
The Cyperaceae are a family of graminoid (grass-like), monocotyledonous flowering plants known as sedges. The family is large; botanists have described some 5,500 known species in about 90 genera – the largest being the "true sedges", with over 2,000 species.

Cyperus is a large genus of about 700 species of sedges, distributed throughout all continents in both tropical and temperate regions.

The Saint Helena olive is an extinct species of flowering plant. It is the only member of the genus Nesiota. It was endemic to the island of Saint Helena in the South Atlantic Ocean. Despite its name, it is unrelated to the true olive, but is instead a member of the family Rhamnaceae, the family which contains buckthorns and jujube. The last remaining tree in the wild died in 1994, and the last remaining individual in cultivation died in December 2003, despite conservation efforts. It is thus a prime example of recent plant extinction. The Saint Helena olive belongs to the tribe Phyliceae, which are mostly endemic to Southern Africa.

Trochetiopsis ebenus, the dwarf ebony or Saint Helena ebony, is a species of flowering plant that is endemic to the island of Saint Helena in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is not related to the ebony of commerce, but is instead a member of the mallow family, Malvaceae. Saint Helena ebony is now critically endangered in the wild, being reduced to two wild individuals on a cliff, but old roots are sometimes found washed out of eroding slopes. These are collected on the island and used for inlay work, an important craft on Saint Helena. A related species, Trochetiopsis melanoxylon, is now completely extinct.

Anogramma ascensionis, the Ascension Island parsley fern, is a species of fern in the family Pteridaceae that is endemic to Ascension Island, a volcanic island in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is one of eight putative species in the genus Anogramma. It was thought to have become extinct due to habitat loss, until four plants were found on the island in 2010. Over 60 specimens were then successfully cultivated at Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and on Ascension Island. It is now classified as Critically Endangered.

Prosperous Bay Plain is an area on the eastern coast of Saint Helena, a British island territory in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is the site of the Saint Helena Airport, and is notable for its high invertebrate biodiversity.

Fimbristylis is a genus of sedges. A plant in this genus may be known commonly as a fimbry or fimbristyle. There are 200 to 300 species distributed worldwide. Several continents have native species but many species have been introduced to regions where they are not native. Some are considered weeds. These are typical sedges in appearance, with stiff, ridged stems and cone-shaped terminal panicles of spikelets. They are found in wet environments, and are most diverse in tropical and subtropical regions.

Bulbostylis is a genus of plants in the sedge family. They are sometimes called hairsedges. There are over 200 species of these clump-forming plants of dry grasslands and warm and tropical savannas worldwide. They have solid, rounded, grooved stems and long, thin basal leaves. They bear spikelets of flowers.

Ficinia is a genus of tufted or rhizomatous sedges in the family Cyperaceae. There are around 70 recognised species in Africa, four species that occur in New Zealand and a single species Ficinia nodosa that occurs in Australia.
The South Atlantic Invasive Species Project (SAISP) was a three-year project funded under the European Union EDF 9. Its aim was to increase the capacity of the UK's South Atlantic Overseas Territories to deal with invasive species issues. The territories involved were Saint Helena, Tristan da Cunha, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, the Falkland Islands and Ascension Island. The project was managed by the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) on behalf of the partner governments. In addition to the partner governments, two NGOs: Falklands Conservation and the Saint Helena National Trust were key stakeholders. It was also supported by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
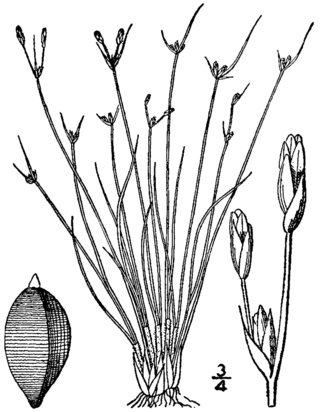
Bulbostylis capillaris is a species of sedge known by the common names densetuft hairsedge and threadleaf beakseed. It is native to much of North America, South America and the West Indies from Canada to Bolivia.

Cyperus laevigatus is a species of sedge known by the common name smooth flatsedge.

Schoenoplectus pungens is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family known as common threesquare, common three-square bulrush and sharp club-rush. It is a herbaceous emergent plant that is widespread across much of North and South America as well as Europe, New Zealand and Australia.
B. neglecta may refer to:

Schoenoplectus subterminalis is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family known by the common names water bulrush, water club-rush, and swaying bulrush. It is native to North America, where it is known from many parts of the Canada and the United States. It has been common in the northeastern US and eastern Canada as well as the Great Lakes region, as well as many locations in the mountains of the West, though apparently absent from the Southwest and from most of the Great Plains.

Lepironia is a genus of the sedge family, comprising only one species, Lepironia articulata, known as the grey sedge. It is found in Madagascar, India, Sri Lanka, southern China, Southeast Asia, New Guinea, and various islands of the western Pacific. It also occurs in northern and eastern Australia, as far south as Thirlmere Lakes National Park in New South Wales.

Cyperus vaginatus, commonly known as stiff-leaf sedge or stiff flat-sedge, is a sedge of the family Cyperaceae that is native to Australia.

Carex rupestris, called the curly sedge and rock sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the family Cyperaceae, native to temperate and subarctic North America, Greenland, Iceland, Europe, and Asia.

Bulbostylis lichtensteiniana is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family, Cyperaceae, that is endemic to Saint Helena. Unlike other species native to Saint Helena, such as Bulbostylis neglecta, Bulbostylis lichtensteiniana does not show obvious signs of decline due to the spread of invasive plants. However, the lack of decline is partially attributed to Bulbostylis lichtensteiniana being the only endemic plant to have expanded into new anthropogenic habitats.
Carex alsophila, commonly known as forest sedge, is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to Victoria in south eastern Australia.



















