

The Balearic Sea (endotoponym: Mar Balear in Catalan and Spanish) also known as Iberian Sea, [1] is a body of water in the Mediterranean Sea between the Balearic Islands and the mainland of Spain. [2] The Ebro River flows into this small sea.


The Balearic Sea (endotoponym: Mar Balear in Catalan and Spanish) also known as Iberian Sea, [1] is a body of water in the Mediterranean Sea between the Balearic Islands and the mainland of Spain. [2] The Ebro River flows into this small sea.
The Balearic islands are divided into two groups: Gimnesias in the northeast, and Pitiusas in the southwest. [3]

The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the Balearic Sea as follows: [4]
Between the Islas Baleares and the coast of Spain, bounded:
On the Southwest. A line from Cape Sant Antoni, Valencian Community ( 38°50′N0°12′E / 38.833°N 0.200°E ) to Cape Berberia, the Southwest extreme of Formentera (Balearic Islands).
On the Southeast. The South Coast of Formentera, thence a line from Punta Rotja, its Eastern extreme, to the Southern extreme of Cabrera, Balearic Islands ( 39°07′N2°54′E / 39.117°N 2.900°E ) and to Illa de l'Aire, off the Southern extreme of Menorca.
On the Northeast. The East coast of Menorca up to Cap Favaritx ( 40°00′N4°14′E / 40.000°N 4.233°E ) thence a line to Cape Sant Sebastià Catalonia ( 41°54′N3°10′E / 41.900°N 3.167°E ).

The Tyrrhenian Sea is part of the Mediterranean Sea off the western coast of Italy. It is named for the Tyrrhenian people identified with the Etruscans of Italy.

The Tasman Sea is a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean, situated between Australia and New Zealand. It measures about 2,000 km (1,200 mi) across and about 2,800 km (1,700 mi) from north to south. The sea was named after the Dutch explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman, who in 1642 was the first known person to cross it. British explorer Lieutenant James Cook later extensively navigated the Tasman Sea in the 1770s during his three voyages of exploration.

The Gulf of St. Lawrence is the outlet of the North American Great Lakes via the St. Lawrence River into the Atlantic Ocean. The gulf is a semi-enclosed sea, covering an area of about 226,000 square kilometres (87,000 sq mi) and containing about 34,500 cubic kilometres (8,300 cu mi) of water, at an average depth of 152 metres (500 ft).

The Sulu Sea is a body of water in the southwestern area of the Philippines, separated from the South China Sea in the northwest by Palawan and from the Celebes Sea in the southeast by the Sulu Archipelago. Borneo is found to the southwest and Visayas to the northeast.

The Pityusic Islands, often referenced simply as the Pityuses, or commonly but informally as the Pine Islands, is the name given collectively to the Balearic Islands of Ibiza, Formentera, S'Espalmador and other small islets in the Mediterranean Sea.
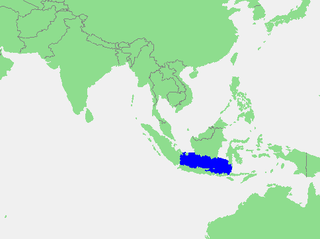
The Java Sea is an extensive shallow sea on the Sunda Shelf, between the Indonesian islands of Borneo to the north, Java to the south, Sumatra to the west, and Sulawesi to the east. Karimata Strait to its northwest links it to the South China Sea. It is a part of the western Pacific Ocean.
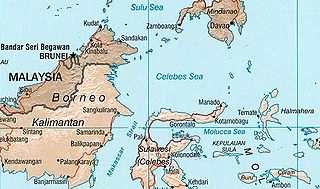
The Celebes Sea, or Sulawesi Sea, of the western Pacific Ocean is bordered on the north by the Sulu Archipelago and Sulu Sea and Mindanao Island of the Philippines, on the east by the Sangihe Islands chain, on the south by Sulawesi's Minahasa Peninsula, and on the west by northern Kalimantan in Indonesia. It extends 420 miles (675 km) north-south by 520 mi (840 km) east-west and has a total surface area of 110,000 square miles (280,000 km2), to a maximum depth of 20,300 feet (6,200 m). South of the Cape Mangkalihat, the sea opens southwest through the Makassar Strait into the Java Sea.

