
Cnidaria is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in fresh water and marine environments, including jellyfish, hydroids, sea anemones, corals and some of the smallest marine parasites. Their distinguishing features are a decentralized nervous system distributed throughout a gelatinous body and the presence of cnidocytes or cnidoblasts, specialized cells with ejectable flagella used mainly for envenomation and capturing prey. Their bodies consist of mesoglea, a non-living, jelly-like substance, sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell thick. Cnidarians are also some of the only animals that can reproduce both sexually and asexually.

A polyp in zoology is one of two forms found in the phylum Cnidaria, the other being the medusa. Polyps are roughly cylindrical in shape and elongated at the axis of the vase-shaped body. In solitary polyps, the aboral end is attached to the substrate by means of a disc-like holdfast called a pedal disc, while in colonies of polyps it is connected to other polyps, either directly or indirectly. The oral end contains the mouth, and is surrounded by a circlet of tentacles.

Hydrozoa is a taxonomic class of individually very small, predatory animals, some solitary and some colonial, most of which inhabit saline water. The colonies of the colonial species can be large, and in some cases the specialized individual animals cannot survive outside the colony. A few genera within this class live in freshwater habitats. Hydrozoans are related to jellyfish and corals and belong to the phylum Cnidaria.

Obelia is a genus of hydrozoans, a class of mainly marine and some freshwater animal species that have both polyp and medusa stages in their life cycle. Hydrozoa belongs to the phylum Cnidaria, which are aquatic organisms that are relatively simple in structure with a diameter around 1mm. There are currently 120 known species, with more to be discovered. These species are grouped into three broad categories: O. bidentata, O. dichotoma, and O. geniculata. O. longissima was later accepted as a legitimate species, but taxonomy regarding the entire genus is debated over.

Aequorea victoria, also sometimes called the crystal jelly, is a bioluminescent hydrozoan jellyfish, or hydromedusa, that is found off the west coast of North America.

Gonionemus is a genus of hydrozoans that uses adhesive discs near the middle of each tentacle to attach to eelgrass, sea lettuce, or various types of algae instead of swimming. They are small and hard to see when hanging onto swaying seaweed. Nevertheless, they are capable of swimming when necessary. The bell is transparent, revealing the four orange to yellowish-tan gonads that lie along most of the length of the four radial canals. The pale yellow manubrium has four short, frilly lips. Up to 80 tentacles line the bell margin, with about an equal number of statocysts. Copepods are a favored prey.

Turritopsis dohrnii, also known as the immortal jellyfish, is a species of small, biologically immortal jellyfish found worldwide in temperate to tropic waters. It is one of the few known cases of animals capable of reverting completely to a sexually immature, colonial stage after having reached sexual maturity as a solitary individual. Others include the jellyfish Laodicea undulata and species of the genus Aurelia.

The flower hat jelly is a species of hydromedusa in the hydrozoan family Olindiidae. Although they look like a jellyfish, they actually belong in the class Hydrozoa, while true jellyfish belong in class Scyphozoa. Flower hat jellies occur in the northwestern Pacific off central and southern Japan, and South Korea's Jeju Island.. The adult form of the flower hat jelly only lives a few months and is typically seen from December to July, with peaks in April and May. During the day they rest on the bottom, often among rocks or algae, but at night they float up to hunt for their prey, typically small fish.

Hydroidolina is a subclass of Hydrozoa and makes up 90% of the class. Controversy surrounds who the sister groups of Hydroidolina are, but research has shown that three orders remain consistent as direct relatives: Siphonophorae, Anthoathecata, and Leptothecata.

Leptothecata, or thecate hydroids, are an order of hydrozoans in the phylum Cnidaria. Their closest living relatives are the athecate hydroids, which are similar enough to have always been considered closely related, and the very apomorphic Siphonophorae, which were placed outside the "Hydroida". Given that there are no firm rules for synonymy for high-ranked taxa, alternative names like Leptomedusa, Thecaphora or Thecata, with or without the ending emended to "-ae", are also often used for Leptothecata.

A gonophore is a reproductive organ in members of the Hydrozoa which produces gametes. It is a sporosac, a medusa or any intermediate stage. The name is derived from the Greek words γόνος and -φόρος.
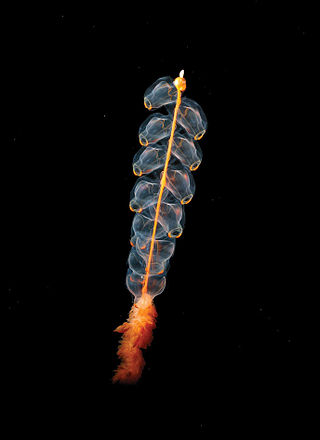
Marrus orthocanna is a species of pelagic siphonophore, a colonial animal composed of a complex arrangement of zooids, some of which are polyps and some medusae. Swimming independently in the mid-ocean, it lives in the Arctic and other cold, deep waters. It is a colonial creature that is born from a single egg which is fertilized. Later on, a protozoan forms that eventually grows to form more duplicating members of the colony. It belongs to the order Siphonophorae and the genus Marrus, which also includes M. antarcticus, M. claudanielis, and M. orthocannoides.

Bougainvillia muscus is a marine invertebrate, a species of hydroid in the suborder Anthomedusae.

Pandeidae is a family of hydroids in the class Hydrozoa. Like other jellyfish there is usually a mature medusa form which is pelagic and reproduces sexually and a hydroid or polyp form which is often benthic and reproduces asexually by budding.
Bougainvillia aberrans is a marine invertebrate, a species of hydroid in the suborder Anthomedusae. It was first described by Dale Calder in 1993. They have four radical clusters of marginal tentacles. Bougainvillia aberrans is found in Bermuda in the western North Atlantic Ocean.

Eudendrium ramosum, sometimes known as the tree hydroid, is a marine species of cnidaria, a hydroid (Hydrozoa) in the family Eudendriidae of the order Anthoathecata.

Obelia longissima is a colonial species of hydrozoan in the order Leptomedusae. Its hydroid form grows as feathery stems resembling seaweed from a basal stolon. It is found in many temperate and cold seas world-wide but is absent from the tropics.

Cassiopea xamachana, commonly known as the upside-down jellyfish, is a species of jellyfish in the family Cassiopeidae. It is found in warm parts of the western Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea, and the Gulf of Mexico. It was first described by the American marine biologist Henry Bryant Bigelow in 1892.

Obelia dichotoma is a broadly distributed, mainly marine but sometimes freshwater, colonial hydrozoan in the order Leptothecata that forms regular branching stems and a distinctive hydrotheca. O. dichotoma can be found in climates from the arctic to the tropics in protected waters such as marches and creeks but not near open coasts like beaches in depths up to 250m. O. dichotoma uses asexual and sexual reproduction and feeds on mainly zooplankton and fecal pellets. Obelia dichotoma has a complex relationship with the ecosystem and many economic systems.

Obelia geniculata is a species of cnidarian belonging to the family Campanulariidae. Its common name is the Knotted Thread Hydroid.


















