Protein
Primary sequence, molecular weight and pI
| Protein | Accession number | Length (amino acids) | Molecular Weight (kDa) | Predicted pI |
|---|
| Isoform 1 [11] | XP_005264617 | 442 | 50.8 | 9.80 |
| Isoform 2 [12] | NP_001136155 | 440 | 50.9 | 9.81 |
| Isoform 3 [13] | NP_078860 | 278 | 33.1 | 9.84 |
Molecular weight and pI were calculated using ExPasy. [14]
Compositional analysis
Compositional analysis of all isoforms shows that they have below-average levels of aspartate (D) and valine (V) and above-average levels of glutamine (Q). In addition, they have above-average levels of lysine (K) and arginine (R) groupings. Isoform 3 also exhibits above-average lysine levels and below-average proline and glycine levels. Chimpanzee, dog, and ferret orthologs also exhibited above-average glutamine levels and lysine and arginine groupings. [15]
Secondary and tertiary structure
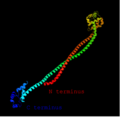
The secondary structure prediction for CCDC121 was obtained using Ali2D. [16] CCDC121 adopts a predominant alpha helical secondary structure (shown in red) due to the presence of the Coiled-coil motif. [17]
The tertiary structure of CCDC121 is composed mostly of alpha helices and contains some random coil. [18]
Subcellular localization
Current evidence suggests that CCDC121 is partially localized in the nucleus. CCDC121 has a predicted nuclear localization signal from amino acids R327 to L337. This sequence has a score of 7, which is consistent with being a partial nuclear protein. [28] In addition, PSORT II found that there is 56.5% chance that CCDC121 is found in the nucleus. [29]
There is also evidence to suggest that CCDC121 is partially located in the cytosol. Cytochemistry studies of the Anti-CCDC121 antibody from The Human Protein Atlas indicate that CCDC121 is expressed in the cytosol and actin filaments. These tentative results are promising but further research of other anti-CCDC121 antibodies is needed. [30] Additionally, TargetP did not find a mitochondrial transfer peptide, which suggests that CCDC121 is likely not a mitochondrial protein. [31]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.