Bass is a name shared by many species of fish. The term encompasses both freshwater and marine species, all belonging to the large order Perciformes, or perch-like fishes. The word bass comes from Middle English bars, meaning 'perch'.
Sea bass is a common name for a variety of different species of marine fish. Many fish species of various families have been called sea bass.

Arripis is a genus of marine fishes from Australia and New Zealand, known as Australian salmon, kahawai and Australian herring. They are the only members of the family Arripidae. Despite the common name, Australian salmon are not related to the salmon family Salmonidae of the Northern Hemisphere, just as Australian herring are not related to herring of the Northern Hemisphere, but belong to the order Perciformes of perch-like fishes. Australian salmon were named so by early European settlers after their superficial resemblance to the salmoniform fishes.

The grunt sculpin or grunt-fish is a small fish mainly found in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The grunt sculpin generally remains close to shore and is often found in empty giant barnacle shells. The common name comes from reports that the fish vibrate or "grunt" when held. Its defining feature is its tendency to “hop” along the ocean floor on its orange fins. The short, stout body of the grunt sculpin has a long, small mouth which is adapted for eating smaller prey.

The Australian bass is a small- to medium-sized species of primarily freshwater fish found in coastal rivers and streams along the east coast of Australia. A member of the genus Macquaria from the family Percichthyidae, the Australian bass is an important member of the native fish assemblages found in east coast river systems. It is a native predatory fish and an extremely popular game fish species among anglers. The species was simply called perch in most coastal rivers where it was caught until the 1960s, when the name "Australian bass" started to gain popularity.

The European plaice, commonly referred to as simply plaice, is a species of marine flatfish in the genus Pleuronectes of the family Pleuronectidae.

The European bass is a primarily ocean-going fish native to the waters off Europe's western and southern and Africa's northern coasts, though it can also be found in shallow coastal waters and river mouths during the summer months. It is one of only six species in its family, Moronidae, collectively called the temperate basses.

The Sillaginidae, commonly known as the smelt-whitings, whitings, sillaginids, sand borers and sand-smelts, are a family of benthic coastal marine fish in the order Perciformes. The smelt-whitings inhabit a wide region covering much of the Indo-Pacific, from the west coast of Africa east to Japan and south to Australia. The family comprises only five genera and 35 species, of which a number are dubious, with the last major revision of the family in 1992 unable to confirm the validity of a number of species. They are elongated, slightly compressed fish, often light brown to silver in colour, with a variety of markings and patterns on their upper bodies. The Sillaginidae are not related to a number of fishes commonly called 'whiting' in the Northern Hemisphere, including the fish originally called whiting, Merlangius merlangus.

The King George whiting, also known as the spotted whiting or spotted sillago, is a coastal marine fish of the smelt-whitings family Sillaginidae. The King George whiting is endemic to Australia, inhabiting the south coast of the country from Jurien Bay, Western Australia to Botany Bay, New South Wales in the east. The King George whiting is the only member of the genus Sillaginodes and the largest member of the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae, growing to a length of 80 cm and 4.8 kg in weight. The species is readily distinguishable from other Australian whitings by its unique pattern of spots, as well as its highly elongate shape. King George whiting are often found in bays and protected waterways over sand and seagrass beds, also venturing out onto deep continental shelf reefs during adulthood. The species is a benthic carnivore, consuming a variety of crustaceans, polychaete worms, molluscs and fish. The King George whiting forms the basis of one of southern Australia's most important commercial fisheries, reportedly worth over five million Australian dollars per year. The species is also heavily targeted by recreational anglers, who value the whiting for its sporting and eating qualities.

The southern school whiting, Sillago bassensis, is a common species of coastal marine fish of the smelt-whiting family that inhabits the south and south-west coasts of Australia. Its distribution overlaps a number of other common sillaginids, with careful observation of anatomical features occasionally needed to distinguish between species. The southern school whiting is closely related to the eastern school whiting, Sillago flindersi, and initially were thought to be all one species. The species inhabits both shallow inshore sandy waters, as well as deeper offshore waters, with a transition of habitats occurring with increasing age. It is a predatory fish, taking a variety of crustaceans, polychaetes and bivalves as prey. It reaches sexual maturity at three years of age, and spawns multiple times between December and April. The southern school whiting is commonly caught by commercial and recreational fishermen, often while fishing for related species, especially the sought after King George whiting. The species is marketed fresh in southern Australia.

