
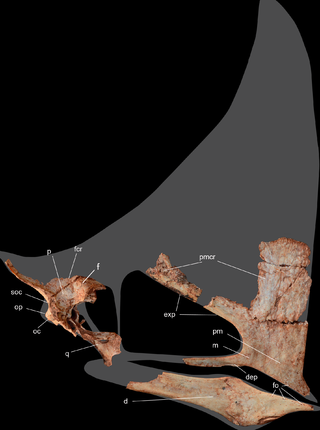
Irritator is a genus of spinosaurid dinosaur that lived in what is now Brazil during the Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous Period, about 113 to 110 million years ago. It is known from a nearly complete skull found in the Romualdo Formation of the Araripe Basin. Fossil dealers had acquired this skull and sold it to the State Museum of Natural History Stuttgart. In 1996, the specimen became the holotype of the type species Irritator challengeri. The genus name comes from the word "irritation", reflecting the feelings of paleontologists who found the skull had been heavily damaged and altered by the collectors. The species name is a homage to the fictional character Professor Challenger from Arthur Conan Doyle's novels.

Spinosauridae is a clade or family of tetanuran theropod dinosaurs comprising ten to seventeen known genera. Spinosaurid fossils have been recovered worldwide, including Africa, Europe, South America and Asia. Their remains have generally been attributed to the Early to Mid Cretaceous.

Koolasuchus is an extinct genus of brachyopoid temnospondyl in the family Chigutisauridae. Fossils have been found from Victoria, Australia and date back 125-120 million years ago to Barremian-Aptian stages of the Early Cretaceous. Koolasuchus is the youngest known temnospondyl. It is known from several fragments of the skull and other bones such as vertebrae, ribs, and pectoral elements. The type species Koolasuchus cleelandi was named in 1997. K. cleelandi was adopted as the fossil emblem for the state of Victoria, Australia on 13 January 2022.

Venaticosuchus is a genus of pseudosuchian archosaurs from the family Ornithosuchidae. Known from a single species, Venaticosuchus rusconii, this genus is described based on an incomplete skull and jaw collected from the Late Triassic (Carnian) Ischigualasto Formation in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina, which was deposited around 230 million years ago. This fossil material has been termed the holotype specimen PVL 2578. Venaticosuchus incorporated a myriad of features present in the other two genera of ornithosuchids, Ornithosuchus and Riojasuchus. However, it also had several unique traits, relating to the lower jaw.

Australosuchus is an extinct monospecific genus of crocodylian belonging to the subfamily Mekosuchinae. The type and only known species Australosuchus clarkae lived during the Late Oligocene and the Early Miocene in the Lake Eyre Basin of South Australia. It was described in 1991 by Paul Willis and Ralph Molnar from fossil material discovered at Lake Palankarinna.

Doswellia is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Late Triassic of North America. It is the most notable member of the family Doswelliidae, related to the proterochampsids. Doswellia was a low and heavily built carnivore which lived during the Carnian stage of the Late Triassic. It possesses many unusual features including a wide, flattened head with narrow jaws and a box-like rib cage surrounded by many rows of bony plates. The type species Doswellia kaltenbachi was named in 1980 from fossils found within the Vinita member of the Doswell Formation in Virginia. The formation, which is found in the Taylorsville Basin, is part of the larger Newark Supergroup. Doswellia is named after Doswell, the town from which much of the taxon's remains have been found. A second species, D. sixmilensis, was described in 2012 from the Bluewater Creek Formation of the Chinle Group in New Mexico; however, this species was subsequently transferred to a separate doswelliid genus, Rugarhynchos. Bonafide Doswellia kaltenbachi fossils are also known from the Chinle Formation of Arizona.
Hyposaurus is a genus of extinct marine dyrosaurid crocodyliform. Fossils have been found in Paleocene aged rocks of the Iullemmeden Basin in West Africa, Campanian–Maastrichtian Shendi Formation of Sudan and Maastrichtian through Danian strata in New Jersey, Alabama and South Carolina. Isolated teeth comparable to Hyposaurus have also been found in Thanetian strata of Virginia. It was related to Dyrosaurus. The priority of the species H. rogersii has been debated, however there is no sound basis for the recognition of more than one species from North America. The other North American species are therefore considered nomina vana.
Pinacosuchus is an extinct genus of crocodylomorph. Its fossils were found in the Late Cretaceous-age North Horn Formation of Utah. Pinacosuchus was a diminutive crocodylomorph with spiky armor, and is known only from meagre remains.

Asiatosuchus is an extinct genus of crocodyloid crocodilians that lived in Eurasia during the Paleogene. Many Paleogene crocodilians from Europe and Asia have been attributed to Asiatosuchus since the genus was named in 1940. These species have a generalized crocodilian morphology typified by flat, triangular skulls. The feature that traditionally united these species under the genus Asiatosuchus is a broad connection or symphysis between the two halves of the lower jaw. Recent studies of the evolutionary relationships of early crocodilians along with closer examinations of the morphology of fossil specimens suggest that only the first named species of Asiatosuchus, A. grangeri from the Eocene of Mongolia, belongs in the genus. Most species are now regarded as nomina dubia or "dubious names", meaning that their type specimens lack the unique anatomical features necessary to justify their classification as distinct species. Other species such as "A." germanicus and "A." depressifrons are still considered valid species, but they do not form an evolutionary grouping with A. grangeri that would warrant them being placed together in the genus Asiatosuchus.
Arganasuchus is an extinct genus of "rauisuchian" (loricatan) archosaur. It is known from a single species, Arganasuchus dutuiti. Fossils of this genus have been found in Upper Triassic rocks of the Argana Basin, Morocco. Though its remains were initially referred to Ticinosuchus when discovered during the 1970s, in 2007 it was identified as a distinct genus with unique features of the pubis and maxilla. Arganasuchus also had several anatomical details in common with Batrachotomus, Fasolasuchus, and Postosuchus, though its relations with other loricatans remains unresolved. Arganasuchus is considered a carnivore due to its large, knife-shaped teeth.

