
The Croajingolong National Park is a coastal national park located in the East Gippsland region of the Australian state of Victoria. The 88,355-hectare (218,330-acre) national park is situated approximately 450 kilometres (280 mi) east of Melbourne and 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of Sydney.

A nature reserve is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, funga, or features of geological or other special interest, which is reserved and managed for purposes of conservation and to provide special opportunities for study or research. They may be designated by government institutions in some countries, or by private landowners, such as charities and research institutions. Nature reserves fall into different IUCN categories depending on the level of protection afforded by local laws. Normally it is more strictly protected than a nature park. Various jurisdictions may use other terminology, such as ecological protection area or private protected area in legislation and in official titles of the reserves.

Man and the Biosphere Programme (MAB) is an intergovernmental scientific program, launched in 1971 by UNESCO, that aims to establish a scientific basis for the 'improvement of relationships' between people and their environments.
The Royal Botanical Gardens (RBG) is a heritage-listed botanical garden located in the cities of Burlington and Hamilton in Ontario, Canada. It covers extensive environmentally protected areas, historic sites, and culturally relevant gardens from Burlington to Hamilton. It is one of the major tourist attractions between Niagara Falls and Toronto, as well as being a significant local and regional horticultural, education, conservation, and scientific resource.
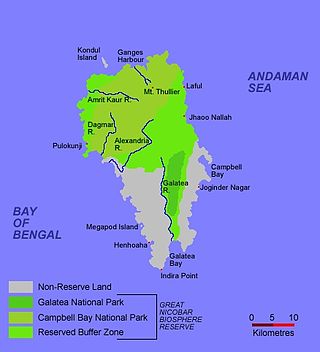
The Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve encompasses a large part of the island of Great Nicobar, the largest of the Nicobar Islands in the Indian Union Territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The Nicobars lie in the Bay of Bengal, eastern Indian Ocean, 190 km (120 mi) to the north of the Indonesian island of Sumatra. The reserve has a total core area of approximately 885 km2, surrounded by a 12 km-wide "forest buffer zone". In year 2013 it was included in the list of Man and Biosphere program of UNESCO to promote sustainable development based on local community effort and sound science.

Protected areas of Canada consist of approximately 12.1 percent of the nation's landmass and freshwater are considered conservation areas, including 11.4 percent designated as protected areas. Approximately 13.8 percent of Canada's territorial waters are conserved, including 8.9 percent designated as protected areas. Terrestrial areas conserved have increased by 65 percent in the 21st century, while marine areas conserved have increased by more than 3,800 percent.

Protected areas of Poland include the following categories, as defined by the Act on Protection of Nature of 16 April 2004, by the Polish Parliament:

Ancient and Primeval Beech Forests of the Carpathians and Other Regions of Europe is a transnational serial nature UNESCO World Heritage Site, encompassing 93 component parts in 18 European countries. Together, the sites protect the largest and least disturbed forests dominated by the beech tree. In many of these stands, especially those in the Carpathians, beech forests have persisted without interruption or interference since the last ice age. These sites document the undisturbed postglacial repopulation of the species.

Despite being a relatively small country, Albania is exceedingly rich in biodiversity. Its ecosystems and habitats support over 5,550 species of vascular and non-vascular plants and more than 15,600 species of coniferous and non-coniferous evergreens, most of which are threatened at global and European levels. The country has made recent efforts to expand its network of protected areas which now include: 11 national parks, 1 marine park, 718 nature monuments, 23 managed nature reserves, 11 protected landscapes, 4 World Heritage Sites, 4 Ramsar sites and other protected areas of various categories, that when combined, account for 21.36% of the territory. Furthermore, a biosphere reserve, 45 important plant areas and 16 important bird areas are found in the country.
Categories of Natural Environment Protected Areas of Ukraine were reestablished (redefined) by the Verkhovna Rada after the fall of the Soviet Union. On 16 June 1992 the President of Ukraine Leonid Kravchuk signed the law on the Nature-Preservation Fund of Ukraine. The law redefined already the established system of environment protection management for Ukraine as a fully sovereign and independent country. National Parks in Ukraine and other protected areas of Ukraine include Ramsar sites in Ukraine, biosphere reserves of Ukraine, National Nature Parks of Ukraine, Nature Reserves of Ukraine, Regional landscape parks of Ukraine, Nature monuments of Ukraine, Protected tracts of Ukraine and Habitat/Species Managed Areas of Ukraine.

The Fundy Biosphere Region is an area of rugged woodlands and coastline that lies along next the upper Bay of Fundy in New Brunswick, Canada. The area covers 442,250 hectares, and was named and designated as a biosphere reserve by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 2007.
Biosphere reserves are areas comprising terrestrial, marine and coastal ecosystems. The biosphere reserve title is handed over by UNESCO. Each reserve promotes solutions reconciling the conservation of biodiversity with its sustainable use. Biosphere reserves are 'Science for Sustainability support sites' – special places for testing interdisciplinary approaches to understanding and managing changes and interactions between social and ecological systems, including conflict prevention and management of biodiversity. Biosphere reserves are nominated by national governments and remain under the sovereign jurisdiction of the states where they are located. Their status is internationally recognized.

Riding Mountain Biosphere Reserve (RMBR) is a UNESCO World Biosphere Reserve designated by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 1986 as part of its Man and the Biosphere Programme. The RMBR, which encompasses Riding Mountain National Park and twelve surrounding municipalities in the province of Manitoba, is one of 16 Biosphere Reserves in Canada. Ecologically sensitive ecosystems include the grasslands, deciduous forest and boreal forest. Although grasslands occupy only 7,400 of the total 1,331,800 hectares, they are considered of national importance since they exist as discrete units and the rare climax rough fescue community represents the eastern extent of its range. The Biosphere Reserve extends the protection of these ecosystems outside of park boundaries. Municipalities in the Riding Mountain Biosphere Reserve include Clanwilliam – Erickson, Dauphin, Gilbert Plains, Grandview, Harrison Park, Lakeshore, McCreary, Rosedale, St. Rose, Riding Mountain West, Rossburn, and Yellowhead. First Nations in the Biosphere Reserve include Rolling River First Nation, Keeseekoowenin First Nation, Waywayseecappo First Nation, and Tootinaowaziibeeng First Nation. Asessippi Provincial Park and Duck Mountain Provincial Forest also border the Biosphere Reserve.

The Manicouagan Uapishka Biosphere Reserve is a biosphere reserve in Canada. The area was designated as such by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 2007.

Clayoquot Sound Biosphere Reserve is a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve situated in Clayoquot Sound on the west coast of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. A diverse range of ecosystems exist within the biosphere reserve boundaries, including temperate coastal rainforest, ocean and rocky coastal shores.

Mount Arrowsmith Biosphere Region (MABR) is a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve located on the east coast of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. It was designated in 2000 by UNESCO to protect a large second-growth coast Douglas fir ecosystem in the watersheds of the Little Qualicum and Englishman Rivers from being developed.
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) Biosphere Reserves are significant institutions of international status as described in the established order of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves within the framework of the Man and the Biosphere Programme. The biosphere reserves specifically promote and support sustainable development for conservation of biological and cultural diversity.































