
Regulator of nonsense transcripts 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF1 gene.

Regulator of nonsense transcripts 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF2 gene.

Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HNRNPL gene.

Regulator of nonsense transcripts 3B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF3B gene.

Regulator of nonsense transcripts 3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF3A gene.

Telomerase-binding protein EST1A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SMG6 gene on chromosome 17. It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types. The C-terminus of the EST1A protein contains a PilT N-terminus (PIN) domain. This structure for this domain has been determined by X-ray crystallography. SMG6 functions to bind single-stranded DNA in telomere maintenance and single-stranded RNA in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). The SMG6 gene also contains one of 27 SNPs associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease.

C11orf49 is a protein coding gene that in humans encodes for the C11orf49 protein. It is heavily expressed in brain tissue and peripheral blood mononuclear cells, with the latter being an important component of the immune system. It is predicted that the C11orf49 protein acts as a kinase, and has been shown to interact with HTT and APOE2.
mRNA surveillance mechanisms are pathways utilized by organisms to ensure fidelity and quality of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. There are a number of surveillance mechanisms present within cells. These mechanisms function at various steps of the mRNA biogenesis pathway to detect and degrade transcripts that have not properly been processed.
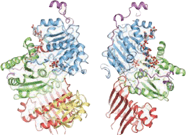
An exon junction complex (EJC) is a protein complex which forms on a pre-messenger RNA strand at the junction of two exons which have been joined together during RNA splicing. The EJC has major influences on translation, surveillance and localization of the spliced mRNA. It is first deposited onto mRNA during splicing and is then transported into the cytoplasm. There it plays a major role in post-transcriptional regulation of mRNA. It is believed that exon junction complexes provide a position-specific memory of the splicing event. The EJC consists of a stable heterotetramer core, which serves as a binding platform for other factors necessary for the mRNA pathway. The core of the EJC contains the protein eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-III bound to an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) analog, as well as the additional proteins Magoh and Y14. The binding of these proteins to nuclear speckled domains has been measured recently and it may be regulated by PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways. In order for the binding of the complex to the mRNA to occur, the eIF4AIII factor is inhibited, stopping the hydrolysis of ATP. This recognizes EJC as an ATP dependent complex. EJC also interacts with a large number of additional proteins; most notably SR proteins. These interactions are suggested to be important for mRNA compaction. The role of EJC in mRNA export is controversial.

HIKESHI is a protein important in lung and multicellular organismal development that, in humans, is encoded by the HIKESHI gene. HIKESHI is found on chromosome 11 in humans and chromosome 7 in mice. Similar sequences (orthologs) are found in most animal and fungal species. The mouse homolog, lethal gene on chromosome 7 Rinchik 6 protein is encoded by the l7Rn6 gene.

CZIB is a gene in the human genome that encodes the protein CXXC motif containing zinc binding protein. CZIB was previously referred to as C1orf123.

Cilia And Flagella Associated Protein 206 (CFAP206) is a gene that in humans encodes a protein “DUF3508”. This protein has a function that is not currently very well understood. Other known aliases are “dJ382I10.1, UPF0704 Protein C6orf165.” In humans, the gene coding sequence is 56,501 base pairs long, with an mRNA of 2,215 base pairs, and a protein sequence of 622 amino acids. The C6orf165 gene is conserved in chimpanzee, rhesus monkey, dog, cow, mouse, rat, chicken, zebrafish, mosquito, frog, and more C6orf165 is rarely expressed in humans, with relatively high expression in brain, lungs (trachea) and testis. The molecular weight of UPF0704 is 71,193 Da and the PI is 6.38

C7orf25 protein UPF0415 (UPF0415) is a protein encoded on chromosome 7, in open reading frame 25 (C7orf25) and are located at domain of unknown function 1308. C7orf25 is located at the minus strand and encodes 12 proteins, one of them being UPF0415. This protein is believed to be active in the proteosome pathway. C7orf25 protein UPF0415 is not a transmembrane protein and has no signal peptide. UPF0415 has two isoforms, Q9BPX7-1 and Q9BPX7-2. Both consists of two exons that are both highly conserved among vertebrates.

UPF0488 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C8orf33 gene. Chromosome 8 open reading frame 33 (C8orf33) is a human protein-coding gene of currently unknown function.

Chromosome 1 Opening Reading Frame 94 or C1orf94 is a protein in human coded by the C1orf94 gene. The function of this protein is still poorly understood.

C6orf136 is a protein in humans encoded by the C6orf136 gene. The gene is conserved in mammals, mollusks, as well some porifera. While the function of the gene is currently unknown, C6orf136 has been shown to be hypermethylated in response to FOXM1 expression in Head Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) tissue cells. Additionally, elevated expression of C6orf136 has been associated with improved survival rates in patients with bladder cancer. C6orf136 has three known isoforms.

C5orf24 is a protein encoded by the C5orf24 gene (5q31.1) in humans. C5orf24 is primarily localized to the nucleus and is highly conserved with orthologs in mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish.

Chromosome 12 Open Reading Frame 50 (C12orf50) is a protein-encoding gene which in humans encodes for the C12orf50 protein. The accession id for this gene is NM_152589. The location of C12orf50 is 12q21.32. It covers 55.42 kb, from 88429231 to 88373811, on the reverse strand. Some of the neighboring genes to C12orf50 are RPS4XP15, LOC107984542, and C12orf29. RPS4XP15 is upstream C12orf50 and is on the same strand. LOC107984542 and C12orf29 are both downstream. LOC107984542 is on the opposite strand while C12orf29 is on the same strand. C12orf50 has six isoforms. This page is focusing on isoform X1. C12orf50 isoform X1 is 1711 nucleotides long and has a protein with a length of 414 aa.

Chromosome 5 open reading frame 22 (c5orf22) is a protein-coding gene of poorly characterized function in Homo sapiens. The primary alias is unknown protein family 0489 (UPF0489).

Coiled-coil domain-containing 184 (CCDC184) is a protein which, in humans, is encoded by the CCDC184 gene

















