
In chemistry, an ester is a functional group derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.

A triglyceride is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids. Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates as well as vegetable fat. They are also present in the blood to enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose from the liver and are a major component of human skin oils.
Acetaldehyde is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3CH=O, sometimes abbreviated as MeCH=O. It is a colorless liquid or gas, boiling near room temperature. It is one of the most important aldehydes, occurring widely in nature and being produced on a large scale in industry. Acetaldehyde occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit, and is produced by plants. It is also produced by the partial oxidation of ethanol by the liver enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase and is a contributing cause of hangover after alcohol consumption. Pathways of exposure include air, water, land, or groundwater, as well as drink and smoke. Consumption of disulfiram inhibits acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, the enzyme responsible for the metabolism of acetaldehyde, thereby causing it to build up in the body.
Xanthine oxidase is a form of xanthine oxidoreductase, a type of enzyme that generates reactive oxygen species. These enzymes catalyze the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and can further catalyze the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid. These enzymes play an important role in the catabolism of purines in some species, including humans.
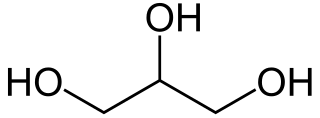
Glycerol ,is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pharmaceutical formulations. Because of its three hydroxyl groups, glycerol is miscible with water and is hygroscopic in nature.
In chemistry, a hydration reaction is a chemical reaction in which a substance combines with water. In organic chemistry, water is added to an unsaturated substrate, which is usually an alkene or an alkyne. This type of reaction is employed industrially to produce ethanol, isopropanol, and butan-2-ol.

Shark liver oil is an oil obtained from the livers of sharks. It has been used for centuries as a folk remedy to promote the healing of wounds and as a remedy for respiratory tract and digestive system problems. It is still promoted as a dietary supplement, and additional claims have been made that it can treat other maladies such as cancer, HIV, radiation sickness, swine flu, and the common cold. To date, none of these claims has been medically validated and shark liver oil (alone) is not a medication prescribed or utilized by American physicians. However, it is a component of some moisturizing skin lotions and hemorrhoid medications.

In biochemistry, an ether lipid refers to any lipid in which the lipid "tail" group is attached to the glycerol backbone via an ether bond at any position. In contrast, conventional glycerophospholipids and triglycerides are triesters. Structural types include:

In organic chemistry an enol ether is an alkene with an alkoxy substituent. The general structure is R2C=CR-OR where R = H, alkyl or aryl. A common subfamily of enol ethers are vinyl ethers, with the formula ROCH=CH2. Important enol ethers include the reagent 3,4-dihydropyran and the monomers methyl vinyl ether and ethyl vinyl ether.

Allyl alcohol is an organic compound with the structural formula CH2=CHCH2OH. Like many alcohols, it is a water-soluble, colourless liquid. It is more toxic than typical small alcohols. Allyl alcohol is used as a precursor to many specialized compounds such as flame-resistant materials, drying oils, and plasticizers. Allyl alcohol is the smallest representative of the allylic alcohols.

Hydroperoxides or peroxols are compounds of the form ROOH, where R stands for any group, typically organic, which contain the hydroperoxy functional group. Hydroperoxide also refers to the hydroperoxide anion and its salts, and the neutral hydroperoxyl radical (•OOH) consist of an unbond hydroperoxy group. When R is organic, the compounds are called organic hydroperoxides. Such compounds are a subset of organic peroxides, which have the formula ROOR. Organic hydroperoxides can either intentionally or unintentionally initiate explosive polymerisation in materials with unsaturated chemical bonds.
sn-Glycerol 3-phosphate is the organic ion with the formula HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OPO32-. It is one of two stereoisomers of the ester of dibasic phosphoric acid (HOPO32-) and glycerol. It is a component of bacterial and eukaryotic glycerophospholipids. From a historical reason, it is also known as L-glycerol 3-phosphate, D-glycerol 1-phosphate, L-α-glycerophosphoric acid.

Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPDH) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible redox conversion of dihydroxyacetone phosphate to sn-glycerol 3-phosphate.

Flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3), also known as dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 3 and trimethylamine monooxygenase, is a flavoprotein enzyme (EC 1.14.13.148) that in humans is encoded by the FMO3 gene. This enzyme catalyzes the following chemical reaction, among others:
Alkylglycerol monooxygenase (AGMO) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydroxylation of alkylglycerols, a specific subclass of ether lipids. This enzyme was first described in 1964 as a pteridine-dependent ether lipid cleaving enzyme. In 2010 finally, the gene coding for alkylglycerol monooxygenase was discovered as transmembrane protein 195 (TMEM195) on chromosome 7. In analogy to the enzymes phenylalanine hydroxylase, tyrosine hydroxylase, tryptophan hydroxylase and nitric oxide synthase, alkylglycerol monooxygenase critically depends on the cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin and iron.

2-Arachidonyl glyceryl ether is a putative endocannabinoid discovered by Lumír Hanuš and colleagues at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel. It is an ether formed from the alcohol analog of arachidonic acid and glycerol. Its isolation from porcine brain and its structural elucidation and synthesis were described in 2001.

Glyceric acid refers to organic compounds with the formula HOCH2CH(OH)CO2H. It occurs naturally and is classified as three-carbon sugar acid. It is chiral. Salts and esters of glyceric acid are known as glycerates.
Cytochrome P450 omega hydroxylases, also termed cytochrome P450 ω-hydroxylases, CYP450 omega hydroxylases, CYP450 ω-hydroxylases, CYP omega hydroxylase, CYP ω-hydroxylases, fatty acid omega hydroxylases, cytochrome P450 monooxygenases, and fatty acid monooxygenases, are a set of cytochrome P450-containing enzymes that catalyze the addition of a hydroxyl residue to a fatty acid substrate. The CYP omega hydroxylases are often referred to as monoxygenases; however, the monooxygenases are CYP450 enzymes that add a hydroxyl group to a wide range of xenobiotic and naturally occurring endobiotic substrates, most of which are not fatty acids. The CYP450 omega hydroxylases are accordingly better viewed as a subset of monooxygenases that have the ability to hydroxylate fatty acids. While once regarded as functioning mainly in the catabolism of dietary fatty acids, the omega oxygenases are now considered critical in the production or break-down of fatty acid-derived mediators which are made by cells and act within their cells of origin as autocrine signaling agents or on nearby cells as paracrine signaling agents to regulate various functions such as blood pressure control and inflammation.

Chimyl alcohol is an organic compound with the formula HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OC16H33. It is a colorless solid. Chimyl alcohol is a monoether formed by condensation of cetyl alcohol with one of the two primary alcohol sites of glycerol. Together with S-selachyl alcohol and S-batyl alcohol, S-chimyl alcohol is a component of some lipid membranes. It is found in the liver of the shark Centrophorus squamosus. The name chimyl is derived from a classification of ratfish, order Chimaeriformes. Like other glyceryl ethers, those derived from chimyl alcohol are not saponifiable.
Selachyl alcohol is an organic compound with the formula HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OC18H35. It is a colorless oil. Selachyl alcohol is a monoether formed by condensation of oleyl alcohol with one of the two primary alcohol sites of glycerol. Together with S-batyl alcohol and S-chimyl alcohol, S-selachyl alcohol is a component of some lipid membranes. It is found in the liver of the shark Centrophorus squamosus. The name selachyl is derived from a classification of sharks, the neoselachii. Like other glyceryl ethers, those derived from selachyl alcohol are not saponifiable.














