The Beira Railroad Corporation, (Companhia dos Caminhos de Ferro da Beira in Portuguese) or CCFB, was a joint venture railway company that was responsible for operating the railway lines in central Mozambique. It was formed to reform the railway lines that run from the Port of Beira, Mozambique, originally linking to Zimbabwe, although it later also linked to Malawi.
Formed in 2005, it was made up of 51% of Ricon's capital (a consortium of Indian state-owned companies Rites and Ircon International), and 49% of state-owned Mozambique Ports and Railways (CFM). Its concession was revoked in 2011 for non-compliance with contractual obligations.
The Beira railway has two major segments, the Machipanda line to Zimbabwe, and the Sena line to the coal fields of Moatize with further connection to Malawi.[ citation needed ]
In 2005, the Mozambican government privatized the stretch between the cities of Beira and Machipanda, part of the Beira-Bulawayo Railway (or Machipanda line). The privatization contract required the winning company to renovate the railway (which was destroyed by the 1977-2002 civil war), in addition to carrying out periodic maintenance of infrastructure and transporting cargo and passengers between the aforementioned cities. [1]
The winning company was Ricon (a consortium of Indian state-owned companies Rail India Technical and Economic Service and Ircon International). An agreement was signed to create a joint venture company, Beira Railroad Corporation (CCFB). Ricon would hold 51% of the capital of CCFB, while 49% would belong to state-owned Mozambique Ports and Railways (CFM). [2]
In 2011, CCFB's concession was revoked for non-compliance with contractual obligations and for failures in the works. The CCFB Concession was returned to CFM. [3]
Transportation in Malawi is poorly developed. The country of almost 14 million has 39 airports, 6 with paved runways and 33 with unpaved runways. It has 797 kilometres of railways, all narrow-gauge and about 45 percent of its roads are paved. Though it is landlocked, Malawi also has 700 km (435 mi) of waterways on Lake Malawi and along the Shire River.

Modes of transport in Mozambique include rail, road, water, and air. There are rail links serving principal cities and connecting the country with Malawi, Zimbabwe and South Africa. There are over 30,000 km of roads, but much of the network is unpaved.

Nsanje is the main city in Nsanje District within the Southern Region of Malawi.

Zambia Railways (ZR) is the national railway company of Zambia and one of the two major railway organisations in Zambia. The other system is the binational TAZARA Railway (TAZARA) that interconnects with the ZR at Kapiri Mposhi and provides a link to the Tanzanian port of Dar es Salaam.

RITES Ltd, formerly known as Rail India Technical and Economic Service Limited, is an Indian public sector undertaking and engineering consultancy corporation, specializing in the field of transport infrastructure. Established in 1974 by the Indian Railways, the company's initial charter was to provide consultancy services in rail transport management to operators in India and abroad. RITES has since diversified into planning and consulting services for other infrastructure, including airports, ports, highways and urban planning.

Ircon International, or Indian Railway Construction International Limited (IRCON), is an Indian engineering & construction corporation, specialized in transport infrastructure. The public sector undertaking was established in 1976, by the Indian Railways under the Indian Companies Act 1956. IRCON was registered as the Indian Railway Construction International Limited, a wholly owned entity of the Indian Railways. Its primary charter was the construction of railway projects in India and abroad. Ircon has since diversified into other transport and infrastructure segments and with its expanded scope of operations around the world, the name was changed to Indian Railway International Ltd. in October 1995.

Malawi Railways was a government corporation that ran the national rail network of Malawi, Africa, until privatisation in 1999. With effect from 1 December 1999, the Central East African Railways consortium led by Railroad Development Corporation won the right to operate the network. This was the first rail privatisation in Africa which did not involve a parastatal operator.

The Port of Beira is a Mozambican port located in the city of Beira, capital of the Sofala Province. It is located in Sofala Bay, which forms a huge complex with the mouth of the Pungoe River, known as the Beira estuary, facing the Mozambique Channel. It is the second largest port in Mozambique, built to replace the port of Old Sofala in the 1890s.

Portos e Caminhos de Ferro de Moçambique is a state-owned company that oversees the railway system of Mozambique and its connected ports.
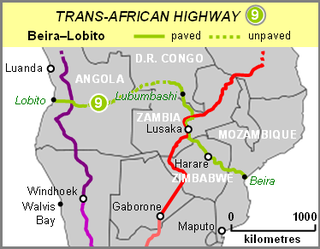
The Beira–Lobito Highway or TAH 9 is Trans-African Highway 9 in the transcontinental road network being developed by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA), the African Development Bank (ADB), and the African Union. The route has a length of 3,523 km (2,189 mi) crossing Angola, the most southerly part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and central Mozambique.
Central East African Railways is a consortium formed in 1999, led by the Railroad Development Corporation, which won the right to operate the Malawi Railways network. The company was sold in September 2008 to INSITEC, an investment group based in Mozambique.
Railway stations in Mozambique include:
The mineral industry of Mozambique plays a significant role in the world's production of aluminium, beryllium, and tantalum. In 2006, Mozambique's share of the world's tantalum mine output amounted to 6%; beryllium, 5%; and aluminium, 2%. Other domestically significant mineral processing operations included cement and natural gas.
Malawi Railways is the national rail network in Malawi, run by a government corporation until privatisation in 1999. As of 1 December 1999 the Central East African Railways, a consortium led by Railroad Development Corporation, won the right to operate the network.

The history of rail transport in Mozambique began in the latter years of the nineteenth century.
CLIN, or the Sociedade do Corredor Logístico Integrado do Norte, is a business company related to logistics, whose main business is railway management in Mozambique and Malawi. The company is a joint venture.

Beira-Bulawayo railway, also called Machipanda railway, Beira-Harare-Bulawayo railway and Beira railway, is a railway that connects the city of Beira, Mozambique, to the city of Bulawayo, in Zimbabwe. It is 850 km long, in a 1067 mm gauge.

Sena railway, also called Shire Highlands railway, Dondo-Malawi railway and North-South Malawi railway, is a railway that connects Dondo, Mozambique, to Chipata, in Zambia. It is c. 1000 km long, in a 1067 mm gauge.

Limpopo Railway, also called Gweru-Maputo railway, is a railway that connects the city of Maputo, Mozambique, to the city from Somabhula, in Zimbabwe. It is 900 km long, in a 1067 mm gauge.