
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, with its introduction occurring at the 1908 Olympics in London. The Olympic disciplines are men's singles, women's singles, pair skating, and ice dance; the four individual disciplines are also combined into a team event, which was first included in the Winter Olympics in 2014. The non-Olympic disciplines include synchronized skating, Theater on Ice, and four skating. From intermediate through senior-level competition, skaters generally perform two programs, which, depending on the discipline, may include spins, jumps, moves in the field, lifts, throw jumps, death spirals, and other elements or moves.
Figure skating jumps are an element of three competitive figure skating disciplines: men's singles, women's singles, and pair skating – but not ice dancing. Jumping in figure skating is "relatively recent". They were originally individual compulsory figures, and sometimes special figures; many jumps were named after the skaters who invented them or from the figures from which they were developed. It was not until the early part of the 20th century, well after the establishment of organized skating competitions, when jumps with the potential of being completed with multiple revolutions were invented and when jumps were formally categorized. In the 1920s Austrian skaters began to perform the first double jumps in practice. Skaters experimented with jumps, and by the end of the period, the modern repertoire of jumps had been developed. Jumps did not have a major role in free skating programs during international competitions until the 1930s. During the post-war period and into the 1950s and early 1960s, triple jumps became more common for both male and female skaters, and a full repertoire of two-revolution jumps had been fully developed. In the 1980s men were expected to complete four or five difficult triple jumps, and women had to perform the easier triples. By the 1990s, after compulsory figures were removed from competitions, multi-revolution jumps became more important in figure skating.

Spins are an element in figure skating in which the skater rotates, centered on a single point on the ice, while holding one or more body positions. They are performed by all disciplines of the sport, single skating, pair skating, and ice dance, and are a required element in most figure skating competitions. As The New York Times says, "While jumps look like sport, spins look more like art. While jumps provide the suspense, spins provide the scenery, but there is so much more to the scenery than most viewers have time or means to grasp". According to world champion and figure skating commentator Scott Hamilton, spins are often used "as breathing points or transitions to bigger things".

Compulsory figures or school figures were formerly a segment of figure skating, and gave the sport its name. They are the "circular patterns which skaters trace on the ice to demonstrate skill in placing clean turns evenly on round circles". For approximately the first 50 years of figure skating as a sport, until 1947, compulsory figures made up 60 percent of the total score at most competitions around the world. These figures continued to dominate the sport, although they steadily declined in importance, until the International Skating Union (ISU) voted to discontinue them as a part of competitions in 1990. Learning and training in compulsory figures instilled discipline and control; some in the figure skating community considered them necessary to teach skaters basic skills. Skaters would train for hours to learn and execute them well, and competing and judging figures would often take up to eight hours during competitions.
The toe loop jump is the simplest jump in the sport of figure skating. It was invented in the 1920s by American professional figure skater Bruce Mapes. The toe loop is accomplished with a forward approach on the inside edge of the blade; the skater then switches to a backward-facing position before their takeoff, which is accomplished from the skater's right back outside edge and left toepick. The jump is exited from the back outside edge of the same foot. It is often added to more difficult jumps during combinations and is the most common second jump performed in combinations. It is also the most commonly attempted jump.

Artistic roller skating is a competitive sport similar to figure skating but where competitors wear roller skates instead of ice skates. Within artistic roller skating, there are several disciplines:
A spiral is an element in figure skating where the skater glides on one foot while raising the free leg above hip level. It is akin to the arabesque in ballet.
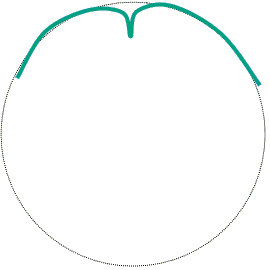
A three-turn is a figure skating element which involves both a change in direction and a change in edge. For example, when a skater executes a forward outside three-turn, the skater begins on a forward outside edge and finishes on a backwards inside edge. There are eight three-turns in all; one for each possible combination of direction, skating foot, and edge.
A choctaw turn is a turn in figure skating that involves both a change of foot and a change of edge and lobe. Choctaws are the two-foot equivalents of rockers and counters, in the same way that mohawk turns are the two-foot equivalents of three turns and brackets.

