
The Philippines is an archipelago that comprises 7,641 islands, and with a total land area of 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi), it is the world's fifth largest island country. The eleven largest islands contain 95% of the total land area. The largest of these islands is Luzon at about 105,000 square kilometers (40,541 sq mi). The next largest island is Mindanao at about 95,000 square kilometers (36,680 sq mi). The archipelago is around 800 kilometers (500 mi) from the Asian mainland and is located between Taiwan and Borneo.

Luzon is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippine archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as well as Quezon City, the country's most populous city. With a population of 64 million as of 2021, it contains 52.5% of the country's total population and is the 4th most populous island in the world. It is the 15th largest island in the world by land area.

The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by South China, in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Philippines, and in the south by Borneo, eastern Sumatra and the Bangka Belitung Islands, encompassing an area of around 3,500,000 km2 (1,400,000 sq mi). It communicates with the East China Sea via the Taiwan Strait, the Philippine Sea via the Luzon Strait, the Sulu Sea via the straits around Palawan, and the Java Sea via the Karimata and Bangka Straits. The Gulf of Thailand and the Gulf of Tonkin are part of the South China Sea.

Romblon, officially the Province of Romblon, is an archipelagic province of the Philippines located in the Mimaropa region. Its main components include Romblon, an archipelagic municipality of the same name that also serves as the provincial capital; Tablas, the largest island, covering nine municipalities ; Sibuyan with its three towns; as well as the smaller island municipalities of Corcuera, Banton, Concepcion, and San Jose. The province lies south of Marinduque and Quezon, east of Oriental Mindoro, north of Aklan and Capiz, and west of Masbate. According to the 2020 census, it has a total population of 308,985.

Southern Tagalog, designated as Region IV, was an administrative region in the Philippines that comprised the current regions of Calabarzon and Mimaropa, the province of Aurora in Central Luzon, and most of the National Capital Region. It was the largest region in the Philippines in terms of both land area and population. After its partition on May 17, 2002, Southern Tagalog continues to exist as a cultural-geographical region.

The Visayan Sea is a sea in the Philippines surrounded by the islands of the Visayas. It is bounded by the islands Masbate to the north, Panay to the west, Leyte to the east, and Cebu and Negros to the south.
The Philippine archipelago is one of the world's great reservoirs of biodiversity and endemism. The archipelago includes over 7000 islands, and a total land area of 300,780 km2.

USS Tingey (DD-539) was a Fletcher-class destroyer of the United States Navy. She was the third Navy ship to be named for Commodore Thomas Tingey (1750–1829).

The genus Chrotomys contain a unique group of rodents found only in the Philippines, specifically the islands of Luzon, Mindoro, and Sibuyan. Instead of being predominantly herbivorous or omnivorous like other murines, these rats feed predominantly on invertebrates although they do eat some vegetable matter. This vermivory is probably the result of a rat-like animal moving into an ecological niche usually filled by shrews. Shrews and other insectivores are absent on these Philippine islands.

Cajidiocan, officially the Municipality of Cajidiocan, is a municipality in the province of Romblon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 23,259 people. The municipality is located on Sibuyan Island, which has been dubbed as the "Galapagos of Asia" due to its pristine natural environment and high endemism rate for flora and fauna.

The 1978 Pacific typhoon season was a very active season that produced 31 tropical storms, 16 typhoons and one intense typhoon. It ran year-round in 1978, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The Samar Sea is a small sea within the Philippine archipelago, situated between the Bicol Region of Luzon and the Eastern Visayas.

Ragay Gulf is a large gulf in the Bicol Peninsula in Luzon, part of the Sibuyan Sea. It is separated from Tayabas Bay by the Bondoc Peninsula in the west. The gulf covers the provinces of Quezon and Camarines Sur.

The celestial monarch is a species of bird in the family Monarchidae, and one of the most attractive of all the monarch flycatchers. It is identified as a turquoise blue bird with a long and spectacular cerulean blue crest and large greenish-yellow wattle. It is endemic to the Philippines with its extant range being in Luzon, Samar, Mindanao Tawi-Tawi and Basilan and it being possibly extinct on Negros and Sibuyan Island.Its natural habitat is tropical moist lowland forests up to 750 masl. There is an unverified report of this bird in 2024 in Leyte. It is one of the most sought after birds by birdwatchers in the Philippines and in the world.
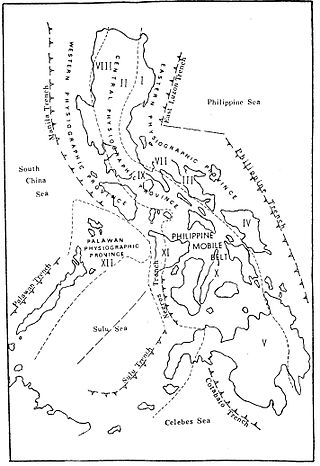
In the geology of the Philippines, the Philippine Mobile Belt is a complex portion of the tectonic boundary between the Eurasian plate and the Philippine Sea plate, comprising most of the country of the Philippines. It includes two subduction zones, the Manila Trench to the west and the Philippine Trench to the east, as well as the Philippine fault system. Within the Belt, a number of crustal blocks or microplates which have been shorn off the adjoining major plates are undergoing massive deformation.
The Philippine fault system is a major inter-related system of geological faults throughout the whole of the Philippine Archipelago, primarily caused by tectonic forces compressing the Philippines into what geophysicists call the Philippine Mobile Belt. Some notable Philippine faults include the Guinayangan, Masbate and Leyte faults.
The Bishop of Romblon is the Ordinary of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Romblon in the Ecclesiastical Province of Capiz, Philippines. The current bishop is Narciso Abellana y Villaver. The local church of the Diocese of Romblon has shown tremendous growth since its erection in April 1974. Although the local situation is characterized by massive poverty because a majority of its people are poor fisher folk and marginalized farmers, the resources and strength of the Romblomanons, as the native inhabitants are called, have come to the fore to solve the vital problems that beset the diocese.

The Guyangan Cave System is a group of caves located in the island municipality of Banton, Romblon in the Philippines. It is located in Guyangan Hill, a limestone formation situated in barangays Togbongan and Toctoc, and consists of seven caves spread in an 85.3-hectare (211-acre) area of forest land.



















