
The SS Appomattox was a wooden-hulled, American Great Lakes freighter that ran aground on Lake Michigan, off Atwater Beach off the coast of Shorewood, Wisconsin in Milwaukee County, Wisconsin, United States in 1905. On the day of January 20, 2005 the remnants of the Appomattox were listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The Mary D. Hume was a steamer built at Gold Beach, Oregon in 1881, by R. D. Hume, a pioneer and early businessman in that area. Gold Beach was then called Ellensburg. The Hume had a long career, first hauling goods between Oregon and San Francisco, then as a whaler in Alaska, as a service vessel in the Alaskan cannery trade, then as a tugboat. She was retired in 1977 and returned to Gold Beach. In 1985 she sank in the Rogue River and has remained there ever since as a derelict vessel on the shoreline. The Hume is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The SS Marquette was a wooden-hulled, American Great Lakes freighter built in 1881, that sank of Lake Superior, five miles east of Michigan Island, Ashland County, Wisconsin, Apostle Islands, United States on October 15, 1903. On the day of February 13, 2008 the remains of the Marquette were listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The Fitzroy was a steel-hulled steamship built in 1912 at Old Kilpatrick, Scotland in 1912. Thirty-one people were killed when Fitzroy capsized in a gale whilst carrying a general cargo between Coffs Harbour and Sydney off Cape Hawke, New South Wales on 26 June 1921.

The Cumberland was a wooden-hulled side paddlewheeler built in 1871; it was wrecked off the shore of Isle Royale in Lake Superior in 1877 and the remains are still on the lake bottom. The wreck was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984.
German submarine U-576 was a Type VIIC U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. She carried out five patrols, sinking four ships of 15,450 gross register tons (GRT) and damaging two more of 19,457 GRT. She was sunk in July 1942 by depth charges from two US aircraft and gunfire from a merchant ship, near the East Coast of the United States. The wreck was discovered in August 2014.
SS United States was a merchant steamship launched in 1864 and lost off Cape Romain, South Carolina, in 1881. She was the most expensive steamer built by the American shipbuilding firm of S. Gildersleeve & Son, which built 120 vessels. The vessel was named for her country and sported the United States' national symbol, an American eagle, as her figurehead.

Elmer S. Dailey, originally known as the Claire B. Follette, is a wooden barge built by William H. Follette in 1915 at Tonawanda, New York, and rebuilt and renamed in 1928 by Brown Drydock on Staten Island, New York. It was used to transport materials from New York, New Jersey and Connecticut. It is the only known surviving Erie Canal boat and is one of a few remaining wooden-hulled canal boats. It sank in 1974 along with the Priscilla Dailey and the Berkshire No. 7 in the harbor of Bridgeport, Connecticut on the west side of the Pequonnock River. It has deteriorated to the point that a salvage operation could result in it breaking apart. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on December 21, 1978.

The SS Benjamin Noble was a lake freighter that operated on the Great Lakes. Built in 1909 by the Detroit Shipbuilding Company, she was 239 feet (73 m) in length and had a beam of 40 feet (12 m). She was built as a "canaller," a vessel designed for use in what were then the dimensions of the Welland Canal, but was converted by her owners for services in the open Great Lakes. Heavily laden and top-heavy with a cargo of railroad rails, she sank in a Lake Superior storm near Knife River, Minnesota, in April 1914 with the loss of all hands.

SS Choctaw was an steel-hulled American freighter in service between 1892 and 1915, on the Great Lakes of North America. She was a so-called monitor vessel, containing elements of traditional lake freighters and the whaleback ships designed by Alexander McDougall. Choctaw was built in 1892 by the Cleveland Shipbuilding Company in Cleveland, Ohio, and was originally owned by the Lake Superior Iron Company. She was sold to the Cleveland-Cliffs Iron Company in 1894 and spent the rest of her working life with it.

SS Robert Wallace was a wooden-hulled American bulk freighter that served on the Great Lakes of North America from her construction in 1882 to her sinking in 1902 on Lake Superior near the town of Palmers, St. Louis County, Minnesota, United States. On November 17, 1902 shortly after leaving Superior, Wisconsin with a cargo of iron ore, Robert Wallace sprang a leak and sank. Her wreck was found in 2006, and on October 14, 2009, the wreck of Robert Wallace was listed in the National Register of Historic Places.

The Australasia was a wooden hulled American Great Lakes freighter that served on the Great Lakes of North America between her construction in 1884 to her burning and sinking in 1896. On October 18, 1896 while loaded with coal, the Australasia sank in Lake Michigan near the town of Sevastopol, Door County, Wisconsin, United States, after burning off Cana Island. On July 3, 2013 the wreck of the Australasia was added to the National Register of Historic Places.

The George Spencer was a wooden lake freighter that sank on along with her schooner barge Amboy on Lake Superior, near Thomasville, Cook County, Minnesota in the Mataafa Storm of 1905. On April 14, 1994, the wrecks of the Spencer and the Amboy were listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The SS Lakeland was an early steel-hulled Great Lakes freighter that sank on December 3, 1924, into 205 feet (62 m) of water on Lake Michigan near Sturgeon Bay, Door County, Wisconsin, United States, after she sprang a leak. On July 7, 2015, the wreck of the Lakeland was added to the National Register of Historic Places.
The following index is provided as an overview of and topical guide to recreational dive sites:

The Amboy was a wooden schooner barge that sank along with her towing steamer, the George Spencer on Lake Superior off the coast of Schroeder, Cook County, Minnesota in the United States. In 1994 the remains of the Amboy were added to the National Register of Historic Places.

The SS Atlanta was a wooden hulled Great Lakes steamer that sank in Lake Michigan off the coast of Cedar Grove, Wisconsin, United States, after burning down. Her wreckage still remains at the bottom of the lake, and on November 6, 2017, the wreck of the Atlanta was listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
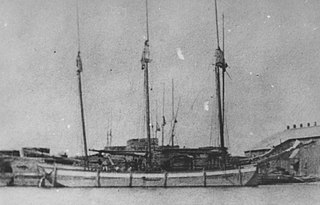
The Mayflower was a wooden hulled scow schooner that sank on June 2, 1891, in Lake Superior near Duluth, Minnesota, United States, after capsizing with a load of sandstone blocks. In 2012 the shipwreck site was added to the National Register of Historic Places.

The Harriet B. was a wooden-hulled barge that served on the Great Lakes of North America, originally as the railroad ferry Shenango No.2, then a bulk carrier and finally as an unpowered barge. She sank four miles off Two Harbors, Minnesota on May 3, 1922 after being rammed by the steel freighter Quincy A. Shaw. Her wreck was accidentally located upright and intact in 2005 in 656 feet (200 m) of water. On August 9, 2018 the wreck of the Harriet B. was listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

SS Etruria was a steel hulled lake freighter that served on the Great Lakes of North America from her construction in 1902 to her sinking in 1905. On June 18, 1905, while sailing upbound on Lake Huron with a cargo of coal, she was rammed and sunk by the freighter Amasa Stone 10 miles (16 km) off Presque Isle Light. For nearly 106 years the location of Etruria's wreck remained unknown, until the spring of 2011 when her wreck was found upside down in 310 feet (94 m) of water.




















