
Boronia molloyae, commonly called the tall boronia, is a plant in the citrus family that is endemic to coastal regions in the south-west of Western Australia. It is a shrub with pinnate leaves that mostly have between three and seven leaflets, and deep rose pink, four-petalled flowers. It usually grows along streams in sandy soil.

Cyanothamnus baeckeaceus is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a slender or straggling shrub with simple or trifoliate leaves and pink and white four-petalled flowers. It is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia.

Cyanothamnus coerulescens, commonly known as blue boronia, is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to southern Australia. It is a small, spindly shrub with glandular stems, small, more or less cylindrical leaves and blue to pinkish mauve, four-petalled flowers. There are two subspecies endemic to Western Australia and a third that also occurs in three eastern states.

Boronia anceps is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to a small area in the south-west of Western Australia. It is a perennial herb with small leaves and pink, four-petalled flowers.
Boronia barrettiorum is a plant in the citrus family Rutaceae and is only known from two populations growing north of the Prince Regent River in the Kimberley Australia region of Western Australia. It is an erect, open shrub with hairy branches and leaves, simple or trifoliate leaves and white, four-petalled flowers.
Boronia coriacea is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to a small area in the south-west of Western Australia. It is a small shrub with pinnate leaves and hairless pink, four-petalled flowers in small clusters on the ends of the branches.
Boronia corynophylla is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to a small area in the south-west of Western Australia. It is a spreading shrub with thin, simple, cylindrical to narrow club-shaped leaves and pale red, four-petalled flowers in groups of up to three on the ends of the branches.

Boronia capitata, commonly known as the cluster boronia, is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a slender, spreading shrub with simple leaves and pink, four-petalled flowers.

Cyanothamnus bussellianus is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a slender perennial herb or shrub with well-spaced, simple leaves and pink, blue or white, four-petalled flowers.

Boronia dichotoma is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect, slender perennial herb or shrub with simple leaves and pink, four-petalled flowers. The species is characterised by sticky glandular hairs on the pedicels.

Boronia humifusa is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a low-growing, mostly hairless, wiry perennial with four-angled branches, simple, flat leaves and pink or red, four-petalled flowers in groups on the ends of the branches.
Boronia interrex, commonly known as the Regent River boronia, is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to a small area in the Kimberley region of Western Australia. It is an erect, sometimes low-lying shrub with pinnate leaves, cream-coloured to pale pink sepals and pink petals, the sepals longer and wider than the petals.
Boronia minutipinna is a plant in the citrus family Rutaceae and is endemic to a small area in the Kimberley region of Western Australia. It is an erect shrub with many branches, hairy stems and leaves, pinnate leaves and white to pink, four-petalled flowers with the sepals longer and wider than the petals.

Boronia pauciflora is a plant in the citrus family Rutaceae and is endemic to the Kimberley region of Western Australia. It is an erect shrub usually with simple leaves and white to pink, four-petalled flowers.

Boronia revoluta, commonly known as Ironcap boronia, is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect shrub with three-part leaves and pink or white, four-petalled flowers.

Boronia stricta is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to near-coastal areas of the south-west of Western Australia. It is a slender shrub with often crowded pinnate leaves with linear leaflets, and pink, four-petalled flowers borne singly or in groups of two or three in leaf axils.
Boronia tetragona is a species of plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae, and is endemic to a small area of the southwest of Western Australia. It is an erect, glabrous, perennial herb with simple, sessile leaves and pink, four-petalled flowers.
Boronia thedae, commonly known as the Theda boronia, is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to a small area in the Kimberley region of Western Australia. It is an erect shrub when young, later a prostrate shrub with many branches, pinnate leaves, four white to cream-coloured or pale pink sepals and four similarly coloured petals, the sepals longer and wider than the petals.
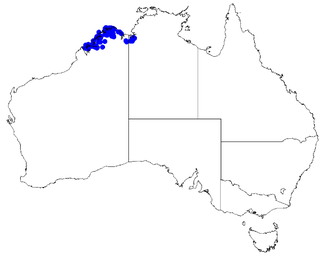
Boronia wilsonii is an erect shrub that is endemic to northern Australia. Its branches, leaves and backs of the flowers are densely covered with woolly hairs. The petals are white to pink or burgundy-coloured.
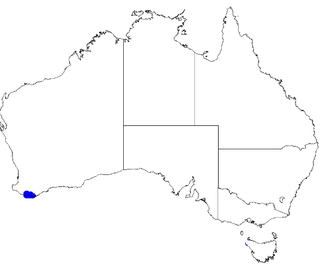
Boronia virgata is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to the south coast of Western Australia. It is a virgate shrub with pinnate leaves with between three and five leaflets, and flowers with red sepals and deep pink, egg-shaped petals.













