Related Research Articles

The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. The pleurae, which are thin, smooth, and moist, serve to reduce friction between the lungs and chest wall during breathing, allowing for easy and effortless movements of the lungs.

The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. At the top of the trachea the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx. The trachea is formed by a number of horseshoe-shaped rings, joined together vertically by overlying ligaments, and by the trachealis muscle at their ends. The epiglottis closes the opening to the larynx during swallowing.

A pulmonary alveolus, also known as an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where pulmonary gas exchange takes place. Oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide at the blood–air barrier between the alveolar air and the pulmonary capillary. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the mammalian lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume.

Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues.
Hemoptysis or haemoptysis is the discharge of blood or blood-stained mucus through the mouth coming from the bronchi, larynx, trachea, or lungs. It does not necessarily involve coughing. In other words, it is the airway bleeding. This can occur with lung cancer, infections such as tuberculosis, bronchitis, or pneumonia, and certain cardiovascular conditions. Hemoptysis is considered massive at 300 mL. In such cases, there are always severe injuries. The primary danger comes from choking, rather than blood loss.

Sputum is mucus that is coughed up from the lower airways. In medicine, sputum samples are usually used for a naked eye examination, microbiological investigation of respiratory infections and cytological investigations of respiratory systems. It is crucial that the specimen does not include any mucoid material from the nose or oral cavity.

The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.

A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. These are the widest bronchi, and enter the right lung, and the left lung at each hilum. The main bronchi branch into narrower secondary bronchi or lobar bronchi, and these branch into narrower tertiary bronchi or segmental bronchi. Further divisions of the segmental bronchi are known as 4th order, 5th order, and 6th order segmental bronchi, or grouped together as subsegmental bronchi. The bronchi, when too narrow to be supported by cartilage, are known as bronchioles. No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi.

Bronchiectasis is a disease in which there is permanent enlargement of parts of the airways of the lung. Symptoms typically include a chronic cough with mucus production. Other symptoms include shortness of breath, coughing up blood, and chest pain. Wheezing and nail clubbing may also occur. Those with the disease often get lung infections.

A pulmonary sequestration is a medical condition wherein a piece of tissue that ultimately develops into lung tissue is not attached to the pulmonary arterial blood supply, as is the case in normally developing lung. This sequestered tissue is therefore not connected to the normal bronchial airway architecture, and fails to function in, and contribute to, respiration of the organism.

Laryngeal papillomatosis, also known as recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP) or glottal papillomatosis, is a rare medical condition in which benign tumors (papilloma) form along the aerodigestive tract. There are two variants based on the age of onset: juvenile and adult laryngeal papillomatosis. The tumors are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infection of the throat. The tumors may lead to narrowing of the airway, which may cause vocal changes or airway obstruction. Laryngeal papillomatosis is initially diagnosed through indirect laryngoscopy upon observation of growths on the larynx and can be confirmed through a biopsy. Treatment for laryngeal papillomatosis aims to remove the papillomas and limit their recurrence. Due to the recurrent nature of the virus, repeated treatments usually are needed. Laryngeal papillomatosis is primarily treated surgically, though supplemental nonsurgical and/or medical treatments may be considered in some cases. The evolution of laryngeal papillomatosis is highly variable. Though total recovery may be observed, it is often persistent despite treatment. The number of new cases of laryngeal papillomatosis cases is approximately 4.3 cases per 100,000 children and 1.8 cases per 100,000 adults annually.
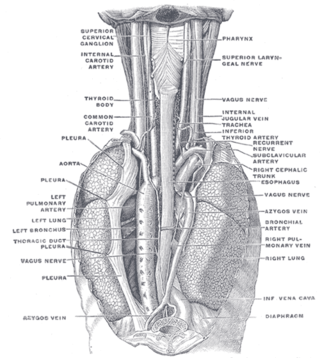
In human anatomy, the bronchial arteries supply the lungs with oxygenated blood, and nutrition. Although there is much variation, there are usually two bronchial arteries that run to the left lung, and one to the right lung, and are a vital part of the respiratory system.

