
The Sulu Sea is a body of water in the southwestern area of the Philippines, separated from the South China Sea in the northwest by Palawan and from the Celebes Sea in the southeast by the Sulu Archipelago. Borneo is found to the southwest and Visayas to the northeast.
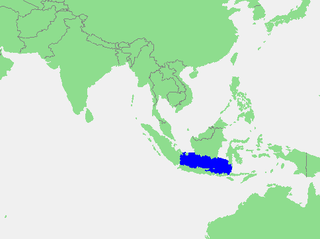
The Java Sea is an extensive shallow sea on the Sunda Shelf, between the Indonesian islands of Borneo to the north, Java to the south, Sumatra to the west, and Sulawesi to the east. Karimata Strait to its northwest links it to the South China Sea. It is a part of the western Pacific Ocean.
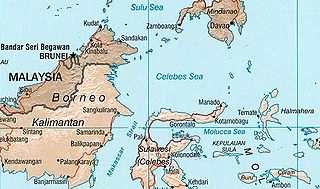
The Celebes Sea or Sulawesi Sea of the western Pacific Ocean is bordered on the north by the Sulu Archipelago and Sulu Sea and Mindanao Island of the Philippines, on the east by the Sangihe Islands chain, on the south by Sulawesi's Minahasa Peninsula, and the west by northern Kalimantan in Indonesia. It extends 420 miles (675 km) north-south by 520 mi (840 km) east-west and has a total surface area of 110,000 square miles (280,000 km2), to a maximum depth of 20,300 feet (6,200 m). South of the Cape Mangkalihat, the sea opens southwest through the Makassar Strait into the Java Sea.

Makassar Strait is a strait between the islands of Borneo and Sulawesi in Indonesia. To the north it joins the Celebes Sea, while to the south it meets the Java Sea. To the northeast, it forms the Sangkulirang Bay south of the Mangkalihat Peninsula. The strait is an important regional shipping route in Southeast Asia.

The Timor Sea is a relatively shallow sea in the Indian Ocean bounded to the north by the island of Timor with Timor-Leste to the north, Indonesia to the northwest, Arafura Sea to the east, and to the south by Australia. The Sunda Trench marks the deepest point of the Timor Sea with a depth of more than 3300 metres, separating the continents of Oceania in the southeast and Asia to the northwest and north. The Timor sea is prone to earthquakes and tsunamis north of the Sunda Trench, due to its location on the Ring of Fire as well as volcanic activity and can experience major cyclones, due to the proximity from the Equator.

The Banda Sea is one of four seas that surround the Maluku Islands of Indonesia, connected to the Pacific Ocean, but surrounded by hundreds of islands, including Timor, as well as the Halmahera and Ceram Seas. It is about 1000 km (600 mi) east to west, and about 500 km (300 mi) north to south.

Rote Island is an island of Indonesia, part of the East Nusa Tenggara province of the Lesser Sunda Islands. According to legend, this island got its name accidentally when a lost Portuguese sailor arrived and asked a farmer where he was. The surprised farmer, who could not speak Portuguese, introduced himself, "Rote".

The Halmahera Sea is a regional sea located in the central eastern part of the Australasian Mediterranean Sea. It is centered at about 1°S and 129°E and is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the north, Halmahera to the west, Waigeo and West Papua to the east, and the Seram Sea to the south. It covers about 95,000 km (59,000 mi) and its topography comprises a number of separate basins and ridges, the chief of which is the Halmahera Basin reaching a depth of 2039 m.

The Arafura Sea lies west of the Pacific Ocean, overlying the continental shelf between Australia and Western New Guinea, which is the Indonesian part of the Island of New Guinea.

Waingapu is the largest town in the eastern half of Sumba island, East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. It is the capital town of the East Sumba Regency.

The Flores Sea covers 240,000 square kilometres (93,000 sq mi) of water in Indonesia. The sea is bounded on the north by the island of Celebes and on the south by the Sunda Islands of Flores and Sumbawa.