The Hong Kong grouper is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is found in eastern and southeastern Asian waters of the Western Pacific Ocean. Its natural habitats are shallow seas and coral reefs.

The sand whiting, also known as the summer whiting, yellowfin whiting or blue-nose whiting, is a common species of coastal marine fish of the family Sillaginidae, the smelt-whitings. It is a slender, slightly compressed fish that is very similar to other species of Sillago, with detailed spine, ray and lateral line scale counts needed to distinguish the species between its nearest relative Sillago analis. The sand whiting is distributed along the east coast of Australia from Cape York south to Tasmania, as well as Lord Howe Island and New Caledonia in the Pacific Ocean.

The Japanese whiting, Sillago japonica, is a common species of coastal marine fish belonging to the smelt-whiting family, Sillaginidae. As suggested by its name, the Japanese whiting was first recorded from Japan in 1843, but has subsequently been found to extend to Korea, China and Taiwan.
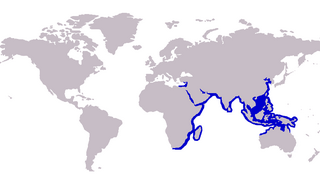
The northern whiting, also known as the silver whiting and sand smelt, is a marine fish, the most widespread and abundant member of the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae. The northern whiting was the first species of sillaginid scientifically described and is therefore the type species of both the family Sillaginidae and the genus Sillago. The species is distributed in the Indo-Pacific region from South Africa in the west to Japan and Indonesia in the east, also becoming an invasive species to the Mediterranean through the Suez Canal. The northern whiting inhabits coastal areas to 60 m, but is most often found in shallow water around bays and estuaries, often entering freshwater. It is a carnivore, taking a variety of polychaetes and crustaceans. The species is of major economic importance throughout the Indo-Pacific. It is most frequently taken by seine nets and cast nets and marketed fresh.

The small-scale whiting, is a species of inshore marine fish of the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae. The small-scale whiting is very similar in body shape and colour to other species in the genus Sillago, but is distinguished by having 12 or 13 spines in the first dorsal fin compared to 11 in all other species. The species is distributed through parts of the west Pacific Ocean including Japan, Taiwan, Korea and India, inhabiting the tidal flats of major estuaries. It is a benthic predator taking crustaceans, molluscs and annelids. Spawning in the species takes place from May to September, with peaks identified in June and July. The eggs and larvae have been extensively studied in order to distinguish them from the more abundant Sillago sihama. Minor fisheries exist for the small-scale whiting, although it is thought be endangered by habitat loss and pollutionIUCN.

The Japanese sea bass is a species of catadromous marine ray-finned fish from the Asian sea bass family Lateolabracidae which is found in the Western Pacific. In Japan this species is known as suzuki.
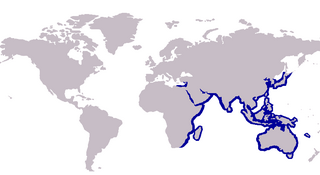
Smelt-whiting is the common name for various species of the family Sillaginidae. The Sillaginidae are distributed throughout the Indo-Pacific region, ranging from the west coast of Africa to Japan and Taiwan in the east, as well occupying as a number of small islands including New Caledonia in the Pacific Ocean. Well known members of this family include King George whiting, Japanese whiting, northern whiting, sand whiting and school whiting.

Porgy is the common name in the US for any fish which belongs to the family Sparidae. They are also called bream. Porgies live in shallow temperate marine waters and are bottom-dwelling carnivores. Most species possess grinding, molar-like teeth. They are often good eating fish, particularly the gilt-head bream and the dentex.

The blackfin snapper, also known as the blackspot snapper, blackfin red snapper, gun-mouth backfin, gun-mouth snapper, redfish and wrenchman is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a snapper belonging to the family Lutjanidae. It is native to the western Atlantic Ocean. It is a commercially important species, though it has been reported to carry the ciguatera toxin.

Sebastes pachycephalus is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae. It is found in shallow rocky reefs of Northwest Pacific.


















