
Skunks are North and South American mammals in the family Mephitidae. While related to polecats and other members of the weasel family, skunks have as their closest Old World relatives the stink badgers. The animals are known for their ability to spray a liquid with a strong, unpleasant smell. Different species of skunk vary in appearance from black-and-white to brown, cream or ginger colored, but all have warning coloration.

A thiol is any organosulfur compound of the form R−SH, where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols, and the word is a portmanteau of "thio-" + "alcohol", with the first word deriving from Greek θεῖον (theion) meaning "sulfur". The –SH functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfanyl group.

Methanethiol is an organosulfur compound with the chemical formula CH
4S. It is a colorless gas with a distinctive putrid smell. It is a natural substance found in the blood and brain of humans and animals, as well as in plant tissues. It is disposed of through animal feces. It also occurs naturally in certain foods, such as some nuts and cheese. It is one of the main compounds responsible for bad breath and the smell of flatus. Methanethiol is classified as a thiol and is sometimes abbreviated as MeSH. It is very flammable.

Ethanethiol, commonly known as ethyl mercaptan and stench, is a clear liquid with a distinct odor. It is an organosulfur compound with the formula CH3CH2SH. Abbreviated EtSH, it consists of an ethyl group (Et), CH3CH2, attached to a thiol group, SH. Its structure parallels that of ethanol, but with sulfur in place of oxygen. The odor of EtSH is infamous. Ethanethiol is more volatile than ethanol due to a diminished ability to engage in hydrogen bonding. Ethanethiol is toxic. It occurs naturally as a minor component of petroleum, and may be added to otherwise odorless gaseous products such as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) to help warn of gas leaks. At these concentrations, ethanethiol is not harmful.

An aroma compound, also known as an odorant, aroma, fragrance, or flavor, is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor. For a chemical compound to have a smell or odor it must be sufficiently volatile to be transported to the olfactory system in the upper part of the nose.

Ethyl acetate is the organic compound with the formula CH
3−COO−CH
2−CH
3, simplified to C
4H
8O
2. This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell and is used in glues, nail polish removers, and in the decaffeination process of tea and coffee. Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent.

A stink bomb is a device designed to create an unpleasant smell. They range in effectiveness from simple pranks to military grade malodorants or riot control chemical agents.

2-Butanol, or sec-butanol, is an organic compound with formula CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3. This secondary alcohol is a flammable, colorless liquid that is soluble in 3 parts water and completely miscible with organic solvents. It is produced on a large scale, primarily as a precursor to the industrial solvent methyl ethyl ketone. 2-Butanol is chiral and thus can be obtained as either of two stereoisomers designated as (R)-(−)-2-butanol and (S)-(+)-2-butanol. It is normally encountered as a 1:1 mixture of the two stereoisomers — a racemic mixture.

tert-Butyl alcohol (TBA), also called tert-butanol or t-butanol, is the simplest tertiary alcohol, with a formula of (CH3)3COH (sometimes represented as t-BuOH). It is one of the four isomers of butanol. tert-Butyl alcohol is a colorless solid, which melts near room temperature and has a camphor-like odor. It is miscible with water, ethanol and diethyl ether.

n-Butyl acetate, also known as butyl ethanoate, is an ester that is a colorless, flammable liquid at room temperature. It is found in many types of fruit, where along with other chemicals, it imparts characteristic flavors and has a sweet smell of banana or apple. It is used as a synthetic fruit flavoring in foods such as candy, ice cream, cheeses, and baked goods. Butyl acetate is often used as a high-boiling solvent of moderate polarity. It is also used as a solvent in nail polish along with ethyl acetate.

The chemical compound isobutyl acetate, also known as 2-methylpropyl ethanoate or β-methylpropyl acetate, is a common solvent. It is produced from the esterification of isobutanol with acetic acid. It is used as a solvent for lacquer and nitrocellulose. Like many esters it has a fruity or floral smell at low concentrations and occurs naturally in raspberries, pears and other plants. At higher concentrations the odor can be unpleasant and may cause symptoms of central nervous system depression such as nausea, dizziness and headache.

Thiophenol is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H5SH, sometimes abbreviated as PhSH. This foul-smelling colorless liquid is the simplest aromatic thiol. The chemical structures of thiophenol and its derivatives are analogous to phenols except the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to the aromatic ring is replaced by a sulfur atom. The prefix thio- implies a sulfur-containing compound and when used before a root word name for a compound which would normally contain an oxygen atom, in the case of 'thiol' that the alcohol oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom.
1,2-Dichlorotetrafluoroethane, or R-114, also known as cryofluorane (INN), is a chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) with the molecular formula ClF2CCF2Cl. Its primary use has been as a refrigerant. It is a non-flammable gas with a sweetish, chloroform-like odor with the critical point occurring at 145.6 °C and 3.26 MPa. When pressurized or cooled, it is a colorless liquid. It is listed on the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's list of ozone depleting chemicals, and is classified as a Montreal Protocol Class I, group 1 ozone depleting substance.

2-Methoxyethanol, or methyl cellosolve, is an organic compound with formula C
3H
8O
2 that is used mainly as a solvent. It is a clear, colorless liquid with an ether-like odor. It is in a class of solvents known as glycol ethers which are notable for their ability to dissolve a variety of different types of chemical compounds and for their miscibility with water and other solvents. It can be formed by the nucleophilic attack of methanol on protonated ethylene oxide followed by proton transfer:

Dinitro-ortho-cresol (DNOC) is an organic compound with the structural formula CH3C6H2(NO2)2OH. It is a yellow solid that is only slightly soluble in water. DNOC and some related derivatives have been used as herbicides.

tert-Butylthiol, also known as 2-methylpropane-2-thiol, 2-methyl-2-propanethiol, tert-butyl mercaptan (TBM), and t-BuSH, is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)3CSH. This thiol is used as an odorant for natural gas, which is otherwise odorless. It may also have been used as a flavoring agent.

Perchloromethyl mercaptan is the organosulfur compound with the formula CCl3SCl. It is mainly used as an intermediate for the synthesis of dyes and fungicides (captan, folpet). It is a colorless oil, although commercial samples are yellowish. It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. It has a foul, unbearable, acrid odor. Perchloromethyl mercaptan is the original name. The systematic name is trichloromethanesulfenyl chloride, because the compound is a sulfenyl chloride, not a mercaptan.
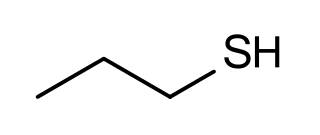
Propanethiol is an organic compound with the molecular formula C3H8S. It belongs to the group of thiols. It is a colorless liquid with a strong, offensive odor. It is moderately toxic and is less dense than water and slightly soluble in water. It is used as a feedstock for insecticides. It is highly flammable and it gives off irritating or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fire. Heating it will cause rise in pressure with risk of bursting.
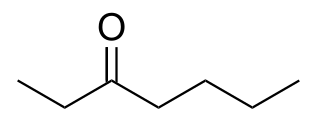
3-Heptanone, is a seven carbon ketone. It is a colorless liquid with a "green odor," also described to have a fruity scent. It is often used as a perfume/fragrance, as a solvent for cellulose, nitrocellulose, or vinyl resins, and as a synthetic building block in the preparation of other organic molecules.

tert-Butyl chromate is an industrial chemical and carcinogen. It is prepared by treatment of t-butanol with chromic anhydride. It forms red crystals at temperatures below –5 °C, above which it melts to give a red oil.





