Athletes from the Netherlands competed at the 2006 Winter Olympics in Turin, Italy. The team of 35 competed in speed skating, bobsleigh, short track speed skating and snowboarding. The Dutch flag bearer during the opening ceremony was speedskater Jan Bos.
A twizzle is "a multirotational, one-foot turn that moves across the ice" in the sport of figure skating. First performed by David Grant in 1990 the International Skating Union (ISU) defines a twizzle as "a traveling turn on one foot with one or more rotations which is quickly rotated with a continuous (uninterrupted) action". It is most often performed in ice dance, although single skaters and pair skaters also perform the element. Twizzles have been called "the quads of ice dance" because like quadruple jumps in other disciplines, twizzles are risky and technically demanding.
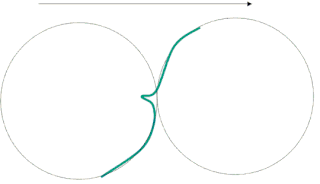
A rocker turn is a kind of one-foot turn in figure skating. Unlike three turns and brackets, where the entry and exit edges follow the same curve, in a rocker, the entry and exit are on opposite curves. When executing a rocker, the skater turns inward on the curve of the entry edge, but exits on a curve in the opposite sense. Another way to look at it is that a rocker is similar to the entry of a three turn combined with the exit of a bracket. In a rocker turn, the skating edge is maintained; for example, a rocker from a forward outside edge ends on a backward outside edge.

A counter turn is a kind of one-foot turn in figure skating. Unlike three turns and brackets, where the entry and exit edges follow the same curve, in a counter the entry and exit are on opposite curves. When executing a counter, the skater turns outward to the curve of the entry edge, and exits on a curve in the same sense as the turn. Another way to look at it is that a counter is similar to the entry of a bracket turn combined with the exit of a three turn.

Pair skating is a figure skating discipline defined by the International Skating Union (ISU) as "the skating of two persons in unison who perform their movements in such harmony with each other as to give the impression of genuine Pair Skating as compared with independent Single Skating". The ISU also states that a pairs team consists of "one Woman and one Man". Pair skating, along with men's and women's single skating, has been an Olympic discipline since figure skating, the oldest Winter Olympic sport, was introduced at the 1908 Summer Olympics in London. The ISU World Figure Skating Championships introduced pair skating in 1908.
The ISU Judging System or the International Judging System (IJS), occasionally referred to as the Code of Points (COP) system, is the scoring system that has been used since 2004 to judge the figure skating disciplines of men's and ladies' singles, pair skating, ice dance, and synchronized skating. It was designed and implemented by the International Skating Union (ISU), the ruling body of the sport.
The following is a glossary of figure skating terms, sorted alphabetically.

Single skating is a discipline of figure skating in which male and female skaters compete individually. Men's singles and women's singles are governed by the International Skating Union (ISU). Figure skating is the oldest winter sport contested at the Olympics, with men's and women's single skating appearing as two of the four figure skating events at the London Games in 1908.
British Ice Skating is the national governing body of ice skating within the United Kingdom. Formed in 1879, it is responsible for overseeing all disciplines of ice skating: figure skating ; synchronised skating; and speed skating.
A step sequence is a required element in all four disciplines of figure skating, men's single skating, women's single skating, pair skating, and ice dance. Step sequences have been defined as "steps and turns in a pattern on the ice". Skaters earn the most points in step sequences by performing steps and movements with "flair and personality", by turning in both directions, by using one foot and then the other, and by including up and down movements.
The 2012 Skate Canada International was the second event of six in the 2012–13 ISU Grand Prix of Figure Skating, a senior-level international invitational competition series. It was held at the WFCU Centre in Windsor, Ontario on October 26–28. Medals were awarded in the disciplines of men's singles, ladies' singles, pair skating, and ice dancing. Skaters earned points toward qualifying for the 2012–13 Grand Prix Final.








