
Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew is a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. An internationally important botanical research and education institution, it employs 1,100 staff. Its board of trustees is chaired by Dame Amelia Fawcett.

A seed bank stores seeds to preserve genetic diversity; hence it is a type of gene bank. There are many reasons to store seeds. One is to preserve the genes that plant breeders need to increase yield, disease resistance, drought tolerance, nutritional quality, taste, etc. of crops. Another is to forestall loss of genetic diversity in rare or imperiled plant species in an effort to conserve biodiversity ex situ. Many plants that were used centuries ago by humans are used less frequently now; seed banks offer a way to preserve that historical and cultural value. Collections of seeds stored at constant low temperature and low moisture are guarded against loss of genetic resources that are otherwise maintained in situ or in field collections. These alternative "living" collections can be damaged by natural disasters, outbreaks of disease, or war. Seed banks are considered seed libraries, containing valuable information about evolved strategies to combat plant stress, and can be used to create genetically modified versions of existing seeds. The work of seed banks often span decades and even centuries. Most seed banks are publicly funded and seeds are usually available for research that benefits the public.
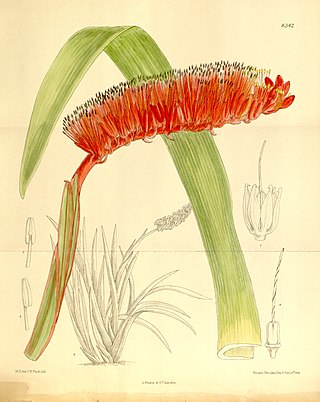
Xeronema is a genus of flowering plants containing two species, Xeronema moorei from New Caledonia, and Xeronema callistemon from the Poor Knights Islands and Taranga Island in New Zealand. The plants are herbaceous monocots, spreading by rhizomes, and have large flowers set on terminal spikes, with stamens towering above the flowers.

Anthericum is a genus of about 65 species, rhizomatous perennial plants in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Agavoideae. It was formerly placed in its own family, Anthericaceae. The species have rhizomatous or tuberous roots, long narrow leaves and branched stems carrying starry white flowers. The members of this genus occur mainly in the tropics and southern Africa and Madagascar, but are also represented in Europe.

Amaryllis belladonna, the Jersey lily, belladonna-lily, naked-lady-lily, or March lily, is a plant species native to Cape Province in South Africa but widely cultivated as an ornamental. It is reportedly naturalized in many places: Corsica, Portugal, the Azores, Madeira, the Canary Islands, the Scilly Isles of Great Britain, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ascension Island, Australia, New Zealand, Mexico, Cuba, Haiti, the Dominican Republic, Chile, California, Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Michigan and the Juan Fernández Islands.

Wakehurst, previously known as Wakehurst Place, is a house and botanic gardens in West Sussex, England, owned by the National Trust but used and managed by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. It is near Ardingly, West Sussex in the High Weald, and comprises a late 16th-century mansion, a mainly 20th-century garden and, in a modern building, Kew's Millennium Seed Bank. Visitors are able to see the gardens, the Mansion, and also visit the seed bank. The garden today covers some 2 km2 and includes walled and water gardens, woodland and wetland conservation areas.

Bulbine bulbosa, commonly known as bulbine lily, native leek, golden lily, or native onion, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asphodelaceae and is endemic to Australia. It is a perennial herb with thick roots, channelled leaves, and yellow flowers with hairy stamen filaments.

The Millennium Seed Bank Partnership, formerly known as the Millennium Seed Bank Project, is the largest ex situ plant conservation programme in the world coordinated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. After being awarded a Millennium Commission grant in 1995, the project commenced in 1996, and is now housed in the Wellcome Trust Millennium Building situated in the grounds of Wakehurst Place, West Sussex. Its purpose is to provide an "insurance policy" against the extinction of plants in the wild by storing seeds for future use. The storage facilities consist of large underground frozen vaults preserving the world's largest wild-plant seedbank or collection of seeds from wild species. The project had been started by Dr Peter Thompson and run by Paul Smith after the departure of Roger Smith. Roger Smith was awarded the OBE in 2000 in the Queen's New Year Honours for services to the Project.

Bulbine is a genus of plants in the family Asphodelaceae and subfamily Asphodeloideae, named for the bulb-shaped tuber of many species. It was formerly placed in the Liliaceae. It is found chiefly in Southern Africa, with a few species extending into tropical Africa and a few others in Australia and Yemen.
Bulbine namaensis is a species of plant in the genus Bulbine. It is native to Namibia and to the Cape Provinces in South Africa. Its natural habitat is dry savanna.

Crinum asiaticum, commonly known as poison bulb, giant crinum lily, grand crinum lily, or spider lily, is a plant species widely planted in many warmer regions as an ornamental. It is a bulb-forming perennial producing an umbel of large, showy flowers that are prized by gardeners. However, all parts of the plant are poisonous if ingested. Some reports indicate exposure to the sap may cause skin irritation.

Sir Henry Philip Price, 1st Baronet was a British businessman and philanthropist.
The Great Plant Hunt is a primary school plant science learning initiative, developed by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, and funded by the Wellcome Trust. It is supported by DEFRA, Sir David Attenborough, and Science Learning Centres in the UK.
Roger Smith is a UK biologist and founder of the Millennium Seed Bank Project. He was awarded an OBE in the 2000 New Year Honours List for services to the project.

Nematolepis wilsonii is an endangered shrub or small tree species which is endemic to Victoria in Australia. It may grow up to 10 metres tall and has mottled bark. The shiny green leaves are 30 to 80 mm long and 5 to 15 mm wide, and have silvery scales underneath. Star-shaped white flowers are produced in groups of 1 to 9 in the leaf axils in spring.

Gloriosa superba is a species of flowering plant in the family Colchicaceae. Common names include flame lily, climbing lily, creeping lily, glory lily, gloriosa lily, tiger claw, agnishikha and fire lily.

The Australian PlantBank is a seed bank located in the Australian Botanic Gardens, Mount Annan. The seedbank is part of the Millennium Seed Bank Project. The SeedBank replaced the former NSW Seedbank as part of an upgrade.

The UK Native Seed Hub (UKNSH) is a project of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew's Millennium Seed Bank Partnership growing and distributing seeds of UK native plant species. It is in part a response to the 2010 report Making Space for Nature by Sir John Lawton. The project, located at Wakehurst Place, in West Sussex, in the High Weald of southern England, is dedicated to enhancing the resilience and coherence of the UK's ecological networks by improving the quality, quantity, and diversity of UK seed species available for use in conservation, rehabilitation, and restoration projects.

Bulbine glauca is also known as rock lily. The genus Bulbine is made up of about fifty species. Most are native to Southern or Eastern Africa, but five species, including B. glauca, are native to Australia.

Bulbine praemorsa is a species of geophyte in the genus Bulbine. It is also known by the Afrikaans names Blougif, Slymstok, and Slymuintjie.















