
Ferdinand Heinrich Herman Strecker was an American entomologist specialising in butterflies and moths (Lepidoptera).

Schinia, commonly called flower moths, is a large genus of moths belonging to the family Noctuidae. The genus has a Holarctic distribution with the vast majority of species being found in North America, many with a very restricted range and larval food plant.

Clepsis melaleucana, the black-patched clepsis, is a moth of the family Tortricidae. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1863. It is found in North America from Alberta to Newfoundland, south to North Carolina and Missouri.

Brachylomia is a genus of moths of the family Noctuidae.

Catocala luciana, the shining underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Herman Strecker in 1874. It is found in western North America, as far east as Minnesota and Illinois and northward into extreme southern Alberta and Saskatchewan. It occurs widely across the Great Plains, south to New Mexico, Arizona and California.

Catocala semirelicta, the semirelict underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1874. It is found in North America from Nevada, Colorado, Utah, California, and Nova Scotia south to Maine, west across Canada to British Columbia, and southward in the mountains.
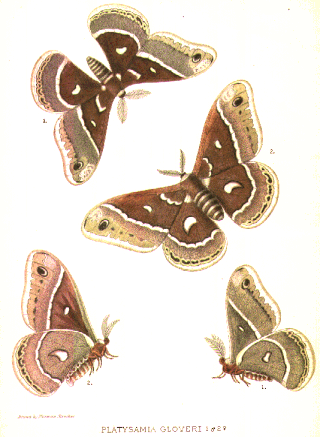
Hyalophora gloveri, or Glover's silkmoth, is a moth of the family Saturniidae. The species was first described by Ferdinand Heinrich Hermann Strecker in 1872. It is found in the Rocky Mountain states, the western parts of the northern Great Plains, and the Canadian prairie provinces, north-west to at least central Alberta. It is also found in northern Mexico.

Anicla exuberans is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by John Bernhardt Smith in 1898. It is found in North America from central Mexico north to the dry interior of southern British Columbia, southern Alberta and south-western Saskatchewan.
Apamea longula is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1879. It is found in western North America, mostly from California to the Great Plains. There are also a few records from areas north, including Alberta, Yukon, and Alaska.

Apamea occidens, the western apamea, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1878. It is native to western North America as far east as Alberta and Kansas.

Brachionycha borealis is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Smith in 1899. It is found in North America from Maine and Pennsylvania west to central Alberta.

Copablepharon grandis, the pale yellow dune moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Strecker in 1878. It is found in North America from southern Alberta east to south-western Manitoba, the eastern parts of South Dakota, North Dakota and Iowa, west to California and south to southern Arizona, New Mexico and western Texas.

Drasteria fumosa, the smoky arches, is a species of moth in the family Erebidae first described by Strecker in 1898. It is found from the US state of California east to Utah and Texas.

Heliothis borealis, the boreal gem, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by George Hampson in 1903. It is found in North America from Quebec west to Alberta, and south in the mountains to south-western Montana.
Euxoa aequalis is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Leon F. Harvey in 1876. It is found in Canada from British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan and Yukon, south into the United States, where it has been recorded from Colorado, Wyoming and California.
Euxoa dargo is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Ferdinand Heinrich Hermann Strecker in 1898. It is found in North America from south-eastern Manitoba west to the southern interior of British Columbia, south to Oregon, southern Idaho and northern New Mexico, and east to eastern South Dakota.
Diarsia calgary, the Calgary dart, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Smith in 1898. It is found in North America in the mountains and foothills from Yukon, south to Arizona and New Mexico, west to the coast of British Columbia. There is a disjunct population in central western California.

Aspitates aberrata is a moth of the family Geometridae first described by Henry Edwards in 1884. It is found in North America from northern Minnesota north and west across southern Manitoba to western Alberta and the Peace River area of British Columbia. The habitat consists of open aspen parklands and low elevation grasslands.

Macaria aemulataria, the common angle moth, is a moth in the family Geometridae. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1861. It is found from Nova Scotia to Florida, west to Texas, north to Oregon and Alberta.

Eupithecia niveifascia is a moth in the family Geometridae first described by George Duryea Hulst in 1898. It is found in North America from south-western Alberta west to Vancouver Island, north to northern coastal British Columbia and south to New Mexico.











