In elementary algebra, the binomial theorem (or binomial expansion) describes the algebraic expansion of powers of a binomial. According to the theorem, it is possible to expand the polynomial (x + y)n into a sum involving terms of the form axbyc, where the exponents b and c are nonnegative integers with b + c = n, and the coefficient a of each term is a specific positive integer depending on n and b. For example, for n = 4,

Diffraction is the interference or bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the propagating wave. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word diffraction and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1660.
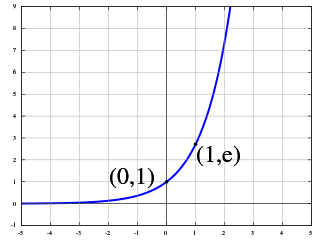
The exponential function is a mathematical function denoted by or . Unless otherwise specified, the term generally refers to the positive-valued function of a real variable, although it can be extended to the complex numbers or generalized to other mathematical objects like matrices or Lie algebras. The exponential function originated from the operation of taking powers of a number, but various modern definitions allow it to be rigorously extended to all real arguments , including irrational numbers. Its ubiquitous occurrence in pure and applied mathematics led mathematician Walter Rudin to consider the exponential function to be "the most important function in mathematics".
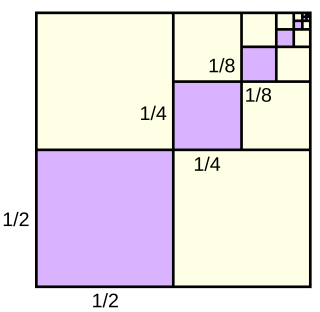
In mathematics, a geometric series is the sum of an infinite number of terms that have a constant ratio between successive terms. For example, the series

In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion.

Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current. Oscillations can be used in physics to approximate complex interactions, such as those between atoms.
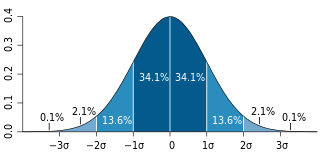
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of a random variable expected about its mean. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. The standard deviation is commonly used in the determination of what constitutes an outlier and what does not.

In mathematics, a tensor is an algebraic object that describes a multilinear relationship between sets of algebraic objects related to a vector space. Tensors may map between different objects such as vectors, scalars, and even other tensors. There are many types of tensors, including scalars and vectors, dual vectors, multilinear maps between vector spaces, and even some operations such as the dot product. Tensors are defined independent of any basis, although they are often referred to by their components in a basis related to a particular coordinate system; those components form an array, which can be thought of as a high-dimensional matrix.

In probability theory and statistics, the negative binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution that models the number of failures in a sequence of independent and identically distributed Bernoulli trials before a specified (non-random) number of successes occurs. For example, we can define rolling a 6 on some dice as a success, and rolling any other number as a failure, and ask how many failure rolls will occur before we see the third success. In such a case, the probability distribution of the number of failures that appear will be a negative binomial distribution.
In mathematics, rings are algebraic structures that generalize fields: multiplication need not be commutative and multiplicative inverses need not exist. Informally, a ring is a set equipped with two binary operations satisfying properties analogous to those of addition and multiplication of integers. Ring elements may be numbers such as integers or complex numbers, but they may also be non-numerical objects such as polynomials, square matrices, functions, and power series.

In calculus, Taylor's theorem gives an approximation of a -times differentiable function around a given point by a polynomial of degree , called the -th-order Taylor polynomial. For a smooth function, the Taylor polynomial is the truncation at the order of the Taylor series of the function. The first-order Taylor polynomial is the linear approximation of the function, and the second-order Taylor polynomial is often referred to as the quadratic approximation. There are several versions of Taylor's theorem, some giving explicit estimates of the approximation error of the function by its Taylor polynomial.
The molar gas constant is denoted by the symbol R or R. It is the molar equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, expressed in units of energy per temperature increment per amount of substance, rather than energy per temperature increment per particle. The constant is also a combination of the constants from Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. It is a physical constant that is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law, the Arrhenius equation, and the Nernst equation.

The Elo rating system is a method for calculating the relative skill levels of players in zero-sum games such as chess. It is named after its creator Arpad Elo, a Hungarian-American physics professor.
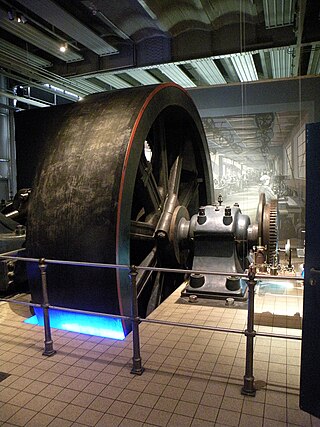
The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular/rotational mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular acceleration about a rotational axis, akin to how mass determines the force needed for a desired acceleration. It depends on the body's mass distribution and the axis chosen, with larger moments requiring more torque to change the body's rate of rotation by a given amount.
Some Buddhist terms and concepts lack direct translations into English that cover the breadth of the original term. Below are given a number of important Buddhist terms, short definitions, and the languages in which they appear. In this list, an attempt has been made to organize terms by their original form and give translations and synonyms in other languages along with the definition.
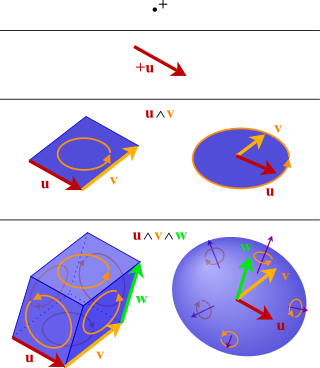
In mathematics, the exterior algebra or Grassmann algebra of a vector space is an associative algebra that contains which has a product, called exterior product or wedge product and denoted with , such that for every vector in The exterior algebra is named after Hermann Grassmann, and the names of the product come from the "wedge" symbol and the fact that the product of two elements of are "outside"

Chaetocerotaceae is a diatom family (Bacillariophyta). This family comprise the three genera Attheya T. West, Bacteriastrum Shadbolt and Chaetoceros Ehrenberg. Chaetoceros is perhaps the largest and most species rich genus of marine planktonic diatoms. The taxonomic status within Chaetocerotaceae at present is somewhat unclear.

Bacteriastrum is a genus of diatoms in family Chaetocerotaceae. There are more than 30 described species in genus Bacteriastrum, but many of these are not currently accepted, and new species are still added to the genus. The type species for the genus is Bacteriastrum furcatum Shadbolt.

In physics, Lagrangian mechanics is a formulation of classical mechanics founded on the stationary-action principle. It was introduced by the Italian-French mathematician and astronomer Joseph-Louis Lagrange in his presentation to the Turin Academy of Science in 1760 culminating in his 1788 grand opus, Mécanique analytique.
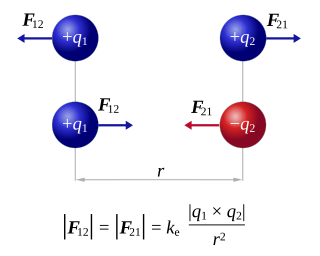
Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law of physics that calculates the amount of force between two electrically charged particles at rest. This electric force is conventionally called the electrostatic force or Coulomb force. Although the law was known earlier, it was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb. Coulomb's law was essential to the development of the theory of electromagnetism and maybe even its starting point, as it allowed meaningful discussions of the amount of electric charge in a particle.
















