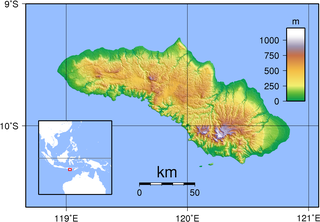
Sumba, natively also spelt as Humba or Hubba is an Indonesian island located in the Eastern Indonesia and administratively part of the East Nusa Tenggara provincial territory. Sumba has an area of 11,006.62 square kilometres, and the population was 779,049 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as of mid-2021 was 788,190. To the northwest of Sumba is Sumbawa, to the northeast, across the Sumba Strait, is Flores, to the east, across the Savu Sea, is Timor, and to the south, across part of the Indian Ocean, is Australia.

East Nusa Tenggara is the southernmost province of Indonesia. It comprises the eastern portion of the Lesser Sunda Islands, facing the Indian Ocean in the south and the Flores Sea in the north. It consists of more than 500 islands, with the largest ones being Sumba, Flores, and the western part of Timor; the latter shares a land border with the separate nation of East Timor. The province is subdivided into twenty-one regencies and the regency-level city of Kupang, which is the capital and largest city.

The Savu Sea is a small sea within Indonesia named for the island of Savu (Sawu) on its southern boundary. It is bounded by Savu and Rai Jua to the south, the islands of Rote and Timor to the east, Flores and the Alor archipelago to the north/northwest, and the island of Sumba to the west/northwest. Between these islands, it flows into the Indian Ocean to the south and west, the Flores Sea to the north, and the Banda Sea to the northeast.

Rote Island is an island of Indonesia, part of the East Nusa Tenggara province of the Lesser Sunda Islands. According to legend, this island got its name accidentally when a lost Portuguese sailor arrived and asked a farmer where he was. The surprised farmer, who could not speak Portuguese, introduced himself, "Rote".
Alor Strait divides the Solor Archipelago from the Alor Archipelago, in the Lesser Sunda Islands of Indonesia. It lies mainly between the larger islands of Pantar and Lembata. The strait connects the western part of the Banda Sea in the north to the Savu Sea in the south.

Ombai Strait is an international strait in Southeast Asia. It separates the Alor Archipelago from the islands of Wetar, Atauro, and Timor in the Lesser Sunda Islands. The strait is also the western portion of a pair of international straits, the other one being Wetar Strait; the two straits combine to link the Pacific Ocean with the Indian Ocean.
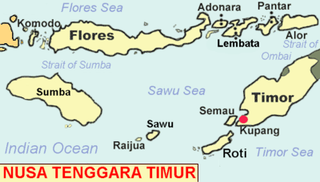
Savu is the largest of a group of three islands, situated midway between Sumba and Rote, west of Timor, in Indonesia's eastern province, East Nusa Tenggara. Ferries connect the islands to Waingapu on Sumba, Ende on Flores, and Kupang in West Timor. Flying to Savu through Susi Air from Kupang, Ende, and Waingapu is also possible.

The Sumba roundleaf bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It lives in Indonesia and East Timor. It is present on the islands of Sumba, Rote, Sumbawa, Flores, Semau, and Savu.

The Sape Strait or Sapie Strait is a strait connecting the Flores Sea to the Sumba Strait. It separates the islands of Sumbawa and Komodo. It joins the Indonesian provinces of West Nusa Tenggara and East Nusa Tenggara.
The Sumba–Hawu languages are a group of closely related Austronesian languages, spoken in East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia.
The Sumba–Flores languages, which correspond to the traditional "Bima–Sumba" subgroup minus Bima, are a proposed group of Austronesian languages spoken on and around the islands of Sumba and western–central Flores in the Lesser Sundas, Indonesia. The main languages are Manggarai, which has half a million speakers on the western third of Flores, and Kambera, with a quarter million speakers on the eastern half of Sumba Island.
The East Indian Archipelago is an area designated by the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO). It encompasses twelve seas, two gulfs, and one strait in the East Indies.

Sabu Raijua Regency is one of the regencies in the province of East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. It comprises the three Savu Islands, lying between Sumba and Rote Island in the Savu Sea. The regency was established by Indonesia's Minister of Home Affairs, Mardiyanto, on 29 October 2008, partitioned from Kupang Regency. The population was 72,960 at the 2010 census, and 89,327 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 92,792.
Savu is an island in East Nusa Tenggara province, Indonesia.

The Hawu language is the language of the Savu people of Savu Island in Indonesia and of Raijua Island off the western tip of Savu. Hawu has been referred to by a variety of names such as Havu, Savu, Sabu, Sawu, and is known to outsiders as Savu or Sabu. Hawu belongs to the Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian language family, and is most closely related to Dhao and the languages of Sumba. Dhao was once considered a dialect of Hawu, but the two languages are not mutually intelligible.

The Savu languages, Hawu and Dhao, are spoken on Savu and Ndao Islands in East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia.

The Lesser Sunda Islands, also known as Nusa Tenggara Islands are an archipelago in Maritime Southeast Asia, most of the Lesser Sunda Islands are located within the Wallacea region, except for the Bali province which is west of the Wallace Line and is within the Sunda Shelf. Together with the Greater Sunda Islands to the west they make up the Sunda Islands. The islands are part of a volcanic arc, the Sunda Arc, formed by subduction along the Sunda Trench in the Java Sea. A bit more than 20 million people live on the islands. Etymologically, Nusa Tenggara means "Southeast Islands" from the words of nusa which means 'island' from Old Javanese language and tenggara means 'southeast'.

The Australasian Mediterranean Sea is a mediterranean sea located in the area between Southeast Asia and Australasia. It connects the Indian and Pacific oceans. It has a maximum depth of 7,440 m and a surface area of 9.08 mil. km².