The Savu Sea is a small sea within Indonesia named for the island of Savu (Sawu) on its southern boundary. It is bounded by Savu and Rai Jua to the south, the islands of Rote and Timor to the east, Flores and the Alor archipelago to the north/northwest, and the island of Sumba to the west/northwest. Between these islands, it flows into the Indian Ocean to the south and west, the Flores Sea to the north, and the Banda Sea to the northeast.

This is a list of the extreme points of North America: the points that are highest and lowest, and farther north, south, east or west than any other location on the continent. Some of these points are debatable, given the varying definitions of North America.
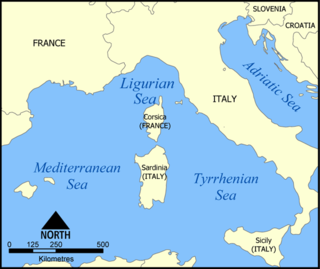
The Ligurian Sea is an arm of the Mediterranean Sea. It lies between the Italian Riviera (Liguria) and the island of Corsica. The sea is thought to have been named after the ancient Ligures people.
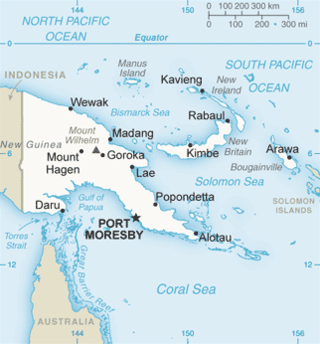
The Solomon Sea is a sea located within the Pacific Ocean. It lies between Papua New Guinea and Solomon Islands. Many major battles were fought there during World War II.

The Molucca Sea is located in the western Pacific Ocean, around the vicinity of Indonesia, specifically bordered by the Indonesian Islands of Celebes (Sulawesi) to the west, Halmahera to the east, and the Sula Islands to the south. The Molucca Sea has a total surface area of 77,000 square miles. The Molucca Sea is rich in coral and has many diving sites due to the deepness of its waters. The deepness of the water explains the reasoning behind dividing the sea into three zones, which functions to transport water from the Pacific Ocean to the shallower seas surrounding it. The deepest hollow in the Molucca Sea is the 15,780-foot (4,810-meter) Batjan basin. This region is known for its periodic experiences of earthquakes, which stems from the sea itself being a micro plate, in which the Molucca Sea is being subducted in two opposite directions: one in the direction of the Eurasian Plate to the west and the other in the direction of the Philippine Sea Plate to the east.

Sant Lluís is a municipality on the tip of south-east Menorca in the Spanish Balearic Islands.

The Balearic Islands are an archipelago in the western Mediterranean Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago conforms a province and autonomous community of Spain, with Palma de Mallorca being its capital and largest city.

The Sea of Sardinia is a body of water in the Mediterranean Sea between the Spanish archipelago of Balearic Islands and the Italian island of Sardinia.

The Inner Seas off the West Coast of Scotland is a marine area designated by the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO). It consists of a number of waterbodies between the Scottish mainland, the Outer Hebrides islands, and the coast of Ireland.
The Coastal Waters of Southeast Alaska and British Columbia is a marine area designated by the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO).

The borders of the oceans are the limits of Earth's oceanic waters. The definition and number of oceans can vary depending on the adopted criteria. The principal divisions of the five oceans are the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern (Antarctic) Ocean, and Arctic Ocean. Smaller regions of the oceans are called seas, gulfs, bays, straits, and other terms. Geologically, an ocean is an area of oceanic crust covered by water.