
Calabarzon, sometimes referred to as Southern Tagalog and designated as Region IV‑A, is an administrative region in the Philippines. The region comprises five provinces: Batangas, Cavite, Laguna, Quezon, and Rizal; and one highly urbanized city, Lucena. It is the most populous region in the Philippines, according to the Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA), having over 16.1 million inhabitants in 2020, and is also the country's second most densely populated after the National Capital Region. It is situated southeast of Metro Manila, and is bordered by Manila Bay and South China Sea to the west, Lamon Bay and the Bicol Region to the east, Tayabas Bay and the Sibuyan Sea to the south, and Central Luzon to the north. It is home to places like Mount Makiling near Los Baños, Laguna, and Taal Volcano in Batangas. Calamba is the regional center while Antipolo is the most populous city in the region.

Marinduque, officially the Province of Marinduque, is an island province in the Philippines located in Southwestern Tagalog Region or Mimaropa, formerly designated as Region IV-B. Its capital is the municipality of Boac, the most populous in the province. Marinduque lies between Tayabas Bay to the north and Sibuyan Sea to the south. It is west of the Bondoc Peninsula of Quezon province in mainland Luzon; east of Mindoro Island; and north of the island province of Romblon. Some parts of the Verde Island Passage, the center of the center of world's marine biodiversity and a protected marine area, are also within Marinduque's provincial waters.

Camarines Norte, officially the Province of Camarines Norte, is a province in the Philippines located in the Bicol Region in Luzon. Its capital is Daet, the most populous town in the province. The province borders Quezon to the west, Camarines Sur to the south, and the Philippine Sea to the north. It has historically been a Bikol-speaking region. However, there has been a language shift in recent years to Tagalog, which is more commonly used nowadays.

Aurora, officially the Province of Aurora, is a province in the Philippines located in the eastern part of Central Luzon region, facing the Philippine Sea. Its capital is Baler and borders, clockwise from the south, the provinces of Quezon, Bulacan, Nueva Ecija, Nueva Vizcaya, Quirino, and Isabela. Maria Aurora is the only landlocked town in the province and yet, the most populous. It is the only province in Central Luzon that has no chartered cities.

Padre Burgos, officially the Municipality of Padre Burgos, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Quezon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 23,488 people.

Buenavista, officially the Municipality of Buenavista, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Quezon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 31,160 people.

Catanauan, officially the Municipality of Catanauan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Quezon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 72,752 people.

General Luna, officially the Municipality of General Luna, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Quezon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 24,804 people.

Lopez, officially the Municipality of Lopez, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Quezon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 94,657 people.

Mulanay, officially the Municipality of Mulanay, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Quezon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 55,576 people.

San Francisco, officially the Municipality of San Francisco, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Quezon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 62,097 people.

Unisan, officially the Municipality of Unisan, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Quezon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 25,448 people.

Quezon, officially the Province of Quezon and historically known as Tayabas, is a province in the Philippines located in the Calabarzon region on Luzon. Lucena, a highly urbanized city governed separately from the province, serves as its the provincial capital and its most populous city. The name of the province came from Manuel L. Quezon, the president of the Philippines from 1935 to 1944. The province was known as Kalilayan upon its creation in 1591, renamed as Tayabas by the 18th century, before settling on its current name in 1946. To distinguish the province from Quezon City, it is also known as Quezon Province, a variation of the province's official name.
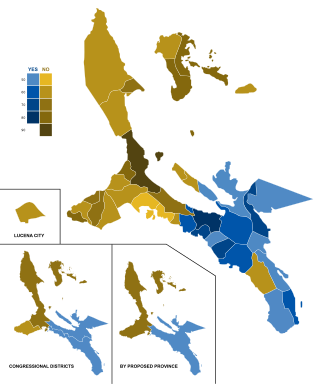
The Quezon del Sur creation plebiscite was a plebiscite on the creation of the province of Quezon del Sur from Quezon; the original Quezon province would have been renamed to "Quezon del Norte" had the plebiscite been approved by the residents of Quezon. The plebiscite was held on December 13, 2008, and the result was a slight majority rejecting the creation of the province.
The Maulawin Spring Protected Landscape is a protected landscape area of forested hills and several rivers and streams located in the province of Quezon on southern Luzon island in the Philippines. It was originally created in 1939 to protect the watershed in the municipality of Guinayangan known as the Maulawin Spring Watershed Forest Reserve declared through Proclamation No. 365 by President Manuel Luis Quezon. It had an initial area of 60 hectares. In 2000, the forest reserve was enlarged and was redesignated as a protected landscape under the National Integrated Protected Areas System by virtue of Proclamation No. 295 issued by President Joseph Estrada. It is the only source of potable water for domestic consumption of the more than 40,000 residents of Guinayangan.
The Buenavista Protected Landscape is a conservation area and an archaeological site located on Bondoc Peninsula in the southern Luzon province of Quezon in the Philippines. It conserves an important watershed area composed of secondary-growth forest, grassland and coconut land in the rural village of Buenavista within the coastal municipality of Mulanay. The area was primarily set aside for watershed protection and timber production in 1937 by President Manuel L. Quezon covering approximately 356 hectares. In 2000, it was reestablished by President Joseph Estrada as a protected landscape area under the National Integrated Protected Areas System. The area is known as the site of an ancient village containing unique limestone graves discovered in 2011. The protected area, including the limestone tombs of Kamhantik were recommended by various scholars to be included in the tentative list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites, yet government or private entities have yet to file a tentative nomination to the UNESCO Secretariat.

The Limestone Tombs of Kamhantik refer to the excavated remains of a thousand-year-old barangay found in the jungles of Mount Maclayao in Sitio Kamhantik within the Buenavista Protected Landscape of Mulanay, Quezon, Philippines. It is widely believed that pre-colonial Tagalog people were responsible for the creation of the tombs.

Local elections were held in the Province of Quezon on May 13, 2019 as part of the 2019 general election. Voters selected candidates for all local positions: a town mayor, vice mayor and town councilors, as well as members of the Sangguniang Panlalawigan, the vice-governor, governor and representatives for the four districts of Quezon.

Quezon's 2nd congressional district is one of the four congressional districts of the Philippines in the province of Quezon, formerly Tayabas. It has been represented in the House of Representatives of the Philippines since 1916 and earlier in the Philippine Assembly from 1907 to 1916. The district consists of Quezon's capital city of Lucena and adjacent municipalities of Candelaria, Dolores, San Antonio, Sariaya and Tiaong. It is currently represented in the 19th Congress by David C. Suarez of Lakas–CMD.
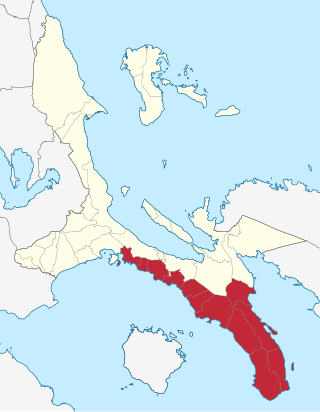
Quezon's 3rd congressional district, also known as the Bondoc Peninsula, is one of the four congressional districts of the Philippines in the province of Quezon, formerly Tayabas. It has been represented in the House of Representatives of the Philippines since 1987. The district consists of municipalities in the Bondoc Peninsula, the southern part of Tayabas Isthmus and southwest coast of Ragay Gulf, namely Agdangan, Buenavista, Catanauan, General Luna, Macalelon, Mulanay, Padre Burgos, Pitogo, San Andres, San Francisco, San Narciso and Unisan. It is currently represented in the 19th Congress by Reynante Arrogancia of the Nationalist People's Coalition.




