A hamartoma is a mostly benign, local malformation of cells that resembles a neoplasm of local tissue but is usually due to an overgrowth of multiple aberrant cells, with a basis in a systemic genetic condition, rather than a growth descended from a single mutated cell (monoclonality), as would typically define a benign neoplasm/tumor. Despite this, many hamartomas are found to have clonal chromosomal aberrations that are acquired through somatic mutations, and on this basis the term hamartoma is sometimes considered synonymous with neoplasm. Hamartomas are by definition benign, slow-growing or self-limiting, though the underlying condition may still predispose the individual towards malignancies.

Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, pleurae, pleural cavity, the nerves and muscles of respiration. Respiratory diseases range from mild and self-limiting, such as the common cold, influenza, and pharyngitis to life-threatening diseases such as bacterial pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, tuberculosis, acute asthma, lung cancer, and severe acute respiratory syndromes, such as COVID-19. Respiratory diseases can be classified in many different ways, including by the organ or tissue involved, by the type and pattern of associated signs and symptoms, or by the cause of the disease.

Bronchoscopy is an endoscopic technique of visualizing the inside of the airways for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. An instrument (bronchoscope) is inserted into the airways, usually through the nose or mouth, or occasionally through a tracheostomy. This allows the practitioner to examine the patient's airways for abnormalities such as foreign bodies, bleeding, tumors, or inflammation. Specimens may be taken from inside the lungs. The construction of bronchoscopes ranges from rigid metal tubes with attached lighting devices to flexible optical fiber instruments with realtime video equipment.
Williams–Campbell syndrome (WCS) is a disease of the airways where cartilage in the bronchi is defective. It is a form of congenital cystic bronchiectasis. This leads to collapse of the airways and bronchiectasis. It acts as one of the differential to allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. WCS is a deficiency of the bronchial cartilage distally.

Geotrichosis is a mycosis caused by Geotrichum candidum.
Genital leiomyomas are leiomyomas that originate in the dartos muscles, or smooth muscles, of the genitalia, areola, and nipple. They are a subtype of cutaneous leiomyomas that affect smooth muscle found in the scrotum, labia, or nipple. They are benign tumors, but may cause pain and discomfort to patients. Genital leiomyoma can be symptomatic or asymptomatic and is dependent on the type of leiomyoma. In most cases, pain in the affected area or region is most common. For vaginal leiomyoma, vaginal bleeding and pain may occur. Uterine leiomyoma may exhibit pain in the area as well as painful bowel movement and/or sexual intercourse. Nipple pain, enlargement, and tenderness can be a symptom of nipple-areolar leiomyomas. Genital leiomyomas can be caused by multiple factors, one can be genetic mutations that affect hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. Moreover, risk factors to the development of genital leiomyomas include age, race, and gender. Ultrasound and imaging procedures are used to diagnose genital leiomyomas, while surgically removing the tumor is the most common treatment of these diseases. Case studies for nipple areolar, scrotal, and uterine leiomyoma were used, since there were not enough secondary resources to provide more evidence.

Fetal adenocarcinoma (FA) of the lung is a rare subtype of pulmonary adenocarcinoma that exhibits tissue architecture and cell characteristics that resemble fetal lung tissue upon microscopic examination. It is currently considered a variant of solid adenocarcinoma with mucin production.

Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma (HLRCC) or Reed's syndrome is rare autosomal dominant disorder associated with benign smooth muscle tumors and an increased risk of renal cell carcinoma. It is characterised by multiple cutaneous leiomyomas and, in women, uterine leiomyomas. It predisposes for renal cell cancer, an association denominated hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer, and it is also associated with increased risk of uterine leiomyosarcoma. The syndrome is caused by a mutation in the fumarate hydratase gene, which leads to an accumulation of fumarate. The inheritance pattern is autosomal dominant and screening can typically begin in childhood.
References
- 1 2 3 Saoud M, Patil M, Dhillon SS, Pokharel S, Picone A, Hennon M, et al. (August 2016). "Rare airway tumors: an update on current diagnostic and management strategies". Journal of Thoracic Disease. 8 (8): 1922–1934. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.07.40 . PMC 4999752 . PMID 27621844.-a protocol
- 1 2 3 4 5 Cárdenas-García J, Lee-Chang A, Chung V, Shim C, Factor S, Tibb A (2014). "Bronchial leiomyoma, a case report and review of literature". Respiratory Medicine Case Reports. 12: 59–62. doi:10.1016/j.rmcr.2014.04.004. PMC 4061443 . PMID 26029544.
- ↑ "Bronchial leiomyoma". Humpath.com. 17 January 2017.