
Gars are members of the Lepisosteiformes, an ancient holosteian order of ray-finned fish; fossils from this order are known from the Late Jurassic onwards. The family Lepisosteidae includes seven living species of fish in two genera that inhabit fresh, brackish, and occasionally marine waters of eastern North America, Central America and Cuba in the Caribbean. Gars have elongated bodies that are heavily armored with ganoid scales, and fronted by similarly elongated jaws filled with long, sharp teeth. Gars are sometimes referred to as "garpike", but are not closely related to pike, which are in the fish family Esocidae. All of the gars are relatively large fish, but the alligator gar is the largest – the alligator gar often grows to a length of over 2 m (6.5 ft) and a weight of over 45 kg (100 lb), and specimens of up to 3 m (9.8 ft) in length have been reported. Unusually, their vascularised swim bladders can function as lungs, and most gars surface periodically to take a gulp of air. Gar flesh is edible and the hard skin and scales of gars are used by humans, but gar eggs are highly toxic.
Beloniformes is an order composed of six families of freshwater and marine ray-finned fish:

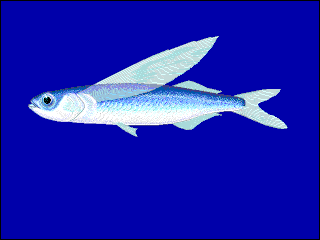
Needlefish or long toms are piscivorous fishes primarily associated with very shallow marine habitats or the surface of the open sea. Some genera include species found in marine, brackish, and freshwater environments, while a few genera are confined to freshwater rivers and streams, including Belonion, Potamorrhaphis, and Xenentodon. Needlefish closely resemble North American freshwater gars in being elongated and having long, narrow jaws filled with sharp teeth, and some species of needlefishes are referred to as gars or garfish despite being only distantly related to the true gars. In fact, the name "garfish" was originally used for the needlefish Belone belone in Europe and only later applied to the North American fishes by European settlers during the 18th century.

The term billfish refers to a group of predatory fish characterised by prominent bills, or rostra, and by their large size; some are longer than 4 m (13 ft). Billfish include sailfish and marlin, which make up the family Istiophoridae, and swordfish, sole member of the family Xiphiidae. They are apex predators which feed on a wide variety of smaller fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods. These two families are sometimes classified as belonging to the order Istiophoriformes, a group with origins in the Late Cretaceous around 71 million years ago with the two families diverging from one and another in the Late Miocene around 15 million years ago. However, they are also classified as being closely related to the mackerels and tuna within the suborder Scombroidei of the order Perciformes. However, the 5th edition of the Fishes of the World does recognise the Istiophoriformes as a valid order, albeit including the Sphyraenidae, the barracudas.
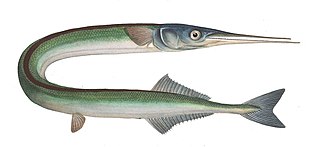
The garfish, also known as the garpike or sea needle, is a pelagic, oceanodromous needlefish found in brackish and marine waters of the Atlantic Ocean, the Pacific Ocean and the Mediterranean, Caribbean, Black, and Baltic Seas.
Tripolis, formerly Ischopolis (Ἰσχόπολις), was an ancient fortress city in Pontus Polemoniacus, on a river of the same name, and with a tolerably good harbour; it is now the site and namesake of the city of Tirebolu in Giresun Province, Black Sea Region, Turkey. It belonged to the Mossynoeci and was situated at a distance of 18 km east from Cape Zephyrium. The place is situated on a rocky headland.

Xenentodon cancila, the freshwater garfish, is a species of needlefish found in freshwater and brackish habitats in South and Southeast Asia.

Tetrapturus is a genus of marlins found in tropical and subtropical oceans throughout the world. Some are popular in big-game fishing.

Belone is a genus of needlefish common in brackish and marine waters. It is one of ten genera in the family Belonidae.
The longbill spearfish is a species of marlin native to the Atlantic Ocean where it is found above the thermocline in open waters between 40°N and 35°S. This species can reach a length of 254 centimetres (100 in) FL and the maximum weight recorded is 58 kilograms (128 lb). It feeds on pelagic fishes such as needlefish, tuna, and jack, as well as squids. They spawn once a year. The specific name honours the Florida game fisherman and taxidermist Albert Pflueger Sr, who died in 1962.
Myxodagnus is a genus of sand stargazers, native to the Pacific and Atlantic coastal waters of the Americas.
Myxodagnus belone, the dartfish, is a species of sand stargazer native to the waters around the Bahamas and Puerto Rico where they can be found on sandy bottoms from near the surface to 4 metres (13 ft) in depth. This species can reach a maximum length of 8.2 centimetres (3.2 in) SL.

