The Rock of Gibraltar, also known as the Jabel-al-Tariq, is a monolithic limestone promontory located in the territory of Gibraltar, near the southwestern tip of Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. It is 426 m (1,398 ft) high. Most of the Rock's upper area is covered by a nature reserve, which is home to around 300 Barbary macaques. These macaques, as well as a labyrinthine network of tunnels, attract many tourists each year.

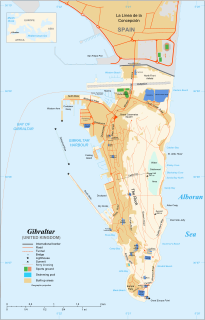
Gibraltar is a British Overseas Territory located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula. It has an area of 6.7 km2 (2.6 sq mi) and is bordered to the north by Spain. The landscape is dominated by the Rock of Gibraltar at the foot of which is a densely populated town area, home to over 32,000 people, primarily Gibraltarians.

The military history of Gibraltar during World War II exemplifies Gibraltar's position as a British fortress since the early 18th century and as a vital factor in British military strategy, both as a foothold on the continent of Europe, and as a bastion of British sea power. During World War II, Gibraltar served a vital role in both the Atlantic Theatre and the Mediterranean Theatre, controlling virtually all naval traffic into and out of the Mediterranean Sea from the Atlantic Ocean.

Princess Caroline's Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located at the northern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, at the junction of Willis's Road and Queen's Road. The nearby Princess Anne's Battery is often mistakenly referred to as Princess Caroline's Battery. The latter was built in 1732 and named after Princess Caroline, the daughter of King George II. Princess Caroline's Battery was updated in 1905, and a 6 inch Mark VII gun was mounted above the magazine. Later, the battery was decommissioned and the gun removed. The underground magazine is now home to the Military Heritage Centre, which includes the Memorial Chamber.

Lord Airey's Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located near the southern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, just north of O'Hara's Battery. It was named after the Governor of Gibraltar, General Sir Richard Airey. Construction of the battery was completed in 1891. The first gun mounted on the battery was a 6-inch breech loading gun, which was replaced with a 9.2-inch Mark X BL gun by 1900. The gun at the battery was last fired in the 1970s. In 1997, it was discovered that Lord Airey's Shelter, adjacent to Lord Airey's Battery, was the site chosen for a covert World War II operation that entailed construction of a cave complex in the Rock of Gibraltar, to serve as an observation post. The battery is listed with the Gibraltar Heritage Trust.

Princess Royal's Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located on Willis's Plateau at the northern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, just southeast of Princess Anne's Battery. Formerly known as Willis' Battery, and later, Queen Anne's Battery or Queen's Battery, it was renamed in the late 18th century after Charlotte, Princess Royal, the eldest daughter of George III. The battery was active from the early 18th century until at least the mid-20th century. However, it has been decommissioned and guns are no longer present. Princess Royal's Battery is listed with the Gibraltar Heritage Trust.

Operation Tracer was a secret Second World War military operation in Gibraltar, a British colony and military base. The impetus for the plan was the 1940 scheme by Germany to capture Gibraltar, code-named Operation Felix. Operation Tracer was the brainchild of Rear Admiral John Henry Godfrey, the Director of the Naval Intelligence Division of the Admiralty.
The Gibraltar Caving Group is an organisation based in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It forms the Caves and Cliffs Section of the Gibraltar Ornithological and Natural History Society. The group of skilled cavers and climbers has multiple roles, engaging in cave exploration and research, avian rescue, and rare plant discovery. It performs surveys and clears areas with limited access. However, it is perhaps most well known for the discovery that four of its members made in December 1996. While exploring tunnels in the southern portion of the Rock of Gibraltar, they found the entrance to Operation Tracer, also known colloquially as Stay Behind Cave. Rumours of a covert World War II observation post had circulated in Gibraltar for decades. The Gibraltar Caving Group continued its exploration and evaluation of the facility under the auspices of the Gibraltar Museum.

