
The Comstock Lode is a lode of silver ore located under the eastern slope of Mount Davidson, a peak in the Virginia Range in Nevada. It was the first major discovery of silver ore in the United States, and named after American miner Henry Comstock.

Ruth is a census-designated place (CDP) in White Pine County, Nevada, United States. Founded in 1903, it had a population of 440 at the 2010 census.
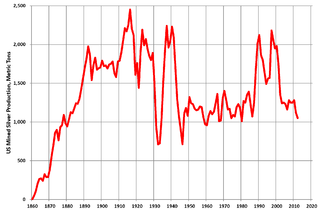
Silver mining in the United States began on a major scale with the discovery of the Comstock Lode in Nevada in 1858. The industry suffered greatly from the demonetization of silver in 1873 by the Coinage Act of 1873, known pejoratively as the "Crime of 73", but silver mining continues today.

The Eldorado Mountains, also called the El Dorado Mountains, are a north-south trending mountain range in southeast Nevada bordering west of the south-flowing Colorado River; the endorheic Eldorado Valley borders the range to the west, and the range is also on the western border of the Colorado River's Black Canyon of the Colorado, and El Dorado Canyon on the river. The range is 50 miles (80 km) southeast of Las Vegas, Nevada; and the Eldorado Mountains connect with the Highland and Newberry mountains.

Sageland is an unincorporated community in Kern County, California. It is located near Kelso Creek 3.5 miles (5.6 km) west-northwest at the base of the Piute Mountains, at an elevation of 4,026 feet (1,227 m).

Steamboats on the Colorado River operated from the river mouth at the Colorado River Delta on the Gulf of California in Mexico, up to the Virgin River on the Lower Colorado River Valley in the Southwestern United States from 1852 until 1909, when the construction of the Laguna Dam was completed. The shallow draft paddle steamers were found to be the most economical way to ship goods between the Pacific Ocean ports and settlements and mines along the lower river, putting in at landings in Sonora state, Baja California Territory, California state, Arizona Territory, New Mexico Territory, and Nevada state. They remained the primary means of transportation of freight until the advent of the more economical railroads began cutting away at their business from 1878 when the first line entered Arizona Territory.
Alturas, now a ghost town, was a mining camp in El Dorado Canyon near the Techatticup Mine in the Colorado Mining District of New Mexico Territory.
Louisville, which is now a ghost town, was a mining camp in El Dorado Canyon near the Techatticup Mine in the Eldorado Mining District, of New Mexico Territory. The camp was probably named for Nat S. Lewis, the superintendent of the Techatticup Mine in the 1860s, and camp doctor.
San Juan or Upper Camp is a ghost town that was a mining camp of the Eldorado Mining District. It was located in the upper reach of El Dorado Canyon, just below the present day location of Nelson in Clark County, Nevada.
El Dorado City, which is now a ghost town, was a mining camp in the Colorado Mining District at the mouth of January Wash at its confluence with El Dorado Canyon. It was located about a mile down the canyon from Huse Spring, at an elevation of 2382 feet. Its site was located nearby to the south southeast of the Techatticup Mine the primary source of the ore its mill processed.
Colorado City is now a ghost town, in Clark County, Nevada, located under Lake Mohave at the mouth of El Dorado Canyon.
Potosi or Potosi Camp, was called Crystal City in the 1870s, a mining ghost town in Clark County, Nevada. It lies at an elevation of 5705 feet.
Colorado Mining District was primarily a silver and gold mining district organized in El Dorado Canyon, New Mexico Territory on the west shore of the Colorado River in what is now Clark County, Nevada. The Colorado District was part of Arizona Territory from 1863 to 1869. In 1869, the land of Arizona Territory north and west of the Colorado River east to the 114th meridian of longitude, including the Colorado District, was turned over to Nevada.
John Thomas Moss was an American frontiersman, prospector, and miner, who discovered several new mining districts in what is now Arizona and Nevada. After living with and learning the languages of many of the tribes in the area, he was a go between and peacemaker between American miners and local Native Americans, in the Southwestern United States.
Quartette or Quartette Mill or Quartette Landing, was a mining settlement, location of the stamp mill of the Quartette Mining Company, owner of the largest mine in the Searchlight Mining District and a steamboat landing on the Colorado River, in what is now Clark County, Nevada. It lay at an elevation of 646 feet.

Johntown is a ghost town in Lyon County, Nevada United States. It was originally an important mining camp in Gold Canyon, midway between Dayton and Silver City. In the late 1850s, Johntown was the largest mining camp in the western Utah Territory.