The Mediterranean spearfish is a species of marlin native to the Mediterranean Sea where it is particularly common around Italy, although there is a probable record of one caught off Madeira. It is an open-water fish, being found within 200 metres (660 ft) of the surface. This species can reach a length of 240 centimetres (94 in) TL. The heaviest recorded specimen weighed in at 70 kilograms (150 lb) This species is of minor importance to commercial fisheries.
The short-beaked garfish is an uncommon species of needlefish in marine waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean. This pelagic needlefish is present off the coasts of Ireland, Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom, and possibly in the Mediterranean Sea, as well. This species was thought to be the same as the garfish because they share the same waters. The short-beaked garfish matures at 30 cm (12 in) and can grow to a maximum of 65 cm (26 in) while Belone belone can be 95 cm (38 in). Like all needlefish, this one has an elongated body with beak-like jaws that are lined with razor sharp teeth. The short-beaked garfish's lower jaw is longer than the upper. Its body is silvery like most needlefish and has a black stripe running across its lateral line. The dorsal and anal fins are very close to the caudal peduncle. These fish are oviparous. Eggs may be found attached to objects in the water by tendrils on the egg's surface. These spherical eggs are dispersed on the sea floor (demersal). Not much is known about this fish's feeding habits. It likely preys on small oceangoing fish. It has been caught using mackerel. Needlefish tend to be surface fish, so are preyed upon like Atlantic mackerel, European pilchard, sand smelt, etc. The specific name honours Anatolii Nikolaevich Svetovidov (1903-1985) who was an ichthyologist at the Zoological Institute in Saint Petersburg, Russia and a colleague of N.V. Parin.

Tylosurus choram, the Red Sea houndfish, is a species of needlefish from the family Belonidae. A marine fish bluish in color with a long slender body, and a pointed long toothed beak, found in most temperate, warm seas, and sometimes rivers, It's found in abundance in the Red Sea. It is a fast predator swimming in small schools near the water surface. Like other species of needlefish this species is oviparous, laying eggs which attach themselves to objects in the water by means of filaments which cover the outer layer of the egg. Tylosurus choram is found in the Red Sea and the coasts around the Arabian Peninsula to the Gulf of Oman, it also occurs in the eastern Mediterranean Sea having colonised that sea via the Suez Canal, a Lessepsian migration. This species was described as Belone choram by Eduard Rüppell in 1837 with the type locality given as the Red Sea, the specific name choram is Arabic for needlefish.
The long tom or freshwater longtom is a species of euryhaline needlefish native to Northern Australia and Papua New Guinea.: This species occurs in the coastal rivers of tropical Australia and New Guinea. In Australia it has been recorded from the Fitzroy River in Western Australia to the Dawson River in Queensland. It is found in areas of still or flowing water in larger rivers from the tidal reaches to far inland and adults are infrequently recorded in coastal marine waters. Preferred habitats include river channels, floodplain lagoons, muddy creeks and billabongs where it often shelters below overhanging vegetation or among submerged roots. It is a nocturnal hunter of small fishes, crustaceans and insects with the adults being almost exclusively piscivorous, ambushing their prey from cover. Strongylura krefftii was described as Belone krefftii by Albert Günther in 1866 with the type locality given as "Australia ". The specific name honours the Australian zoologist Gerard Krefft (1830-1881) who presented Günther with the type.
Ophis was a town of ancient Pontus on the Black Sea near the mouth of the Ophis River, 90 stadia east of Hyssus.
Platybelone lovii is a species of needlefish from the family Belonidae. It is a predatory, pelagic fish which is endemic to the eastern Atlantic Ocean in the waters around Cape Verde. This species was described by Albert Günther in 1866 as Belone lovii and was named in honour of the British naturalist Richard Thomas Lowe (1802-1874).
Strongylura strongylura, the spottail needlefish or blackspot longtom, is a species of needlefish from the family Belonidae. It is found in the Indian and western Pacific Oceans from the Persian Gulf east to Australia and the Philippines. This species occurs in coastal waters and in mangrove-lined lagoons as well as being recorded in estuarine areas and it has even entered freshwater. Living S. strongylura have been found alive and buried in mud during low tide. It is piscivorous, feeding mainly on clupeoids. This species is oviparous and the eggs adhere to objects in the water which catch the tendrils which cover the surface of the egg. Strongylura strongylura under the synonym of Strongylura caudimaculata is the type species of the genus Strongylura. It as originally described as Belone strongylura by Johan Coenraad van Hasselt in 1823 with the type locality given as Vizagapatam, India.







