
Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests such as insects, mites, weeds and plant diseases using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism, herbivory, or other natural mechanisms, but typically also involves an active human management role. It can be an important component of integrated pest management (IPM) programs.

Spider mites are members of the Acari (mite) family Tetranychidae, which includes about 1,200 species. They generally live on the undersides of leaves of plants, where they may spin protective silk webs, and they can cause damage by puncturing the plant cells to feed. Spider mites are known to feed on several hundred species of plants.

Gerbera jamesonii is a species of flowering plant in the genus Gerbera belonging to the basal Mutisieae tribe within the large Asteraceae family. It is indigenous to South Eastern Africa and commonly known as the Barberton daisy, the Transvaal daisy, and as Barbertonse madeliefie or Rooigousblom in Afrikaans. It was the first species of Gerbera to be the subject of a scientific description, studied by J. D. Hooker in Curtis's Botanical Magazine in 1889.

Varroa is a genus of parasitic mesostigmatan mites associated with honey bees, placed in its own family, Varroidae. The genus was named for Marcus Terentius Varro, a Roman scholar and beekeeper. The condition of a honeybee colony being infested with Varroa mites is called varroosis.

Oribatida, also known as oribatid mites, moss mites or beetle mites, are an order of mites, in the "chewing Acariformes" clade Sarcoptiformes. They range in size from 0.2 to 1.4 millimetres. There are currently 12,000 species that have been identified, but researchers estimate that there may be anywhere from 60,000 to 120,000 total species. Oribatid mites are by far the most prevalent of all arthropods in forest soils, and are essential for breaking down organic detritus and distributing fungi.
Notopala is a genus of moderately large to large, freshwater snails with an operculum, aquatic gastropod mollusks in the family Viviparidae, the river snails or mystery snails.
Panonychus ulmi, the European red mite, is a species of mite which is a major agricultural pest of fruit trees. It has a high reproductive rate, a short generation time and produces many broods in a year, all of which contribute to its pest status. It has a cosmopolitan distribution, and a very wide host range, having been found on the following plants:
Eutrombicula is a genus of mites in the family Trombiculidae. The species of this genus are found throughout North America, and Australia.
The Raphignathoidea is a superfamily of the Acari (mite) Order Trombidiformes. It contains many predators of small invertebrates, while some are herbivores and others parasites.
Wildlife of Sri Lanka includes its flora and fauna and their natural habitats. Sri Lanka has one of the highest rates of biological endemism in the world.

Mezium americanum, the American spider beetle or black spider beetle, is a species of beetle in the subfamily Ptininae, the spider beetles. These are sometimes mistaken for spiders or mites because of their rounded abdomens and long legs. It has a cosmopolitan distribution, but it is an exotic species in Australia.

Penthaleus is a genus of earth mites in the family of Penthaleidae, first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1835.
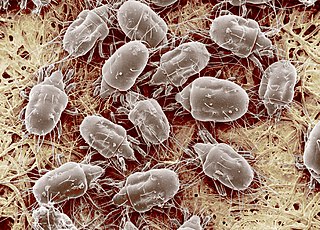
Tyrophagus putrescentiae is a cosmopolitan mite species. Together with the related species T. longior, it is commonly referred to as the mould mite or the cheese mite. The name translates from Greek to something like "putrid cheese eater."

Bryobia is a genus of mites in the spider mite family, Tetranychidae. The taxonomy of the genus is difficult. The genus has been revised several times. It is difficult to distinguish these tiny species from each other on the basis of morphological characters, and there is little agreement on which characteristics are of importance. Also, species can be variable in morphology. Over 130 species have been described, but many of the names are likely synonyms.

Oligonychus is a genus of mites in the family Tetranychidae, the spider mites. Many members of this genus are familiar pests of plants. There are about 200 described species.
Chilo partellus, the spotted stalk borer or spotted stem borer, is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Charles Swinhoe in 1885. It is found in India, Pakistan, Ethiopia, Lesotho, Madagascar, Malawi, South Africa, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda and on Mayotte.

Anthocoris nemoralis is a true bug in the family Anthocoridae. The species is native to Europe and is introduced in North America. It is a predator of aphids, spider mites and jumping plant lice, and is therefore used as a biological pest control agent.

Glycyphagus is a genus of astigs in the family Glycyphagidae. There are about five described species in Glycyphagus.
Magdalena Kathrina Petronella Smith Meyer was a South African acarologist who was regarded as a world authority on plant-feeding mites of agricultural importance and was known as the "mother of red-spider mites of the world". She described more than 700 new species and 25 new genera, mostly of mites of agricultural importance. Meyer was involved in the promotion of biological control of mites using predatory mites, spiders and insects.