The Molucca Sea is located in the western Pacific Ocean, around the vicinity of Indonesia, specifically bordered by the Indonesian Islands of Celebes (Sulawesi) to the west, Halmahera to the east, and the Sula Islands to the south. The Molucca Sea has a total surface area of 77,000 square miles. The Molucca Sea is rich in coral and has many diving sites due to the deepness of its waters. The deepness of the water explains the reasoning behind dividing the sea into three zones, which functions to transport water from the Pacific Ocean to the shallower seas surrounding it. The deepest hollow in the Molucca Sea is the 15,780-foot (4,810-meter) Batjan basin. This region is known for its periodic experiences of earthquakes, which stems from the sea itself being a micro plate, in which the Molucca Sea is being subducted in two opposite directions: one in the direction of the Eurasian Plate to the west and the other in the direction of the Philippine Sea Plate to the east.

The Seram Sea or Ceram Sea is one of several small seas between the scattered islands of Indonesia. It is a section of the Pacific Ocean with an area of approximately 120,000 km2 (46,000 sq mi) located between Buru and Seram, which are two of the islands once called the South Moluccas. These islands are the native habitat of plants long coveted for their use as spices, such as nutmeg, cloves, and black peppercorns, and the seas surrounding them were busy shipping routes. The Seram Sea is also the habitat of several species of tropical goby and many other fish. Like many other small Indonesian seas, the Seram Sea is rocky and very tectonically active.

The Solor Archipelago is a group of islands in the Lesser Sunda Islands, Indonesia, lying to the east of Flores and the west of the Alor Strait and the Alor Archipelago. To the north is the west part of the Banda Sea, while to the south across the Savu Sea lies the island of Timor. The largest islands are, from west to east, Solor, Adonara, and Lembata, although there are many small islands as well.

Ombai Strait is an international strait in Southeast Asia. It separates the Alor Archipelago from the islands of Wetar, Atauro, and Timor in the Lesser Sunda Islands. The strait is also the western portion of a pair of international straits, the other one being Wetar Strait; the two straits combine to link the Pacific Ocean with the Indian Ocean.
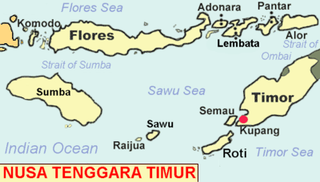
Savu is the largest of a group of three islands, situated midway between Sumba and Rote, west of Timor, in Indonesia's eastern province, East Nusa Tenggara. Ferries connect the islands to Waingapu on Sumba, Ende on Flores, and Kupang in West Timor. Flying to Savu through Susi Air from Kupang, Ende, and Waingapu is also possible.

The Bali Sea is the body of water north of the island of Bali and south of Kangean Island in Indonesia. The sea forms the south-west part of the Flores Sea, and the Madura Strait opens into it from the west.

The Gulf of Boni, also known as the Gulf of Bone, Bay of Boni, and Bone Bay, is the gulf which divides the South and Southeast Peninsulas of the island of Sulawesi (Celebes) in Indonesia. It opens on the south into the Banda Sea.
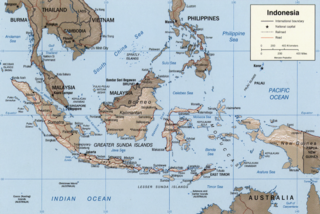
The East Indian Archipelago is an area designated by the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO). It encompasses twelve seas, two gulfs, and one strait in the East Indies.

The borders of the oceans are the limits of Earth's oceanic waters. The definition and number of oceans can vary depending on the adopted criteria. The principal divisions of the five oceans are the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern (Antarctic) Ocean, and Arctic Ocean. Smaller regions of the oceans are called seas, gulfs, bays, straits, and other terms. Geologically, an ocean is an area of oceanic crust covered by water.





