Redondavenator is a genus of sphenosuchian, a type of basal crocodylomorph, the clade that comprises the crocodilians and their closest kin. It is known from a partial upper jaw and left shoulder girdle found in rocks of the Norian-Rhaetian-age Upper Triassic Redonda Formation, northeastern New Mexico. It is notable for its large size; the minimum estimated skull length for the holotype individual is 60 centimetres (2.0 ft). This makes it the largest Triassic crocodylomorph ever recorded.

Sebecus is an extinct genus of sebecid crocodylomorph from Eocene of South America. Like other sebecosuchians, it was entirely terrestrial and carnivorous. The genus is currently represented by two species, the type S. icaeorhinus and S. ayrampu. Several other species have been referred to Sebecus, but were later reclassified as their own genera.

Platyognathus is an extinct genus of protosuchian crocodyliform. Fossils are known from the Early Jurassic Lower Lufeng Formation in Yunnan, China and belong to the type and only species, P. hsui.

Stratiotosuchus is an extinct genus of baurusuchid mesoeucrocodylian from the Adamantina Formation in Brazil. It lived during the Late Cretaceous. The first fossils were found in the 1980s, and the type species Stratiotosuchus maxhechti was named in 2001. A hyperpredator, it and other baurusuchids may have filled niches occupied elsewhere by theropod dinosaurs.

Oxalaia is a genus of spinosaurid dinosaur that lived in what is now the Northeast Region of Brazil during the Cenomanian stage of the Late Cretaceous period, sometime between 100.5 and 93.9 million years ago. Its only known fossils were found in 1999 on Cajual Island in the rocks of the Alcântara Formation, which is known for its abundance of fragmentary, isolated fossil specimens. The remains of Oxalaia were described in 2011 by Brazilian palaeontologist Alexander Kellner and colleagues, who assigned the specimens to a new genus containing one species, Oxalaia quilombensis. The species name refers to the Brazilian quilombo settlements. Oxalaia quilombensis is the eighth officially named theropod species from Brazil and the largest carnivorous dinosaur discovered there. One study suggested that this taxon is a junior synonym of the closely related African genus Spinosaurus, but this was disputed by subsequent studies which consider the genus to be diagnostic.
Acherontisuchus is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid neosuchian from Middle to Late Paleocene deposits of Colombia. The only known species is A. guajiraensis, whose name means "Acheron crocodile of the Guajira Peninsula".
Caiuajara is an extinct genus of tapejarid pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous period of Brazil. It is known from a single type species, Caiuajara dobruskii.
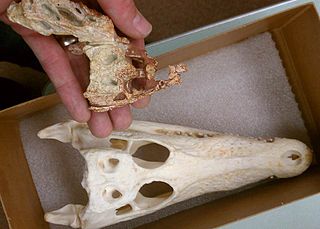
Wannchampsus is an extinct genus of paralligatorid neosuchian, close to but not a true crocodilian. It is known from fossils discovered in Lower Cretaceous rocks in north-central Texas, United States.
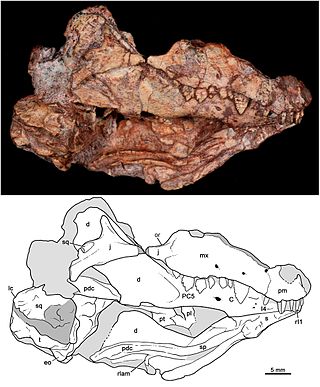
Bonacynodon is an extinct genus of cynodonts that lived in what is now southern Brazil during the Triassic period. The genus is monotypic, containing only the type species Bonacynodon schultzi. B. schultzi is known from two specimens, consisting of two partial skulls and some badly preserved parts of the postcranium. Both specimens were recovered from the Pinheiros-Chiniquá Sequence, part of the Santa Maria Supersequence of the Paraná Basin. This sequence preserves a faunal association known as the Dinodontosaurus Assemblage Zone, which contains numerous other species of cynodonts, dicynodonts and reptiles. Bonacynodon was a small, likely insectivorous cynodont, whose length has been estimated at around 30 centimetres (12 in). It can be distinguished from other cynodonts by its large, serrated (saw-like) canine teeth. Together with the genus Probainognathus of Argentina, it made up the family Probainognathidae, one of the earliest-diverging lineages of the clade Probainognathia. It was a fairly close relative of mammals, the only group of cynodonts alive today.
Titanochampsa is a genus of large mesoeucrocodylian from the Maastrichtian Marilia Formation of Brazil. Although only known from a single skull roof, the material shows that Titanochampsa was not a member of Notosuchia, which were previously believed to have been the only crocodyliforms present in the strata of the Bauru Group. Body size estimates vary greatly and range between 2.98–5.88 m due to the incomplete nature of the holotype fossil. The overall anatomy of the skull roof, alongside its size and possible affinities with Neosuchians, may suggest that it was a semi-aquatic ambush hunter similar to modern crocodilians.














