Related Research Articles
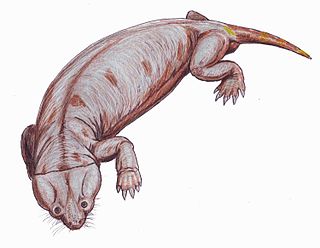
The Cistecephalus Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod assemblage zone or biozone found in the Adelaide Subgroup of the Beaufort Group, a majorly fossiliferous and geologically important geological group of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. This biozone has outcrops located in the Teekloof Formation north-west of Beaufort West in the Western Cape, in the upper Middleton and lower Balfour Formations respectively from Colesberg of the Northern Cape to east of Graaff-Reinet in the Eastern Cape. The Cistecephalus Assemblage Zone is one of eight biozones found in the Beaufort Group, and is considered to be Late Permian in age.
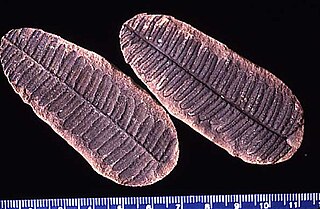
Pecopteris is a very common form genus of leaves. Most Pecopteris leaves and fronds are associated with the marattialean tree fern Psaronius. However, Pecopteris-type foliage also is borne on several filicalean ferns, and at least one seed fern. Pecopteris first appeared in the Devonian period, but flourished in the Carboniferous, especially the Pennsylvanian. Plants bearing these leaves became extinct in the Permian period, due to swamps disappearing and temperatures on Earth dropping.
Ambedus is an extinct genus of possible diadectid reptiliomorph. Fossils have been found from the Early Permian Dunkard Group of Monroe County, Ohio. The type species A. pusillus was named in 2004. The genus name comes from the Latin word ambedo meaning "to nibble", in reference to its herbivorous diet. The specific name pusillus means "tiny" in Latin.

Euromycter is an extinct genus of caseid synapsids that lived in what is now southern France during the Early Permian about 285 million years ago. The holotype and only known specimen of Euromycter (MNHN.F.MCL-2) includes the complete skull with lower jaws and hyoid apparatus, six cervical vertebrae with proatlas, anterior part of interclavicle, partial right clavicle, right posterior coracoid, distal head of right humerus, left and right radius, left and right ulna, and complete left manus. It was collected by D. Sigogneau-Russell and D. Russell in 1970 at the top of the M1 Member, Grès Rouge Group, near the village of Valady, Rodez Basin. It was first assigned to the species "Casea" rutena by Sigogneau-Russell and Russell in 1974. More recently, it was reassigned to its own genus, Euromycter, by Robert R. Reisz, Hillary C. Maddin, Jörg Fröbisch and Jocelyn Falconnet in 2011. The preserved part of the skeleton suggests a size between 1,70 m (5,5 ft) and 1,80 m (5,9 ft) in length for this individual.

Sphenopteris is a genus of seed ferns containing the foliage of various extinct plants, ranging from the Devonian to Late Cretaceous. One species, S. höninghausi, was transferred to the genus Crossotheca in 1911.
Samaropsis is a form genus named by Goeppert in 1864. Later Sewart (1917) redefined the taxon to refer only to the seeds.
Cordaicarpus is a form genus named by Geinitz (1862) and redefined by Seward (1917) to avoid confusion with another genus and to establish that the genus refers only seeds. Seward defined the differences between Cordaicarpus and Samaropsis.
Cheirophyllum is an extinct plant genus that existed during the Permian.

Chiropteris is an extinct genus of plants that existed from the Early Permian to the Late Jurassic.
Stephanophyllites is an extinct genus of plants that lived in the Permian.
Kawizophyllum is an extinct genus of plants that lived in the Permian.
Cyclodendron was a genus of lycophytes dating from the Permian. Plants were vascularized with reproduction by spores.
Neomariopteris is a genus of plants dating from the Permian and Triassic Lower. Vascularized seedless plants (ferns) and reproduction by spores. They leaf type fronds. They lived in locals humid and swampy.
The extinct genus Coricladus of conifers was originally defined by André Jasper, Fresia Ricardi-Branco, and Margot Guerra-Sommer in 2005. The species Coricladus quiteriensis is the type species. The species is named in honor of the place where it was found, the Quitéria outcrop in the city of Pantano Grande in the geopark Paleorrota in Brazil. The outcrop is in the Rio Bonito Formation and dates from the Sakmarian in the Permian.
Portalites is an extinct genus of acritarchs. The species Portalites gondwanensis was located in outcrop Morro do Papaléo in the town of Mariana Pimentel in Brazil, the geopark Paleorrota. The outcrop is in the Rio Bonito Formation and date from Sakmarian in the Permian.
Brazilea is an extinct genus of algae. The species Brazilea helby and Brazilea scissa were located in outcrop Morro do Papaléo in the town of Mariana Pimentel, the geopark Paleorrota. The outcrop dates to the Sakmarian of the Permian.
Leiosphaeridia is an extinct genus of algae or acritarchs. The genus of undefined species were found in outcrop Morro do Papaléo in the town of Mariana Pimentel in Brazil, the geopark Paleorrota. The outcrop date Sakmarian in Permian.
Tetraporina is an extinct genus of algae. The genus of undefined species were found in outcrop Morro do Papaléo in the town of Mariana Pimentel in Brazil, the geopark Paleorrota, on Rio Bonito Formation. The outcrop date Sakmarian in Permian.
Quadrisporites is an extinct genus of acritarchs. The species Q. horridus was located in outcrop Morro do Papaléo in the town of Mariana Pimentel in Brazil, the geopark Paleorrota. The outcrop is in the Rio Bonito Formation and date of Sakmarian in the Permian.

Teyujagua is an extinct genus of small, probably semi-aquatic archosauromorph reptile that lived in Brazil during the Early Triassic period. The genus contains the type and only known species, T. paradoxa. It is known from a well-preserved skull, and probably resembled a crocodile in appearance. It was an intermediary between the primitive archosauromorphs and the more advanced Archosauriformes, revealing the mosaic evolution of how the key features of the archosauriform skull were acquired. Teyujagua also provides additional support for a two-phase model of archosauriform radiation, with an initial diversification in the Permian followed by a second adaptive radiation in the Early Triassic.
References
- ↑ Jasper, André; Guerra-Sommer, Margot; Cazzulo-Klepzig, Miriam; Menegat, Rualdo (2003). "The Botrychiopsis genus and its biostratigraphic implications in Southern Paraná Basin". Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências. 75 (4): 513–535. doi: 10.1590/S0001-37652003000400009 . hdl: 10183/37601 . PMID 14605684.