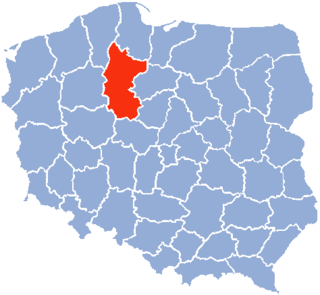
Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, also known as Cuiavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship or simply Kujawsko-Pomorskie, or Kujawy-Pomerania Province (Polish: województwo kujawsko-pomorskie[vɔjɛˈvut͡stfɔ kuˈjafskɔ pɔˈmɔrskʲɛ]; German: Woiwodschaft Kujawien-Pommern is one of the 16 voivodeships into which Poland is divided. It was created on 1 January 1999 and is situated in mid-northern Poland, on the boundary between the two historic regions from which it takes its name: Kuyavia and Pomerania. Its two chief cities, serving as the province's joint capitals, are Bydgoszcz and Toruń.
Bydgoszcz Voivodeship was a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland in the years 1975–1998, superseded by Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship.
Capital city: Bydgoszcz
Area:
Statistics :
Population: inhabitants
Population density: inhabitants/km2
Administrative division: communes
Number of cities and towns :
Major cities and towns :

A powiat is the second-level unit of local government and administration in Poland, equivalent to a county, district or prefecture in other countries. The term "powiat" is most often translated into English as "county" or "district".

Toruń County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, north-central Poland. It was created on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the city of Toruń, although the city is not part of the county. The only town in Toruń County is Chełmża, which lies nineteen kilometers north of Toruń.

Radom County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Masovian Voivodeship, east-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the city of Radom, although the city is not part of the county. The county contains three towns: Pionki, 22 km (14 mi) north-east of Radom, Iłża, 27 km (17 mi) south of Radom, and Skaryszew, 12 km (7 mi) south-east of Radom.

Starostwo, administrative units established from the 14th century in the Polish Crown and later in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until the partitions of Poland in 1795. They were jointly referred to as the crown lands (królewszczyzna).

The administrative division of Poland since 1999 has been based on three levels of subdivision. The territory of Poland is divided into voivodeships (provinces); these are further divided into powiats, and these in turn are divided into gminas. Major cities normally have the status of both gmina and powiat. Poland currently has 16 voivodeships, 380 powiats, and 2,478 gminas.

Tuchola County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, north-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and only town is Tuchola, which lies 55 km (34 mi) north of Bydgoszcz and 81 km (50 mi) north-west of Toruń.

Nakło County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, north-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Nakło nad Notecią, which lies 28 km (17 mi) west of Bydgoszcz and 70 km (43 mi) west of Toruń. The county contains three other towns: Szubin, lying 18 km (11 mi) south-east of Nakło nad Notecią, Kcynia, lying 18 km (11 mi) south-west of Nakło nad Notecią, and Mrocza, 12 km (7 mi) north of Nakło nad Notecią.

Aleksandrów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, north-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Aleksandrów Kujawski, which lies 20 km (12 mi) south of Toruń and 55 km (34 mi) south-east of Bydgoszcz. The county also contains the towns of Ciechocinek, lying 6 km (4 mi) east of Aleksandrów Kujawski, and Nieszawa, 14 km (9 mi) east of Aleksandrów Kujawski.

Żnin County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, north-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Żnin, which lies 36 km (22 mi) south-west of Bydgoszcz and 65 km (40 mi) west of Toruń. The county contains three other towns: Barcin, lying 17 km (11 mi) east of Żnin, Łabiszyn, lying 19 km (12 mi) north-east of Żnin, and Janowiec Wielkopolski, 18 km (11 mi) south-west of Żnin.

Sępólno County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, north-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Sępólno Krajeńskie, which lies 49 km (30 mi) north-west of Bydgoszcz and 86 km (53 mi) north-west of Toruń. The county also contains the towns of Więcbork, lying 11 km (7 mi) south of Sępólno Krajeńskie, and Kamień Krajeński, 10 km (6 mi) north of Sępólno Krajeńskie.

Inowrocław County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, north-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Inowrocław, which lies 36 km (22 mi) south-west of Toruń and 40 km (25 mi) south-east of Bydgoszcz. The county contains four other towns: Kruszwica, lying 14 km (9 mi) south of Inowrocław, Janikowo, lying 12 km (7 mi) south-west of Inowrocław, Gniewkowo, 16 km (10 mi) north-east of Inowrocław, and Pakość, 13 km (8 mi) west of Inowrocław.

Radziejów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, north-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Radziejów, which lies 45 km (28 mi) south of Toruń and 64 km (40 mi) south-east of Bydgoszcz. The only other town in the county is Piotrków Kujawski, lying 10 km (6 mi) south of Radziejów.

Świecie County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, north-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Świecie, which lies 45 km (28 mi) north of Toruń and 45 km (28 mi) north-east of Bydgoszcz. The only other town in the county is Nowe, lying 33 km (21 mi) north-east of Świecie.

Włocławek County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, north-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the city of Włocławek, although the city is not part of the county. The county contains six towns: Brześć Kujawski, which lies 12 km (7 mi) south-west of Włocławek, Kowal, which lies 15 km (9 mi) south-east of Włocławek, Lubraniec, which lies 19 km (12 mi) south-west of Włocławek, Izbica Kujawska, which lies 33 km (21 mi) south-west of Włocławek, Chodecz, which lies 28 km (17 mi) south of Włocławek, and Lubień Kujawski, 29 km (18 mi) south of Włocławek.

Gmina Solec Kujawski is an urban-rural gmina in Bydgoszcz County, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-central Poland. Its seat is the town of Solec Kujawski, which lies approximately 17 kilometres (11 mi) east of Bydgoszcz and 27 km (17 mi) west of Toruń.

Gmina Zławieś Wielka is a rural gmina in Toruń County, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-central Poland. Its seat is the village of Zławieś Wielka, which lies approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) west of Toruń and 23 km (14 mi) east of Bydgoszcz.

Otorowo is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Solec Kujawski, within Bydgoszcz County, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-central Poland. It lies 7 kilometres (4 mi) west of Solec Kujawski, 19 km (12 mi) east of Bydgoszcz, and 52 km (32 mi) west of Toruń.

Przyłubie is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Solec Kujawski, within Bydgoszcz County, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-central Poland. It lies approximately 5 kilometres (3 mi) south-east of Solec Kujawski, 21 km (13 mi) east of Bydgoszcz, and 22 km (14 mi) west of Toruń.