at relatively moderate levels in oronasal epithelium including nasal mucosa, tongue, and salivary gland, as well as esophageal mucosa at lesser levels. Orthologs are present in many vertebrate species including mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians.

Vomeromodulin is a non-human protein also known as BPI fold containing family B, member 9 (BPIFB9) in the rat encoded by the BPIFB9/RYF3 gene, and as BPI fold containing family B, member 9A (BPIFB9A) encoded by the BPIFB9a gene in the mouse. This protein has been characterized in mammals such as rodents, carnivores, even-toed ungulates, insectivores, bats, lagomorphs, and shrews but is apparently absent in primates and other vertebrates such as birds, reptiles, and amphibians. Its function is associated with detection of chemical odorant pheromone molecules.














