Lock picking is the practice of unlocking a lock by manipulating the components of the lock device without the original key.

A warded lock is a type of lock that uses a set of obstructions, or wards, to prevent the lock from opening unless the correct key is inserted. The correct key has notches or slots corresponding to the obstructions in the lock, allowing it to rotate freely inside the lock.

The pin tumbler lock, also known as the Yale lock after the inventor of the modern version, is a lock mechanism that uses pins of varying lengths to prevent the lock from opening without the correct key.

A disc tumbler or disc detainer lock is a lock composed of slotted rotating detainer discs. The lock was invented by Finnish founder of Abloy, Emil Henriksson (1886–1959) in 1907 and first manufactured under the Abloy brand in 1918.

A combination lock is a type of locking device in which a sequence of symbols, usually numbers, is used to open the lock. The sequence may be entered using a single rotating dial which interacts with several discs or cams, by using a set of several rotating discs with inscribed symbols which directly interact with the locking mechanism, or through an electronic or mechanical keypad. Types range from inexpensive three-digit luggage locks to high-security safes. Unlike ordinary padlocks, combination locks do not use keys.

A lock is a mechanical or electronic fastening device that is released by a physical object, by supplying secret information, by a combination thereof, or it may only be able to be opened from one side, such as a door chain.

A lever tumbler lock is a type of lock that uses a set of levers to prevent the bolt from moving in the lock. In the simplest form of these, lifting the tumbler above a certain height will allow the bolt to slide past.

A mortise lock is a lock that requires a pocket—the mortise—to be cut into the edge of the door or piece of furniture into which the lock is to be fitted. In most parts of the world, mortise locks are found on older buildings constructed before the advent of bored cylindrical locks, but they have recently become more common in commercial and upmarket residential construction in the United States. The design is widely used in domestic properties of all vintages in Europe.

Padlocks are portable locks usually with a shackle that may be passed through an opening to prevent use, theft, vandalism or harm.

In machining, boring is the process of enlarging a hole that has already been drilled by means of a single-point cutting tool, such as in boring a gun barrel or an engine cylinder. Boring is used to achieve greater accuracy of the diameter of a hole, and can be used to cut a tapered hole. Boring can be viewed as the internal-diameter counterpart to turning, which cuts external diameters.
Medeco, a subsidiary of the Swedish Assa Abloy Group, is a lock manufacturer located in Roanoke County, Virginia, United States.

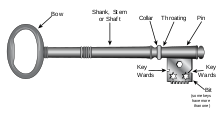
A skeleton key is a type of master key in which the serrated edge has been removed in such a way that it can open numerous locks, most commonly the warded lock. The term derives from the fact that the key has been reduced to its essential parts.
Rekeying a lock is replacing the old lock pins with new lock pins.

Lock bumping is a lock picking technique for opening a pin tumbler lock using a specially crafted bump key, rapping key or 999 key. A bump key must correspond to the target lock in order to function correctly.

A wafer tumbler lock is a type of lock that uses a set of flat wafers to prevent the lock from opening unless the correct key is inserted. This type of lock is similar to the pin tumbler lock and works on a similar principle. However, unlike the pin tumbler lock, where each pin consists of two or more pieces, each wafer in the lock is a single piece. The wafer tumbler lock is often incorrectly referred to as a disc tumbler lock, which uses an entirely different mechanism.
Schlage is an American lock manufacturer founded in 1920 by Walter Schlage. Schlage was headquartered in San Francisco from its inception until it relocated to Colorado Springs, Colorado, in 1997. Schlage also produces high-security key and cylinder lines Primus, Everest, and Everest Primus XP. Schlage is one of the most popular brands of consumer and commercial locks in the United States.

An interchangeable core or IC is an adaptable locking key cylinder, which can be rapidly exchanged in the field via the use of specialized "control keys".

Bilock is a high-security keying system designed and manufactured by Australian Lock Company. It is advertised to be bump-proof, pick-resistant, and drill-resistant. The Bilock cylinder uses a patented locking system with two sidebars, 12 pins, and 12 springs. In the New Generation Bilock, a trigger pin has been added to increase security and extend the registered design of the product. The key design is a U-shape profile with six cuts on each side of the key, along with a central roller to activate the trigger pin in the front and center of the cylinder.
The term protector lock has referred to two unrelated lock designs, one invented in the 1850s by Alfred Hobbs, the other in 1874 by Theodor Kromer.
This is a glossary of locksmithing terms.