
Papua, is a province of Indonesia, comprising the northern coast of Western New Guinea roughly follows the borders of Papuan customary region of Tabi Saireri. It is bordered by the sovereign state of Papua New Guinea to the east, the Pacific Ocean to the north, Cenderawasih Bay to the west, and the provinces of Central Papua and Highland Papua to the south. The province also shares maritime boundaries with Palau in the Pacific. Following the splitting off of twenty regencies to create the three new provinces of Central Papua, Highland Papua, and South Papua on 30 June 2022, the residual province is divided into eight regencies (kabupaten) and one city (kota), the latter being the provincial capital of Jayapura. The province has a large potential in natural resources, such as gold, nickel, petroleum, etc. Papua, along with four other Papuan provinces, has a higher degree of autonomy level compared to other Indonesian provinces.

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, or Indonesian Papua, is the western portion of the Melanesian island of New Guinea which is administered by Indonesia. Since the island is alternatively named as Papua, the region is also called West Papua. Lying to the west of Papua New Guinea and considered a part of the Australian continent, the territory is mostly in the Southern Hemisphere and includes the Schouten and Raja Ampat archipelagoes. The region is predominantly covered with ancient rainforest where numerous traditional tribes live such as the Dani of the Baliem Valley although a large proportion of the population live in or near coastal areas with the largest city being Jayapura.

No. 120 Squadron was a joint Dutch and Australian squadron of World War II. The squadron was first formed in December 1943 as part of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), and saw combat in and around New Guinea during 1944 and 1945 equipped with P-40 Kittyhawk fighters. Following the war, No. 120 Squadron was transferred to the Netherlands East Indies Air Force in 1946 and participated in the Indonesian National Revolution.

No. 42 Wing is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) wing responsible for supporting the service's Boeing E-7A Wedgetail aircraft. It was first formed in February 1943, and commanded RAAF radar stations in north Queensland and the south coast of Dutch New Guinea until being disbanded in October 1944. It was re-raised in its current role in 2006.

Merauke is a regency in the far south of the Indonesian province of South Papua. It covers an area of 46,791.63 km2, and had a population of 195,716 at the 2010 Census and 230,932 at the 2020 Census. The administrative centre is the town of Merauke; this is scheduled to become an independent city (kota) separate from Merauke Regency. It is also the provincial capital of South Papua since 2022.

Merauke is a large town and an administrative district which is also the administrative centre of Merauke Regency in South Papua, Indonesia. It is considered the easternmost city in Indonesia. The town was originally called Ermasoe. It is next to the Maro River where the Port of Merauke is located. As of the 2010 census, Merauke had a population of 87,634 which at the 2020 Census had increased to 102,351.

No. 86 Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) fighter squadron of World War II. The squadron was formed in March 1943 and was deployed to Merauke in Dutch New Guinea in July that year. While No. 86 Squadron was stationed at Merauke until April 1944, it saw little combat. After being transferred back to Australia its aircraft and personnel were transferred to other units, and only a nucleus of the squadron remained. While it was re-equipped with new aircraft in June 1945, the war ended before the squadron was ready for combat and it was disbanded in December 1945.

Merauke Force was an Australian-led military force of World War II which was responsible for defending Merauke in Dutch New Guinea from Japanese attack amidst the Pacific War. The force was established in late 1942 and was disbanded at the end of the war, having never seen combat. The Japanese attack did not eventuate and from mid-1944 the force was progressively drawn down and its assigned units redeployed to Australia or elsewhere in the Pacific. At its height, Merauke Force included troops from Australia, the Netherlands East Indies and the United States, as well as several squadrons of aircraft, including a joint Australian-Dutch fighter unit.

The Papua conflict is an ongoing conflict in Western New Guinea between Indonesia and the Free Papua Movement. Subsequent to the withdrawal of the Dutch administration from the Netherlands New Guinea in 1962 and implementation of Indonesian administration in 1963, the Free Papua Movement has conducted a low-intensity guerrilla war against Indonesia through the targeting of its military, police, and civilian populations.
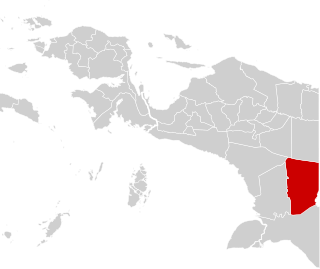
Boven Digoel Regency is a regency (kabupaten) in the northern part of the Indonesian province of South Papua. It is split off from Merauke Regency on 12 November 2002. The regency covers an area of 27,108.29 km2 (10,466.57 sq mi), and the total population was 55,784 at the 2010 Census and 64,285 at the 2020 Census. The administrative centre is the town of Tanahmerah.

The Wasur National Park forms part of the largest wetland in South Papua province of Indonesia and has been one of the least disturbed by human activity. The high value of its biodiversity has led to the park being dubbed the "Serengeti of Papua". The vast open wetland, in particular Rawa Biru Lake, attracts a very rich fauna.
Yei is a Papuan language of New Guinea. The Upper and Lower Yey dialects are only mutually intelligible with difficulty.
19e Transport Squadron, also known as No. 19 Squadron, was a transport and communications unit of the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army Air Force, formed in Australia during the final stages of World War II. The squadron was formed as a Dutch unit in late 1944 from two transport flights that had previously been based in Brisbane and Melbourne, and which had run supplies to joint Australian-NEI combat squadrons in the Northern Territory and in West Papua. Upon formation the squadron was based at Archerfield, near Brisbane. In 1945, it was transferred to the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), but returned to Dutch control in 1947 and subsequently took part in operations during the Indonesian National Revolution.

Agats is a town in Asmat Regency, South Papua, Indonesia. An elevated settlement on a tidal plain, a Dutch outpost was set up in Agats in 1938 and the town became notable for the cultural practices of the Asmat people. Following the formation of Asmat Regency in 2002, the town became its administrative seat.

Operation Oaktree was a Dutch military operation in Dutch New Guinea during World War II. Under the command of Captain Jean Victor de Bruijn, some 40 soldiers operated in the highland region of Western New Guinea for more than two years between December 1942 and July 1944, handled by the Netherlands East Indies Forces Intelligence Service, with Australian assistance.
The Landing on Long Island in the Territory of New Guinea was part of the Huon Peninsula campaign, a series of operations that made up Operation Cartwheel, General Douglas MacArthur's campaign to encircle the major Japanese base at Rabaul. Located at the northern end of the Vitiaz Strait, Long Island was an important staging point for Japanese barges moving between Rabaul and Wewak until 26 December 1943, when a force of 220 Australian and American soldiers landed on the island. It was not occupied by the Japanese at the time, and there was no fighting. At the time, it represented the furthest Allied advance into Japanese-held territory. It was developed into a radar station.
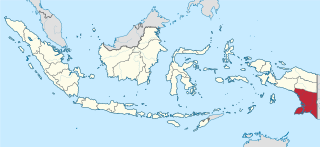
South Papua, officially the South Papua Province, is an Indonesian province located in the southern portion of Papua, which follows the borders of Papuan customary region of Anim Ha. Established on 30 June 2022 and including the four most southern regencies that were previously part of the province of Papua and before 2002 were part of Merauke Regency, it covers an area of 127,280.69 km2 and had a population of 517,623 according to the official estimates for mid 2021.

Okaba is a coastal town in Merauke Regency, South Papua, Indonesia.
Kepi is a town in Mappi Regency, Papua, Indonesia. Following the formation of Mappi Regency in 2002, the town became its administrative seat.
Isyaman is an inland village in Mappi Regency, South Papua, Indonesia.

