Surgeon Lieutenant-Commander Bruce Cooper was a native of Castle Eden, England. He obtained his medical degree from Durham University. Early in his career, he tended to coalminers and joined the Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve. The physician served with distinction in the early period of the Second World War and was mentioned in despatches. In 1941, he was recruited for a highly classified mission, Operation Tracer. In the event that Gibraltar was taken by the Axis powers, he was to be sealed into a secret chamber in the Rock of Gibraltar with five other men for about a year and report the movements of enemy vessels. Over a period of two years, the secret complex was completed and the team assembled and trained. However, the mission was never activated. Cooper returned to England and served in both civilian and military capacities. The location of the secret chamber remained a mystery for decades, but was finally discovered in 1997. However, many questions remained, including the identity of the team members. Upon Cooper's return to Gibraltar in 2008, he confirmed that the cave in question was that which had been destined for himself and his five colleagues. Dr Cooper was the last surviving team member of Operation Tracer in Gibraltar.
Lord Airey's Shelter is a subterranean military shelter in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located near the southern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, adjacent to Lord Airey's Battery. It was named after the Governor of Gibraltar, General Sir Richard Airey. The tunnel system for the shelter was chosen as the site for the highly classified, Second World War military operation known as Operation Tracer.

Poca Roca Cave is a cave in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar.

Coptic Cave is a sea cave in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The cave was intended to be used as a decoy to protect Operation Tracer. This was a plan to leave behind spies should the British lose control of the Rock of Gibraltar in World War II.

Douglas Cave is a cave in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar.

Farringdon's Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. Named after Sir Anthony Farrington, 1st Baronet, it is located above the north face of the Rock of Gibraltar within the Upper Rock Nature Reserve.

AROW Street is a tunnel in Gibraltar that was excavated in 1942. The tunnel, like Gibraltar's Great North Road, was large enough to take Army ammunition trucks.

The Great North Road is a large road tunnel in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It was constructed by the British military during World War II inside the Rock of Gibraltar and remains property of the Ministry of Defence to this day. The road allowed lorries to travel from the north to the south of Gibraltar entirely within the Rock. The tunnel still contains the remains of World War II buildings such as Nissen huts, kitchens, offices as well as a generating station and period anti-submarine nets.

The tunnels of Gibraltar were constructed over the course of nearly 200 years, principally by the British Army. Within a land area of only 2.6 square miles (6.7 km2), Gibraltar has around 34 miles (55 km) of tunnels, nearly twice the length of its entire road network. The first tunnels, excavated in the late 18th century, served as communication passages between artillery positions and housed guns within embrasures cut into the North Face of the Rock. More tunnels were constructed in the 19th century to allow easier access to remote areas of Gibraltar and accommodate stores and reservoirs to deliver the water supply of Gibraltar.

Windmill Hill or Windmill Hill Flats is one of a pair of plateaux, known collectively as the Southern Plateaux, at the southern end of the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located just to the south of the Rock of Gibraltar, which descends steeply to the plateau. Windmill Hill slopes down gently to the south with a height varying from 120 metres (390 ft) at the north end to 90 metres (300 ft) at the south end. It covers an area of about 19 hectares, though about 6 hectares at the north end is built over. The plateau is ringed to the south and east with a line of cliffs which descend to the second of the Southern Plateaux, Europa Flats, which is itself ringed by sea cliffs. Both plateaux are the product of marine erosion during the Quaternary period and subsequent tectonic uplift. Windmill Hill was originally on the shoreline and its cliffs were cut by the action of waves, before the ground was uplifted and the shoreline moved further out to the edge of what is now Europa Flats.
The footpaths of Gibraltar provide access to key areas of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, a refuge for hundreds of species of flora and fauna which in some cases are found nowhere else in Europe. The reserve occupies the upper part of the Rock of Gibraltar, a long and narrow mountain that rises to a maximum height of 424 metres (1,391 ft) above sea level, and constitutes around 40 per cent of Gibraltar's total land area. The unusual geology of the Rock of Gibraltar – a limestone peak adjoining a sandstone hinterland – provides a habitat for plants and animals, such as the Gibraltar candytuft and Barbary partridge, which are found nowhere else in mainland Europe. For many years, the Upper Rock was reserved exclusively for military use; it was fenced off for military purposes, but was decommissioned and converted into a nature reserve in 1993.

















