
Goodsprings is an unincorporated community in Clark County, Nevada, United States. The population was 229 at the 2010 census.

The Southeast Missouri Lead District, commonly called the Lead Belt, is a lead mining district in the southeastern part of Missouri. Counties in the Lead Belt include Saint Francois; Crawford; Dent; Iron; Madison: Reynolds; and Washington. Philip Francois Renault of France led a large exploratory mission in 1719 and started mining operations in Old Mines and Mine La Motte in 1720. The town of Sainte Genevieve was founded as a river port for transportation of lead out of the area. Moses Austin started large-scale mining and smelting at Potosi, originally known as Mine a Breton, and founded Herculaneum as his shipping point on the Mississippi. This lead was originally used as a roofing material. Bonne Terre has large subterranean mines, now used commercially for recreational scuba diving.

Arden, Nevada was an unincorporated community in Clark County, Nevada. The area is now part of the town of Enterprise. Located about 7 miles (11 km) southwest of Las Vegas, the area is experiencing rapid growth in housing development on land formerly owned by the Bureau of Land Management.

Inskip is an unincorporated community in Butte County, California. It lies at an elevation of 4,777 feet in the northern Sierra Nevada.

Tiger is a former populated place in Pinal County in the U.S. state of Arizona. The town was settled as Schultz around 1881 in what was then the Arizona Territory, then later reestablished as Tiger after World War I.

Ivanpah was a short-lived silver mining town located in San Bernardino County, California, United States. It was founded in 1869 and existed until at least the mid-1880s.
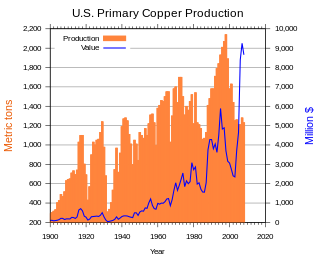
Copper mining in the United States has been a major industry since the rise of the northern Michigan copper district in the 1840s. In 2017 the United States produced 1.27 million metric tonnes of copper, worth $8 billion, making it the world's fourth largest copper producer, after Chile, China, and Peru. Copper was produced from 23 mines in the US. Top copper producing states in 2014 were Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, Nevada, and Montana. Minor production also came from Idaho, and Missouri. As of 2014, the US had 45 million tonnes of known remaining reserves of copper, the fifth largest known copper reserves in the world, after Chile, Australia, Peru, and Mexico.
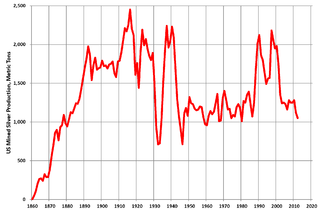
Silver mining in the United States began on a major scale with the discovery of the Comstock Lode in Nevada in 1858. The industry suffered greatly from the demonetization of silver in 1873 by the Coinage Act of 1873, known pejoratively as the "Crime of 73", but silver mining continues today.

Silver mining in Colorado has taken place since the 1860s. In the past, Colorado called itself the Silver state.

Castle Dome Landing, Arizona is a ghost town in the Castle Dome Mountains of Yuma County in the U.S. state of Arizona. It was first settled as a transport depot and mining camp around 1863 in what was then the Arizona Territory.
Mining in Bolivia has been a dominant feature of the Bolivian economy as well as Bolivian politics since 1557. Colonial era silver mining in Bolivia, particularly in Potosí, played a critical role in the Spanish Empire and the global economy. Tin mining supplanted silver by the twentieth century and the central element of Bolivian mining, and wealthy tin barons played an important role in national politics until they were marginalized by the industry's nationalization into the Bolivian Mining Corporation that followed the 1952 revolution. Bolivian miners played a critical part to the country's organized labor movement from the 1940s to the 1980s.

Hunt's Hill is a former mining camp in Nevada County, California, United States. Hunt's Hill was located in the Sierra Nevada foothills about 6 miles in a straight line southeast of Nevada City and about 2 miles northwest of You Bet, on the north side of Greenhorn Creek, not far from the present intersection of Red Dog and Buckeye Roads. Hunt’s Hill was founded in 1852 by a miner named Hunt. It was located on one of the deepest parts of the rich Blue Lead channel of gold-bearing gravel. In 1855, one of the mining claims established by some French miners, was “jumped". During the fight, one of the French miners lost an eye. Thereafter, that mine, and sometimes the town, were called Gouge Eye. By 1857, the town boasted two saloons, a hotel, a blacksmith and stable, a butcher shop, a boot and shoe store, and several grocery stores. In 1858, a stage line from Nevada City arrived. In 1866, seven cement mills for extracting gold from the “blue cement” were operating in the area. By 1880, the town was reduced to a combined store and saloon and a few houses. In 1895, one directory summed up the state of the community thus: "At the present time there is not much doing there." Since that same directory identified the town's justice of the peace and constable, what little happened must have been interesting. Today, it is just a historic site.

Ruby Hill is a ghost town in Eureka County, in the central part of the U.S. state of Nevada, approximately 2.6 mi (4.2 km) west of the town of Eureka, Nevada. In 1910, the town was destroyed by a powerful storm that washed away the railroad and buildings and rendered the town uninhabitable.
El Dorado Canyon is a canyon in southern Clark County, Nevada famed for its rich silver and gold mines. The canyon was named in 1857 by steamboat entrepreneur Captain George Alonzo Johnson when gold and silver was discovered here. It drains into the Colorado River at the former site of Nelson's Landing.

Milligan is an abandoned settlement in San Bernardino County, California.
Lucky Jim Camp sometimes called Lucky Camp is a ghost town site in Clark County, Nevada. It was within New Mexico Territory when founded in 1862.
Buster Falls, now a ghost town, was a mining camp in El Dorado Canyon above Huse Spring and the Techatticup Mine in the Colorado Mining District during the time of the American Civil War. The source of the name of the camp is unknown. Its site lay along the canyon a mile above the site of Lucky Jim Camp. The site would be just above the El Dorado Canyon's confluence with Copper Canyon.
Quartette or Quartette Mill or Quartette Landing, was a mining settlement, location of the stamp mill of the Quartette Mining Company, owner of the largest mine in the Searchlight Mining District and a steamboat landing on the Colorado River, in what is now Clark County, Nevada. It lay at an elevation of 646 feet.

Zinc mining in the United States produced an all-time high of 820,000 tonnes of zinc in 2014, making it the world's fourth-largest zinc producer, after China, Australia, and Peru. Most US zinc came from the Red Dog mine in Alaska. The industry employed about 2,600 in mining, and 257 in smelting.





















